Mastocytosis
Sharon K. Bihlmeyer, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Systemic mastocytosis involves multiple organs (usually bone marrow) ± skin
Clinical Issues
Abdominal pain and diarrhea
Systemic and gastrointestinal symptoms secondary to histamine release
No curative therapy
Manage symptoms with H1 and H2 histamine antagonists with variable improvement
Microscopic Pathology
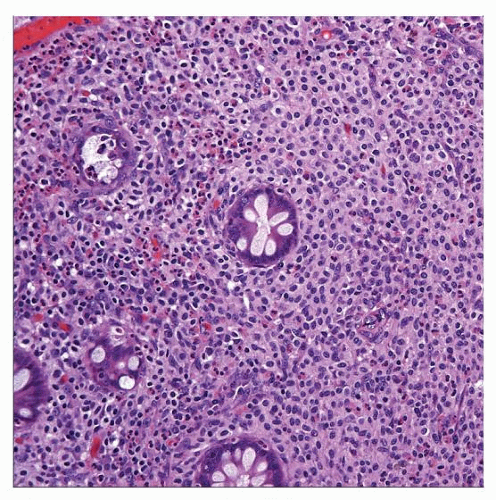
Lamina propria infiltration by round cells with central round nuclei and moderate amount of metachromatic cytoplasm
Cells stain with CD117 and mast cell tryptase
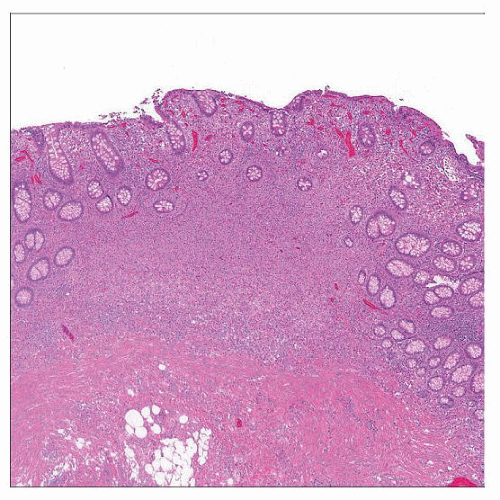 Hematoxylin & eosin shows a low-power view of colonic mucosa with lamina propria expanded by mast cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Systemic mastocytosis
Urticaria pigmentosa
Definitions
Group of disorders with mast cell proliferation and accumulation in 1 or more organs
Systemic mastocytosis involves multiple organs (usually bone marrow) ± skin
Cutaneous mastocytosis (urticaria pigmentosa) limited to skin
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Abnormal Proliferation of Mast Cells
Stem cell factor receptor KIT mutations
Inhibition of mast cell apoptosis involving PDGFRβ
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea
Vomiting
Nausea
Treatment
Drugs
H1 and H2 histamine antagonists
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree