Mesothelial Hyperplasia
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Incidental finding in pleural biopsy specimens done for other causes
Finding in pleural fluid cytology for assessment of pleural effusion
Usually regresses spontaneously when stimulus is removed
Microscopic Pathology
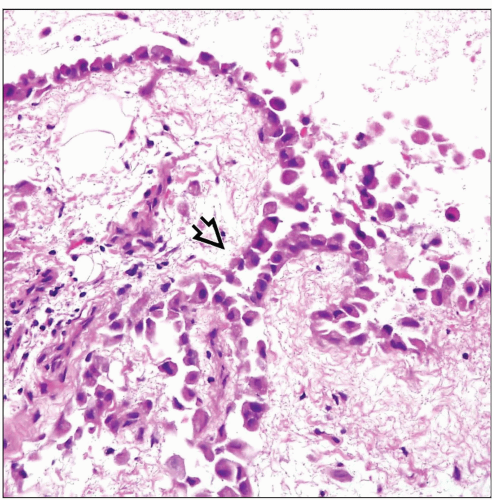
Focal thickening of pleural surface by sheets of mesothelial cells
Formation of small papillary excrescences that project into free pleural space
Process is confined to surface of pleura and does not invade underlying structures
Variable nuclear enlargement with mild increase in chromatin pattern
Nucleolar prominence
Variable mitotic activity
Diagnostic Checklist
Small and focal process; generally seen as incidental finding
Demonstration of absence of invasion is most important feature for distinguishing from early malignant mesothelioma
Role of immunohistochemistry is very limited for separating mesothelial hyperplasia from malignant mesothelioma
Reactive, hyperplastic mesothelial cells share the same markers with malignant mesothelioma
No molecular or cytogenetic markers are available for distinguishing between them
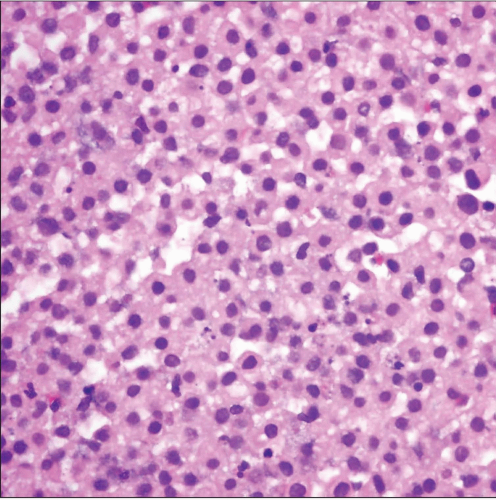 Mesothelial hyperplasia shows sheets of monotonous mesothelial cells with mild cytologic atypia and abundant pale eosinophilic cytoplasm. The cells are quite monotonous. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Mesothelial hyperplasia (MH)
Definitions
Proliferation of benign reactive mesothelial cells lining pleural surface
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Reaction to injury, such as recurrent effusions, inflammation, or neoplasia
As a result of surgical procedures, such as in cardiac MICE (monocytic incidental cardiac excrescences)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Asymptomatic
Incidental finding in pleural biopsies done for other causes
Finding in pleural fluid cytology for assessment of pleural effusion
May arise in pericardium forming small excrescences (cardiac MICE)
Prognosis
Benign
Usually regresses spontaneously when stimulus is removed
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Focal thickening of pleural surface by sheets of mesothelial cells
Formation of small papillary excrescences that project into free pleural space
May harbor psammoma bodies
Process is confined to surface of pleura and does not invade underlying structures
When in pericardium (cardiac MICE), lesions are composed of reactive mesothelial cells admixed with epithelioid histiocytes
Cytologic Features
Variable nuclear enlargement with mild increase in chromatin pattern
Nucleolar prominence
Variable mitotic activity
Process may vary in cytological composition
Simple mesothelial hyperplasia composed of bland-appearing cuboidal mesothelial cells
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree