Mast Cell Leukemia
Kaaren K. Reichard, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Definition: ≥ 10% circulating mast cells and ≥ 20% mast cells in BM aspirate
“Aleukemic” if < 10% circulating mast cells
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Unknown; rare disease
Microscopic Pathology
Mast cells comprise ≥ 20% of nucleated cells in BM aspirate smears
Round cell cytologic variant is most common
BM infiltrates are diffuse
Ancillary Tests
Immunophenotyping
Mast cells identified by bright CD117(+), tryptase(+)
Expression of CD2 &/or CD25 typically aberrant
CD30 expression common; may initially lead to diagnostic confusion with lymphoma
Molecular
KIT D816V mutation often present
KIT mutation confers imatinib resistance
Top Differential Diagnoses
Aggressive systemic mastocytosis
Similar BM histologic picture
Key difference: < 20% mast cells of BM nucleated cells on aspirate smears
Myelomastocytic leukemia
Features of mast cell differentiation
Criteria for systemic mastocytosis are not met
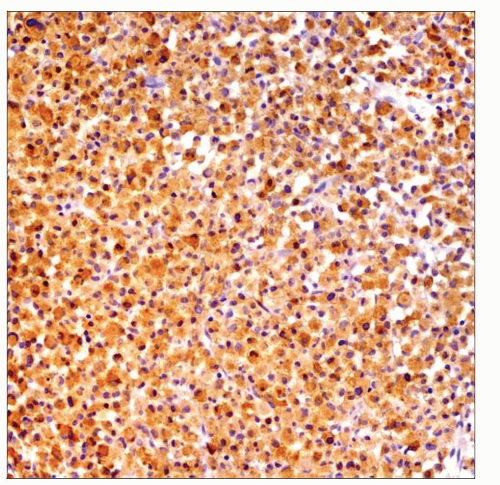
 This photomicrograph shows the typical appearance of mast cell leukemia in the bone marrow. The cells are round and small with variable degrees of degranulated abundant cytoplasm. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Mast cell leukemia (MCL)
Definitions
Clonal hematopoietic myeloid neoplasm
Exclusive or dominant component of bone marrow (BM)-derived mast cells
Mast cells comprise ≥ 20% of BM aspirate nucleated cells
Leukemic MCL: ≥ 10% circulating mast cells
Aleukemic MCL: < 10% circulating mast cells
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Acquired Activating Mutations
Most common is KIT D816V
Other rarer mutations also described
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare
Age
Predominantly adults
Gender
No obvious sex predilection
Presentation
Hepatomegaly
Ascites
Splenomegaly
Abnormal complete blood cell count (CBC)
Cytopenias, leukoerythroblastosis
Lytic bone lesions
Prominent extramedullary leukemia infiltrates
Liver
Spleen
Occasional involvement of other organs (e.g., stomach, kidneys, etc.)
Circulating mast cells
Pathologic bone fractures
Gastrointestinal disturbance
Malabsorption
Weight loss
Skin lesions
Very rare
Elevated serum tryptase level
Treatment
Cytoreductive agents
Chemotherapy
KIT D816V mutation confers imatinib resistance
Novel tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Dasatinib and midostaurin (PKC412)
Exhibit partial remitting activity
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Only chance to achieve durable remission
Prognosis
Unfavorable
Aggressive disease course
Median survival is 6-7 months
Poor response to cytoreductive agents and chemotherapy
Short-term remission
Interferon
2-CDA
Steroids
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Osteolytic lesions
Pathologic fractures
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Peripheral Blood (PB) Findings
Circulating mast cells
Usually ≥ 10% of nucleated cells
If < 10% of nucleated cells, designated as “aleukemic”
Cytopenias
Leukoerythroblastic picture
If there is associated clonal hematological non-mast cell lineage disease (AHNMD)
May see features of non-mast cell neoplasm
e.g., blasts, dysplasia
Bone Marrow Aspirate Findings
Mast cells comprise ≥ 20% of nucleated cells on aspirate smears
Background hematopoiesis usually markedly decreased
2 cytologic subtypes
Round cell variant
Most common
Spindle cell variant
Rare
Mast cell atypia: May not see all features in each case
Hypogranular cytoplasm
Abnormal or bilobed nuclei
Immature-appearing chromatin
Prominent nucleoli
If AHNMD, see features of non-mast cell neoplasm
e.g., increased blasts in acute leukemia
e.g., dysplasia in myelodysplastic syndrome
Bone Marrow Biopsy Findings
Diffuse infiltration pattern on core biopsy
Compact dense aggregate formation
Variable sparing of residual hematopoietic elements
Bone may be osteolytic
If AHNMD, see features of non-mast cell neoplasm
e.g., increased blasts in acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
e.g., dysplasia in myelodysplastic syndrome
Leukemic infiltrate of MCL may obscure underlying AHNMD
May require meticulous assessment of background hematopoietic elements
Would warrant classification as MCL-AML, etc.
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry
Mast cells identified by CD117 and tryptase
Mast cells may demonstrate CD33 positivity
Aberrant expression of CD2 &/or CD25
Useful clue to mast cell neoplasia
Fulfills minor criterion for SM
Majority of MCL cases show CD30 expression
May initially contribute to diagnostic confusion with lymphoma
Mast cells are nonreactive for
CD34
Myeloperoxidase
CD14
CD15
Lymphoid-associated markers
Mast cells lack expression of 2D7 and BB1; markers useful to distinguish basophils