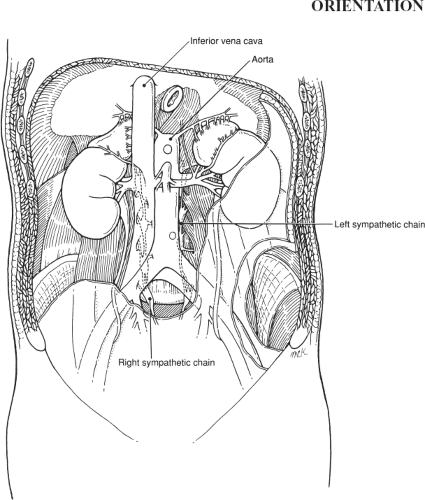
Lumbar Sympathectomy
This procedure is rarely performed; when sympathectomy is needed, either percutaneous chemical ablation or endoscopic techniques are often employed. The procedure was retained in this edition because it illustrates the regional anatomy well (Fig. 113.1) and because it may still rarely have a place.
Sympathectomy is performed for causalgia. Lumbar sympathectomy is sometimes performed in patients with symptomatic ischemia of a lower extremity who are not candidates for a bypass procedure. Results are unpredictable; thus, the operation is presently reserved for a very limited subset of patients who have failed, or who are not candidates for, other medical or surgical treatment modalities.
SCORE™, the Surgical Council on Resident Education, classified sympathectomy as a “COMPLEX” procedure.
STEPS IN PROCEDURE
Supine position, with operated side slightly elevated
Transverse incision; midaxillary line halfway between costal margin and anterosuperior iliac spine to lateral border of rectus muscle
Split muscular and fascia layers in the direction of their fibers and undermine each layer as encountered
Sweep away preperitoneal fat to expose peritoneum
Gently elevate peritoneal sac from underlying muscles to lumbar spine
Identify Sympathetic Chain Lateral to Lumbar Spine
Feels like a taut banjo string, interrupted by periodic swellings
Tethered to underlying paravertebral tissues
Identify the highest sympathetic ganglion just inferior to the diaphragm
Clip and divide the trunk at this point
Elevate sympathetic chain and clip fibers and overlying lumbar veins
Terminal dissection at level of iliac vein
Obtain frozen section confirmation of sympathetic ganglia
Close incision in layers without drainage
HALLMARK ANATOMIC COMPLICATIONS
Injury to ureter
Injury to genitofemoral nerve
Retroperitoneal bleeding
Inadequate sympathectomy or failure of procedure
LIST OF STRUCTURES
External oblique muscle
Internal oblique muscle
Transversus abdominis muscle
Transversalis fascia
Iliac fascia
Peritoneum
Lumbar Sympathetic Chain
Ganglia
Rami communicantes
Preganglionic fibers
Postganglionic fibers
Aorta
Inferior vena cava
Kidney
Ureter
Incision and Exposure of the Peritoneum (Fig. 113.2)