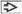Mitochondrial Myopathies
Monica P. Revelo, MD, PhD
Dylan V. Miller, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Heterogeneous group of maternally inherited diseases resulting from dysfunction in mitochondrial DNA-encoded gene products
Microscopic Pathology
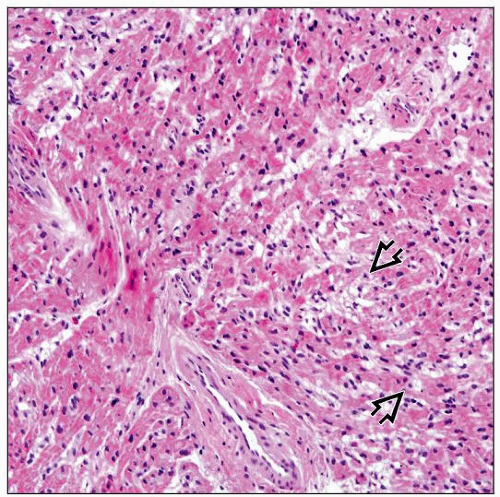
Myocyte vacuolization
Myocyte necrosis
Interstitial fibrosis
Ancillary Tests
Trichrome stain shows ragged red fibrils
Electron microscopy
Increased numbers and size of mitochondria aggregated under sarcolemma
Mitochondria with concentric cristae configuration
Crystalloid or osmophilic globular inclusion bodies
Myofibril loss
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Heterogeneous group of maternally inherited diseases resulting from dysfunction in mitochondrial DNA-encoded gene products
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Genetic Disorders
Kearns-Sayre syndrome (KSS): Heteroplasmic single deletion of mtDNA with reduction in cytochrome C oxidase (COX)
Myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers (MERRF): tRNA gene for lysine (MT-TK), A8344G
Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes syndrome (MELAS): A3243G, tRNA-Leu (MT-TL1) gene
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON): Homoplasmic point mutation in ND4 protein-coding subunit, position G11778A
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
1:22,500 (for cardiomyopathy-associated mitochondrial myopathy)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree