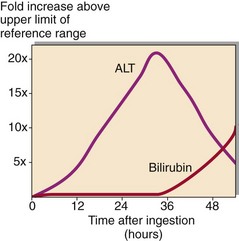
30 Some plant and fungal toxins can also cause catastrophic and fatal liver damage within 48 hours (Fig 30.1). Fig 30.1 Pattern of LFTs following Amanita phalloides (a highly poisonous species of mushroom) ingestion. Acute liver damage can progress in three ways: Hepatic failure may give rise to renal failure due to exposure of the glomeruli to toxins usually metabolized by the liver. There may be an increase in blood ammonia as a result of the failure to detoxify this to urea. The pattern of abnormalities found in hepatic failure is shown in Figure 30.2.
Liver disease
Investigation
Poisoning
Outcome
 It may resolve, as indeed it does in the majority of cases.
It may resolve, as indeed it does in the majority of cases.
 It may progress to acute hepatic failure.
It may progress to acute hepatic failure.
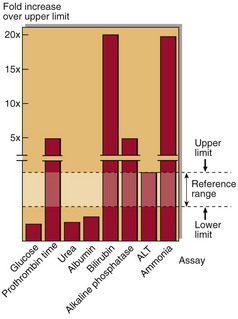
Hepatic failure
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Liver disease