45 Meiosis
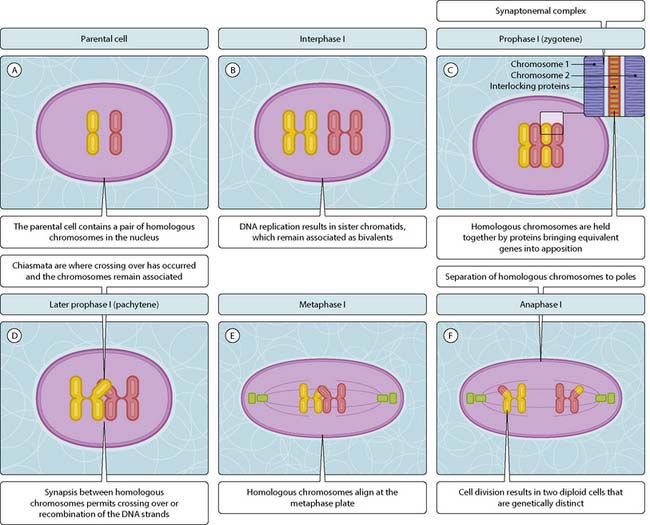
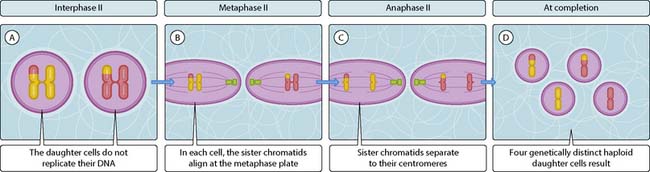
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that produces four genetically distinct haploid cells (containing only a single copy of each chromosome) from a diploid progenitor cell (containing two copies of each chromosome). This reductive form of cell division is found only in gamete production; in oogenesis and spermatogenesis. There are many similarities to mitotic cell division but also some important differences. Unlike mitosis, meiosis requires two rounds of cell division. The first round generates genetic variation (Fig. 3.45.1) and the second round produces haploid cells (Fig. 3.45.2). As in mitosis, meiosis can be divided into several stages.