Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm
Mari Mino-Kenudson, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Neoplasm composed of mucin-producing epithelial cells associated with ovarian-type stroma
Clinical Issues
Comprises 10% of cystic lesions of pancreas
Average age at diagnosis: 40-50 years
Range: 14-95 years
Predominantly female
Female to male ratio is 20:1
Macroscopic Features
90% of mucinous cystic neoplasms arise in body or tail of pancreas
Usually solitary and large
Mean: 7-10 cm
Usually multiloculated with thick walls; filled with thick, tenacious mucoid material
Microscopic Pathology
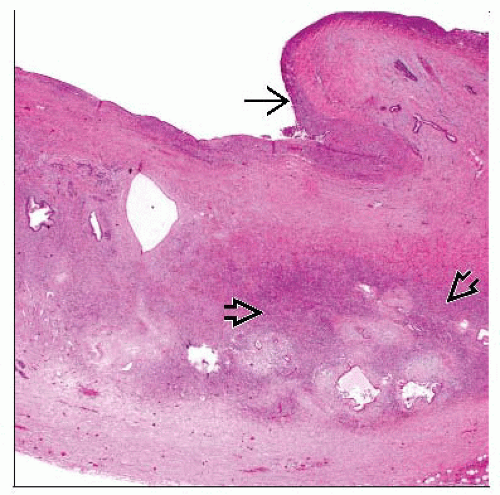
Tall, columnar, mucin-producing epithelium with varying degrees of cellular atypia
Invasive components can be very focal
Recommended to submit entire lesion for microscopic evaluation
Ovarian-type stroma is required for diagnosis
Broad areas of stroma may be hyalinized
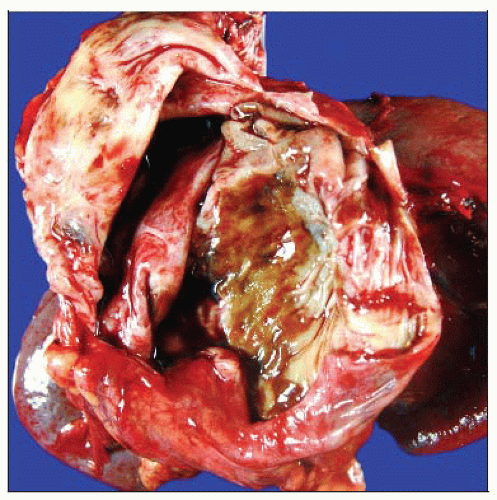 Gross photograph of a mucinous cystic neoplasm features a unilocular cyst with a smooth, partially discolored lining located in the tail of the pancreas. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN)
Definitions
Neoplasm composed of mucin-producing epithelial cells associated with ovarian-type stroma
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
May develop from endodermal immature stroma (periductal stroma) stimulated by female hormones
May develop from primary yolk cells implanted in pancreas during embryogenesis
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
10% of cystic lesions in pancreas
Age
Average age at diagnosis: 40-50 years
Range: 14-95 years
Gender
Predominantly female (female to male ratio is 20:1)
Presentation
Vague abdominal symptoms associated with compression of adjacent organs and tissues; may include epigastric pain and abdominal fullness
Prognosis
Excellent prognosis for patients with benign MCN and MCN with noninvasive carcinoma
5-year survival rate of 50% for invasive MCN
Extent of invasion (confined to pancreas vs. beyond tumor capsule) and age of patient (lower survival rate > 50 years) correlates with survival
IMAGE FINDINGS
CT Findings
Usually large, well-demarcated, thick-walled multilocular cystic mass with peripheral calcification (present in 20% of cases)
Mural nodules and papillary excrescences are more common in mucinous cystic neoplasms with invasive component
ERCP Findings
Main pancreatic duct and large interlobular ducts do not communicate with cysts in majority of cases
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
90% in body or tail of pancreas
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree