Mitochondriopathies
Surya V. Seshan, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Rare genetic disorder of mtDNA
Drug induced with reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Clinical Issues
Clinically, biochemically and genetically heterogeneous
50% have renal involvement
Renal disease occurs in KSS, Pearson syndrome, MERRF, and MELAS
DeToni-Debré-Fanconi syndrome
Urine amino acids, glucose, ketones, carnitines
Microscopic Pathology
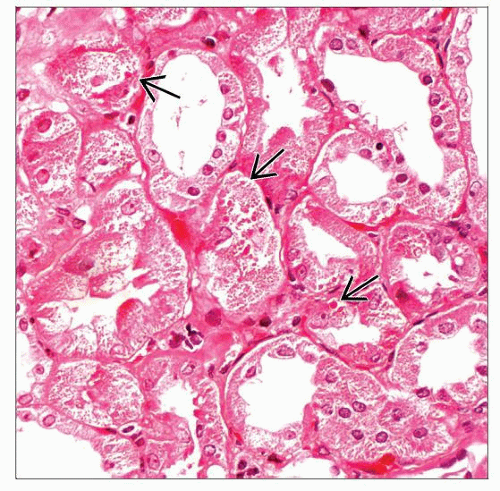
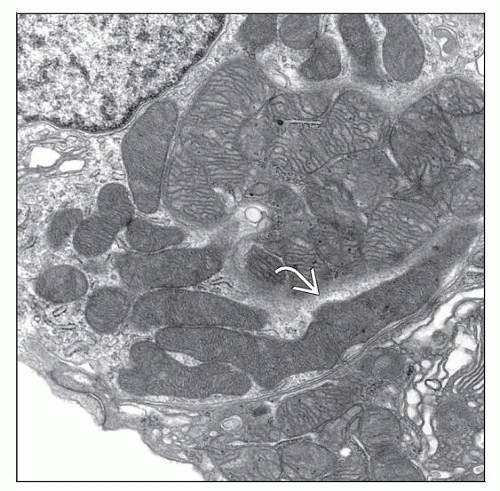
Most common lesion is proximal tubulopathy with dysmorphic mitochondria
Definitive diagnosis is based on integration of clinical, electrophysiological, neuroimaging, histopathological, biochemical, and genetic investigations
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Mitochondriopathies (MCP)
Definitions
Genetic defect of oxidative phosphorylation due to deficiency of one of the mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes; also acquired form due to drug toxicity (e.g., Viramune)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Genetic
Abnormal mitochondrial components from mutated mitochondrial (mtDNA) or nuclear DNA (nDNA)
Mitochondria have own DNA, a circular strand (mtDNA)
Genes that encode for enzymes, structural signaling, carrier/shuttle, channel receptor, tRNAs, rRNAs, or heat shock or assembling proteins are affected
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree