Chapter 3 Membrane Biochemistry and Signal Transduction
I. Basic Properties of Membranes
A. Overview
2. Proteins can be integral, spanning both layers, or peripheral, loosely associated with either surface.
B. Membrane components
1. Cell membrane lipids are arranged in two monolayers, or leaflets, to form the lipid bilayer, the basic structural unit of cellular membranes.
a. Lipid composition differs within membranes of the same cell type, but phospholipids are the major lipid component of most membranes.
c. Phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin are found predominantly in the outer leaflet of the erythrocyte plasma membrane.
C. Membrane proteins
2. Peripheral (extrinsic) proteins are loosely associated with the surface of either side of the membrane.
a. Examples: Protein kinase C on the cytosolic side and certain extracellular matrix proteins on the external side
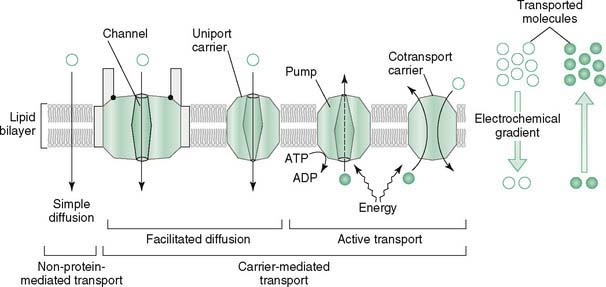
II. Movement of Molecules and Ions Across Membranes (Fig. 3-1 and Table 3-1)
A. Overview
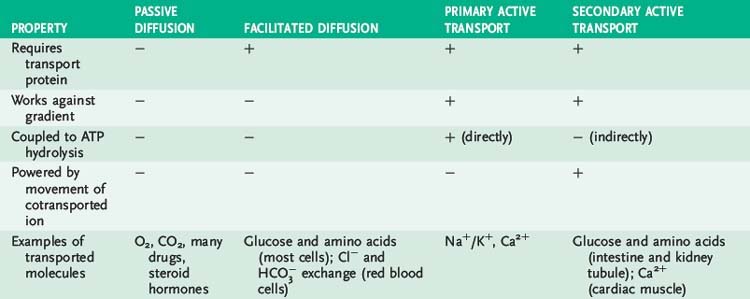
1. Simple diffusion occurs down a concentration gradient without the aid of transport proteins, involving mainly gases and small, uncharged molecules such as water.
2. Facilitated diffusion occurs down a concentration gradient with the aid of transport proteins and involves ions (ion channels) and monosaccharides.
4. Secondary active transport occurs against a concentration gradient by transporting a second molecule using ATP energy.
B. Simple diffusion
1. Movement of molecules or ions down a concentration gradient requires no additional energy and occurs without aid of a membrane protein.
3. Transport in either direction occurs, with net transport depending only on the direction of the gradient.
C. Facilitated diffusion
1. Requires the aid of specialized membrane proteins that move molecules across the membrane down the concentration gradient without input of cellular energy.
2. Ion channels are protein-lined passageways through which ions flow at a high rate when the channel is open.
3. Uniport carrier proteins facilitate diffusion of a single substance (e.g., glucose, particular amino acid).
a. Na+-independent glucose transporters (GLUTs) are uniporters that passively transport glucose, galactose, or fructose from the blood into most cell types down a steep concentration gradient (Table 3-2).
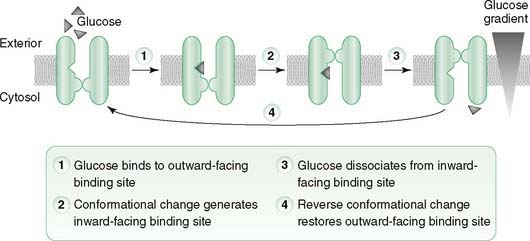
b. Cycling of the uniporter between alternative conformations allows binding and release of the transported molecules (Fig. 3-2).
c. Direction of transport by the uniporter depends on the direction of the concentration gradient for the transported molecule.
TABLE 3-2 Hexose Transport Proteins
| Transporter | Primary Tissue Location | Specificity and Physiologic Functions |
|---|---|---|
| GLUT1 | Most cell types (e.g., brain, erythrocytes, endothelial cells, fetal tissues) but not kidney and small intestinal epithelial cells | Transports glucose (high affinity) and galactose but not fructose; mediates basal glucose uptake |
| GLUT2 | Hepatocytes, pancreatic β cells, epithelial cells of small intestine and kidney tubules (basolateral surface) | Transports glucose (low affinity), galactose, and fructose; mediates high-capacity glucose uptake by liver at high blood glucose levels; serves as glucose sensor for β cells (insulin independent); exports glucose into blood after its uptake from lumen of intestine and kidney tubules |
| GLUT3 | Neurons, placenta, testes | Transports glucose (high affinity) and galactose but not fructose; mediates basal glucose uptake |
| GLUT4 | Skeletal and cardiac muscle, adipocytes | Mediates uptake of glucose (high affinity) in response to insulin stimulation, which induces translocation of GLUT4 transporters from the Golgi apparatus to the cell surface |
| GLUT5 | Small intestine, sperm, kidney, brain, muscle, adipocytes | Transports fructose (high affinity) but not glucose or galactose |
| GLUT7 | Membrane of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in hepatocytes | Transports free glucose produced in ER by glucose-6-phosphatase to cytosol for release into blood by GLUT2 |
| SGLUT1 (Na+/K+ symporter) | Epithelial cells of small intestine and kidney tubules (apical surface) | Cotransports glucose or galactose (but not fructose) and Na+ in same direction; mediates uptake of sugar from lumen against its concentration gradient powered by coupled transport of Na+ down its gradient |
4. Cotransport carrier proteins mediate movement of two different substances at the same time by facilitated diffusion or secondary active transport.
a. The direction of transport depends on the direction of the gradients for the transported molecules (similar to uniporters).
D. Primary active transport
1. Pumps move molecules or ions against the concentration gradient with energy supplied by coupled ATP hydrolysis.
3. Na+/K+-ATPase pump, located in the plasma membrane of every cell, maintains low intracellular Na+ and high intracellular K+ concentrations relative to the external environment.
a. Hydrolysis of 1 ATP is coupled to the translocation of 3 Na+ outward and 2 K+ inward against their concentration gradients.
b. Cardiotonic steroids, including digitalis and ouabain, specifically inhibit the Na+/K+ ATPase pump.
c. Albuterol and insulin enhance the pump and drive K+ from the extracellular compartment into the cell (i.e., hypokalemia).

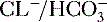 exchange protein (band 3 protein) in erythrocyte membrane, an antiporter that facilitates diffusion of Cl− and
exchange protein (band 3 protein) in erythrocyte membrane, an antiporter that facilitates diffusion of Cl− and 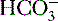 , functions in the transport of CO2 from tissues to the lungs (see
, functions in the transport of CO2 from tissues to the lungs (see 

