Chapter 70 Liver Transplant Evaluation (Case 51)
Case: A 45-year-old man with abnormal liver function tests and a history of heavy alcohol use is referred for liver transplant evaluation.
PATIENT CARE
Clinical Thinking
In evaluating a patient for liver transplantation it is important to:
• Make a dx of irreversible liver disease. Liver transplantation should be considered in all patients with end-stage liver disease (ESLD) who have failed to respond to medical treatment.
History
• Inquire about symptoms of ESLD, including encephalopathy, ascites, GI bleeding, pruritus, altered sleep pattern, tremor.
Tests for Consideration
3. Testing the status of the patient’s immune system and testing for the possible harboring of occult infection
4. Screening for the possibility of underlying, undiagnosed malignancy (as the transplant patient will require immunosuppression)
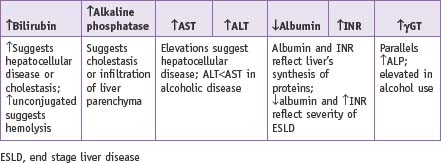
| • ABO blood group | $30 |
| • CBC, metabolic panel, LFTs | $84 |
| • Prothrombin time to assess synthetic function | $25 |
| • EKG (and cardiac evaluation if needed) | $50 ($500) |
| • Anergy panel, PPD, HIV test | $115 |
| • CXR | $136 |
| • Culture urine/sputum/blood to r/o infection | $45 |
| • Hepatitis panel (hepatitis B/C) | $65 |
| • Prostate-specific antigen (men > 50 years) to r/o prostate cancer | $65 |
| • MRA of the abdomen to look at anatomy of liver and to r/o tumors | $2,500 |
| • α-Fetoprotein to screen for hepatocellular tumor | $62 |
| • PAP smear/mammography (women > 40 years) to r/o malignancy | $125 |
The patient’s past medical hx or symptoms may indicate other tests.