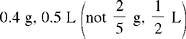CHAPTER 6 After reviewing this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Express metric measures correctly using rules of the metric system 2. State common equivalents in the metric system 1. The metric system is based on the decimal system, in which divisions and multiples of 10 are used. Therefore a lot of math can be done by decimal point movement. 2. Three basic units of measure are used: a) Gram—the basic unit for weight (solid) b) Liter—the basic unit for volume (liquid) c) Meter—the basic unit for length 3. Common prefixes in this system denote the numerical value of the unit being discussed. Memorization of these prefixes is necessary for quick and accurate calculations. The prefixes in bold in Table 6-1 are the ones used most often in health care for dosage calculations. However, some of the prefixes may be used to express other values, such as laboratory values. Kilo is a common prefix used to identify a measure larger than the basic unit. The other common prefixes used in medication administration are smaller units: centi, milli, and micro. TABLE 6-1 Common Prefixes Used in Health Care Let’s look at the following example to see how the prefixes may be used.
Metric System
PARTICULARS OF THE METRIC SYSTEM
Prefix
Numerical Value
Meaning
Kilo*
1,000
one thousand times
Hecto
100
one hundred times
Deka
10
ten times
Deci
0.1
one tenth
Centi*
0.01
one hundredth part of
Milli*
0.001
one thousandth part of
Micro*
0.000001
one millionth part of
Metric System