Metastatic Melanoma
Esther Oliva, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
History of melanoma may be remote
Macroscopic Features
Bilateral or unilateral and multinodular
Black cut surface due to pigment content
Microscopic Pathology
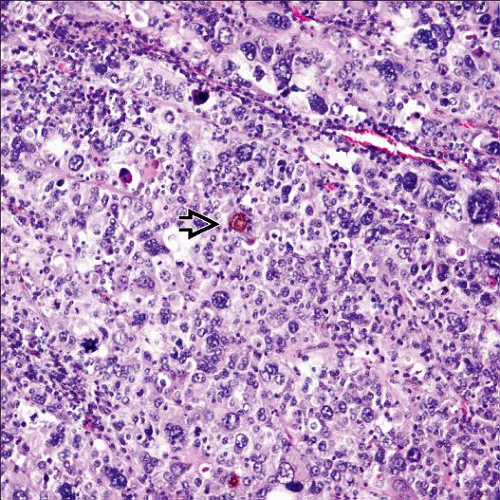
Diffuse or nodular growth > nested (nevoid)
Follicle-like spaces
Large cells with abundant eosinophilic or, less commonly, clear cytoplasm and pseudoinclusions
Focal intracytoplasmic melanin pigment common
Ancillary Tests
HMB-45, Melan-A (MART-1), S100 positive
Top Differential Diagnoses
Primary malignant melanoma
Steroid cell and granulosa cell tumors
Pregnancy luteoma
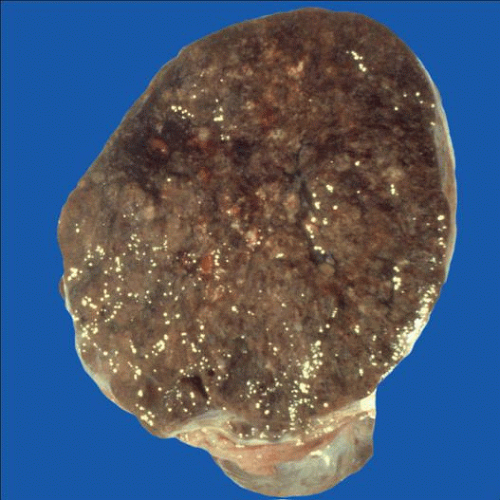 Metastatic malignant melanoma has a vague nodular appearance and may show a strikingly black cut surface due to the presence of melanin pigment. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Malignant melanoma
Definitions
Malignant melanocytic neoplasm secondarily involving 1 or both ovaries typically due to hematogenous spread
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Relatively common finding at autopsy (up to 18%)
Rare finding in living patients
More common than primary ovarian melanoma
Age
Wide range (mean: 37 years)