Multilocular Cystic Nephroma
Aleksandr Vasilyev, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Multilocular cystic nephroma (MCN)
Cystic nephroma (CN), multilocular cyst
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Relationship to sex hormones is suggested
Clinical Issues
Female:male ratio is 8:1 in adult cases and 2:1 in pediatric cases
Conservative surgical excision is curative
Microscopic Pathology
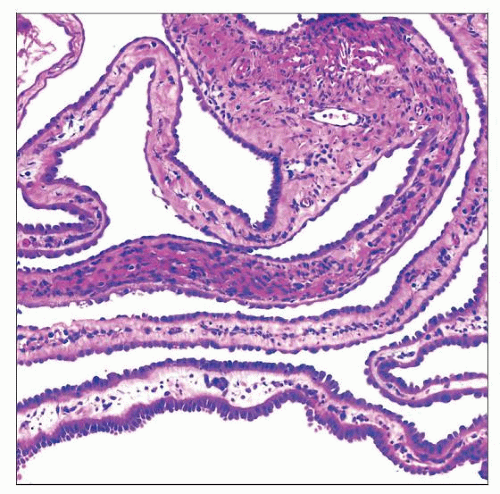
Epithelial lining of cysts ranges from flat to cuboidal to hobnailed to columnar
Fibrous septae show range of cellularity, from paucicellular and hyalinized to highly cellular, reminiscent of ovarian stroma
Cytoplasmic clearing of lining epithelium can be seen
Fibrous pseudocapsule surrounds lesion
Ancillary Tests
ER, PR stains are commonly positive in stroma
Top Differential Diagnoses
Cystic renal cell carcinoma
Tubulocystic carcinoma
Wilms tumor
MEST
If solid nodules are present or if septae are beyond a few millimeters in thickness, MEST diagnosis should be considered
Cystic dysplasia
Polycystic kidney disease
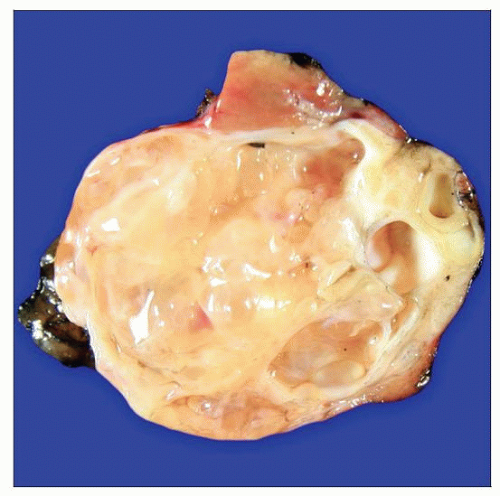 Gross photograph shows a multilocular cystic nephroma (MCN). The multicystic mass is well circumscribed. The cysts contain clear, thin to gelatinous fluid. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Multilocular cystic nephroma (MCN)
Synonyms
Cystic nephroma (CN), multilocular cyst
Definitions
Benign multicystic neoplasm of renal parenchyma overlapping with mixed epithelial and stromal tumor (MEST) of kidney
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Adult Cystic Nephromas
Relationship to sex hormones is suggested
Female preponderance
Estrogen and progesterone receptor (ER/PR) immunopositivity
Associated with sex hormone exposure in both males and females
Pediatric Cystic Nephromas
Thought to be etiologically different from adult CN
ER/PR are negative
Considered to be fully differentiated form of nephroblastoma
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Adult population, wide age distribution
Usually > 30 years
Children
Usually < 4 years
Accounts for ~ 5% of pediatric tumors
Gender
Female:male ratio is 8:1 in adult cases and 2:1 in pediatric cases
Presentation
Most commonly an incidental finding
Can present with pain, hematuria
Treatment
Conservative surgical excision is curative
Very rare cases of local recurrence after surgical excision
Prognosis
Excellent prognosis after surgical excision
IMAGE FINDINGS
Ultrasound, CT, or MR Studies
While useful, these studies do not allow one to discriminate between MCN and other entities in differential diagnosis in both adult and pediatric cases
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well-circumscribed, encapsulated, multicystic mass
Cysts contain clear or gelatinous fluid
Often near hilum but may involve cortex in larger lesions
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Epithelial lining of cysts ranges from flat to cuboidal to hobnailed to columnar
Cytoplasmic clearing of lining epithelium can be seen
Fibrous septae show range of cellularity, from paucicellular and hyalinized to highly cellular, reminiscent of ovarian stroma
Focal calcifications and atrophic renal tubules can be seen in septae
Foamy histiocytes may be present
Fibrous pseudocapsule surrounds lesion
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
ER, PR stains are commonly positive in stroma
Inhibin, calretinin, CD10 can also be positive in stroma
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree