Minute Meningothelial-like Nodule
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Usually asymptomatic
Can present with diffuse, symptomatic bilateral interstitial lung infiltrates (diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis)
Lesions most often represent an incidental finding of no clinical significance
Image Findings
Can present as randomly distributed micronodules on thin section CT
Microscopic Pathology
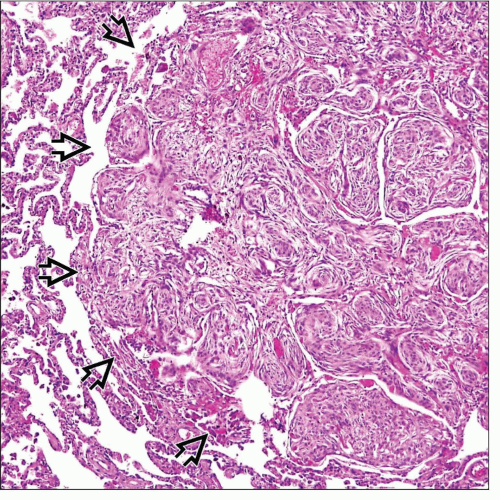
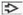
Ill-defined, focal accumulation of oval or epithelioid cells in pulmonary interstitium
Oval or epithelioid cells tend to focally adopt a whorled appearance
Lesions may be microscopic (1-2 mm) or measure up to 1 cm in diameter
Lesions may be seen in close proximity of vessels
Cells are oval or epithelioid and surrounded by an ample rim of eosinophilic cytoplasm with indistinct cell borders
Cells contain small, centrally placed nuclei devoid of mitotic activity
Nuclei may contain intranuclear cytoplasmic inclusions
Ancillary Tests
Tumor cells are positive for vimentin and EMA
Cells contain long, branching, interdigitating cytoplasmic cell processes joined by numerous desmosomes
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Minute meningothelial-like nodules (MMN)
Synonyms
Minute pulmonary chemodectoma
Definitions
Small intrapulmonary nodules composed of cells bearing histologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural features of meningothelial cells
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Believed to arise from rests displaced in the lung during embryogenesis
Distributed interstitially alongside small veins
Often found in association with pulmonary thromboemboli
Pathogenesis
May result from clonal expansion as shown by amplification of the X-chromosome-linked human androgen receptor gene (HUMARA assay)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Found in about 7% of surgically resected lungs
Age
30-75 years (mean = 61 years)
Gender
Female predilection (M:F = 1:2)
Presentation
Usually asymptomatic
Found incidentally in lungs resected for other reasons, particularly lung adenocarcinoma
May present with progressive shortness of breath
Can present with diffuse, symptomatic, bilateral interstitial lung infiltrates (diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis)
Prognosis
Lesions most often represent an incidental finding of no clinical significance
There is currently no known treatment for rare symptomatic, diffuse, and bilateral cases (diffuse pulmonary meningotheliomatosis)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree