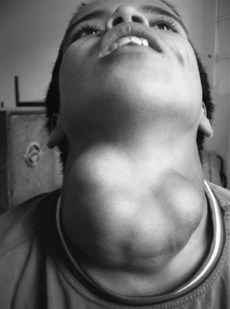
140 Multinodular goitre
Salient features
History
• Stridor: trachea must be narrowed to 20–30% for this symptom
• Hoarseness of voice (caused by pressure on recurrent laryngeal nerve), suggests thyroid malignancy
• Acute painful enlargement, suggests bleeding into thyroid nodule
• Suffusion of face when the patient raises the arms above the head, suggests substernal goitre
• Deafness: if caused by eighth cranial nerve involvement suggests Pendreds syndrome (rare)
• Symptoms of thyroid hyper- or hypofunction
Questions
How would you investigate a nodular goitre?
• Serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and free thyroxine (T4) should be measured to identify those with subclinical or overt hyperthyroidism. If the TSH is suppressed, radionuclide scanning should be performed.
• Ultrasonography of the thyroid gland indicates whether goitre is cystic or solid:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree