Chapter 10 Lipids
 | These are ultimately derived from fatty acids. |
Lipids have several functions. They are:
Characteristics of Fatty Acids
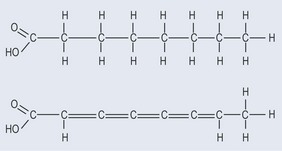
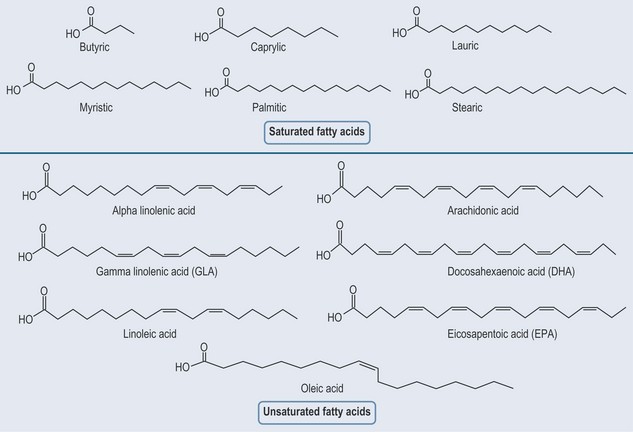
Saturated Fatty Acids
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
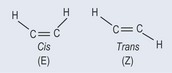
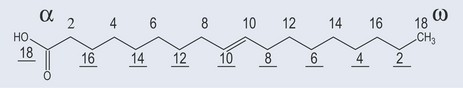
The cis conformations (see Figure 10.2) of the double bonds of unsaturated fatty acids have a bend in their structure of about 30 degrees. This creates significant structural features, particularly for membranes, and as components of membranes the fatty acids tend to have phosphate groups added to them to make phospholipids.
Cis fatty acids can be turned into trans forms by an industrial process. This creates fats with a much higher melting point, which are solid at room temperature and can be made into a spread (e.g. margarines). The natural formation of the bonds has been changed.
• Unsaturated Fatty Acids and the Relevance of its Nomenclature
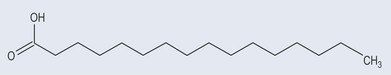
Oleic acid is designated as 18:1 (Figure 10.4)
This short-hand provides quite a bit of information at a glance to a pharmacist.
Linoleic Acid
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree