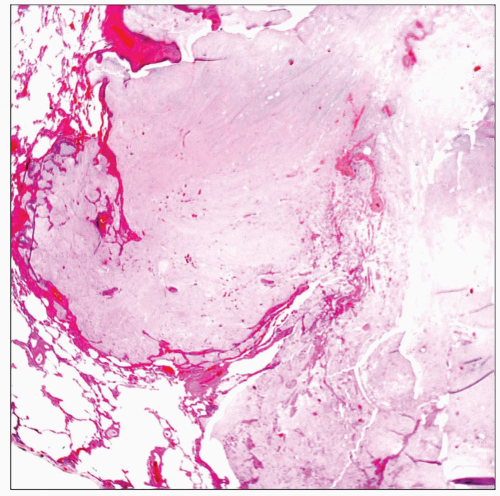
Mucinous (“Colloid”) Carcinoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Mucinous cystadenoma, mucinous cystic tumor, multilocular cystic carcinoma, mucinous cystic tumor of borderline malignancy
Macroscopic Features
Well-defined tumor mass with mucoid consistency, solid &/or cystic
Varies from 1 to > 10 cm
Microscopic Pathology
Extensive areas of mucinous deposition
Alveolar wall lined with mucinous epithelium
Single cells or clusters of cells embedded in mucin
Ancillary Tests
TTF-1 nuclear positivity (may be negative in some cases)
CK7 cytoplasmic positivity
CK20 negative (may be positive in some cases)
CDX2 negative (may be positive in some cases)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Metastatic mucinous carcinoma of extrathoracic origin
Clinical history of or clinical evaluation for colonic, ovarian, breast, or urachal carcinoma will be important
Immunohistochemical studies important in determining primary site
Diagnostic Checklist
Extensive mucin
Alveolar wall lined with mucinous epithelium
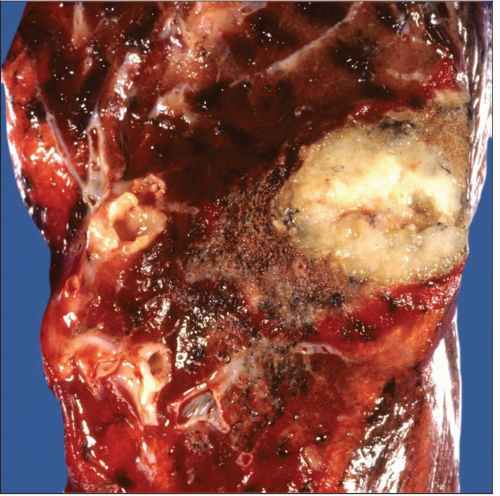 Gross photograph of mucinous carcinoma shows a well-defined subpleural tumor with a mucoid consistency. No evidence of necrosis or hemorrhage is present. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Mucinous cystadenoma, mucinous cystic tumor, multilocular cystic carcinoma, mucinous cystic tumor of borderline malignancy
Definitions
Epithelial neoplasm with extensive mucin production
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Pure colloid carcinomas of the lung are rare
Age
Colloid carcinomas are more common in adult patients
Gender
No gender predilection
Presentation
Cough
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lobectomy
Prognosis
Depends on staging at time of diagnosis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well-defined tumor mass
Mucoid consistency
Cystic changes may be present
Size
Varies from 1 to > 10 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Extensive areas of mucin deposition
Alveolar wall lined with mucinous epithelium
Single cells or clusters of cells are seen floating in the mucin
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Mucinous
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Epithelial
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Metastatic Mucinous Carcinoma of Extrathoracic Origin
Clinical history of or clinical evaluation for colonic, ovarian, breast, or urachal carcinoma will be important
Immunohistochemical studies important in determining primary site
Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma (BAC), Mucinous Variant
In BAC, lepidic growth pattern is characteristic feature in which alveolar lining is substituted by mucinous type of epithelium
BAC commonly will diffusely involve the entire lung or extensive areas of it
Immunohistochemical features of BAC and colloid carcinoma may be similar
DIAGNOSTIC CHECKLIST
Clinically Relevant Pathologic Features
Gross appearance
Pathologic Interpretation Pearls
Extensive mucin
Alveolar wall lined with mucinous epithelium
GRADING
Colloid Carcinoma
Considered low-grade malignant neoplasm
Behavior determined by pathological staging at time of diagnosis
SELECTED REFERENCES
1. Bacha D et al: A pulmonary mucinous cystic tumour of borderline malignancy. Pathologica. 100(3):189-91, 2008
2. Maeda R et al: Primary pulmonary mucinous (colloid) adenocarcinoma. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 56(4):195-8, 2008
3. Moran CA: Pulmonary adenocarcinoma: the expanding spectrum of histologic variants. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 130(7):958-62, 2006
4. Türüt H et al: Primary pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinoma in a 15-year-old boy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 29(5):851-3, 2006
5. Brownlee NA et al: Mucinous (colloid) adenocarcinoma of the lung. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 129(1):121-2, 2005
6. Okimasa S et al: Mucinous (colloid) adenocarcinoma. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 53(6):305-8, 2005
7. Jayaram G et al: Mucinous carcinoma (colloid carcinoma) of the lung diagnosed by fine needle aspiration cytology: a case report. Malays J Pathol. 25(1):63-8, 2003
8. Moran CA. Mucin-rich tumors of the lung. Adv Anat Pathol. 2(5):299-305, 1995
9. Moran CA et al: Mucinous (so-called colloid) carcinomas of lung. Mod Pathol. 5(6):634-8, 1992
10. Graeme-Cook F et al: Pulmonary mucinous cystic tumors of borderline malignancy. Hum Pathol. 22(2):185-90, 1991
Tables
Immunohistochemistry
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|
|---|