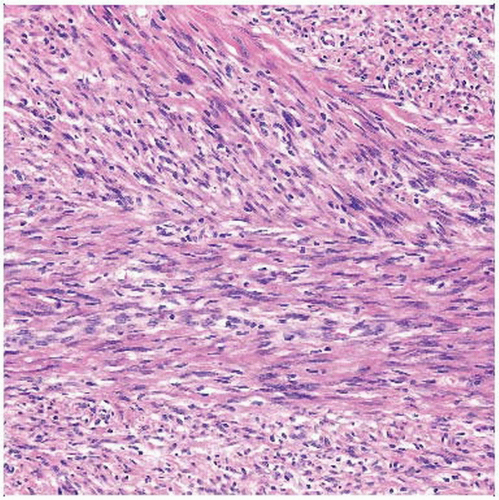
Low-Grade Myofibroblastic Sarcoma
Thomas Mentzel, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Low-grade myofibroblastic sarcoma represents distinct atypical myofibroblastic neoplasm with fibromatosis-like morphologic features
Clinical Issues
Occurs frequently in head and neck region
Occurs frequently in extremities
Occurs only rarely in dermis
Increased rate of local recurrences
Metastases occur only rarely and often after prolonged time interval
Occurs predominantly in adult patients
Occurs only rarely in children
Microscopic Pathology
Diffusely infiltrative growth
Cellular spindle cell fascicles
Low to moderate degree of cytologic atypia
Usually no tumor necrosis
Spindle-shaped tumor cells
Ill-defined, pale eosinophilic cytoplasm
Nuclei are elongated with evenly distributed chromatin
Nuclei are vesicular with indentations and small nucleoli
Variable expression of actin &/or desmin
No expression of HCAD, β-catenin, and myogenin
Tumor cells show ultrastructural features of myofibroblasts
May progress to higher grade malignant neoplasm
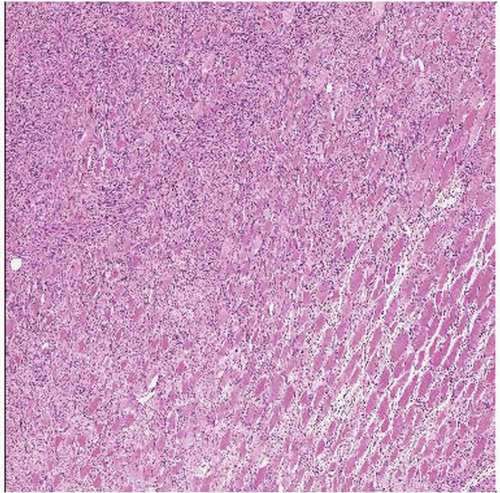 Low-grade myofibroblastic sarcoma is characterized by a diffuse infiltration of preexisting structures, as in this case, in which a diffuse infiltration of preexisting skeletal muscle is seen. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Low-grade myofibroblastic sarcoma (LGMFS)
Synonyms
Myofibrosarcoma
Definitions
Distinct atypical myofibroblastic neoplasm with fibromatosis-like morphologic features
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare low-grade sarcoma
Age
Occurs predominantly in adult patients
Children are rarely affected
Gender
Slight male predominance
Site
Wide anatomic distribution
Occurs frequently in head and neck region
Tongue and oral cavity are preferred locations
Occurs frequently in extremities
Subcutaneous and deep soft tissue
Very rare in dermal location
Presentation
Deep mass
Painless mass
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete excision
Prognosis
Locally aggressive behavior
Increased rate of local recurrences
Often repeated local recurrences
Metastases occur only rarely and often after prolonged time interval
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Destructive growth pattern
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Firm tumor mass
Infiltrative, ill-defined neoplasms
Pale gray-white, fibrous cut surfaces
Size
May reach considerable size
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Diffusely infiltrative growth
Tumor cells may grow diffusely between individual preexisting cells and structures
Cellular spindle cell fascicles
May show storiform growth
Hypocellular neoplasms are rare
Collagenous stroma
Focal stromal hyalinizations may be seen
Stroma may contain increased number of thin-walled capillaries
Low to moderate degree of cytologic atypia
Mitoses may be seen
Usually no tumor necrosis
May progress to higher grade malignant neoplasm
Cytologic Features
Spindle-shaped tumor cells
Ill-defined, pale eosinophilic cytoplasm
Fusiform nuclei
Nuclei are elongated with evenly distributed chromatin
Nuclei are vesicular with indentations and small nucleoli
Moderate nuclear atypia with enlarged, hyperchromatic, and irregular nuclei
ANCILLARY TESTS
Electron Microscopy
Tumor cells show myofibroblastic features
Indented, clefted nuclei
Variable amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum
Subplasmalemmal myofilaments (stress fibers) with focal densities
Paucity of subplasmalemmal attachment plaques
Absent basal lamina and pinocytotic vesicles
Abundant extracellular collagen
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Desmoid Fibromatosis
Infiltrative growth but no diffuse “growing through preexisting structures”
No cytologic atypia
Perivascular edema
β-catenin(+)
Desmin usually negative
Focal and weak expression of actins
Leiomyosarcoma
Often pushing margins
Spindled tumor cells with deep eosinophilic, fibrillary cytoplasm
Spindled, cigar-shaped nuclei
Paranuclear vacuoles
HCAD(+)
Fibrosarcoma
Extremely rare
Herringbone growth pattern
Small rim of cytoplasm and enlarged spindled nuclei
No expression of myogenic immunohistochemical markers
Spindle Cell Rhabdomyosarcoma
Very rare
Scattered rhabdomyoblasts
Focal nuclear expression of myogenin
Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor
Prominent inflammatory infiltrate (lymphocytes, plasma cells)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree