Light Chain Fanconi Syndrome
Lynn D. Cornell, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Chronic tubulointerstitial nephropathy caused by intracytoplasmic crystalline inclusions composed of monoclonal light chains present in proximal tubular epithelial cells
Etiology/Pathogenesis
In LCFS, abnormal light chain, usually kappa (VK1 subgroup), is resistant to enzymatic breakdown
Clinical Issues
Fanconi syndrome
Normoglycemic glycosuria
Aminoaciduria, uricosuria
Hyperphosphaturia with hypophosphatemia
Chronic renal failure, slowly progressive
Monoclonal gammopathy
Ancillary Tests
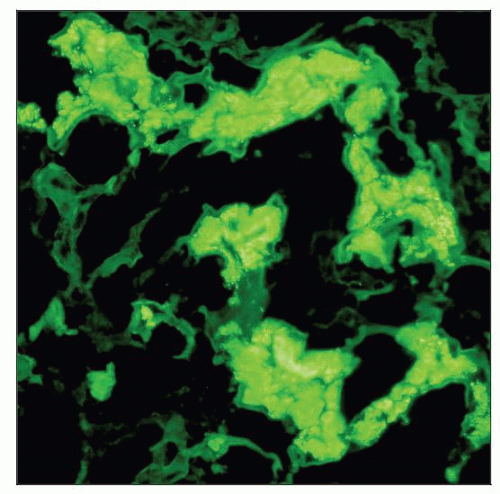
Intracellular monotypic staining for kappa or lambda light chain
Pronase-digested immunofluorescence sections may increase sensitivity of staining in LCFS
Top Differential Diagnoses
Acute tubular injury due to other causes
No light chains present in proximal tubular epithelial cytoplasm
Light chain cast nephropathy
Inflammatory tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with light chains
Protein reabsorption droplets with monotypic light chain staining
Absence of intracytoplasmic crystalline material
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Light chain Fanconi syndrome (LCFS)
Synonyms
Light chain proximal tubulopathy
Acute tubulopathy, light chain related
Related disorder with proximal tubular damage by toxic light chains
Definitions
Chronic tubulointerstitial nephropathy caused by intracytoplasmic crystalline inclusions composed of monoclonal light chains present in proximal tubular epithelial cells
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Light Chains
Produced by clonal proliferation of plasma cells
Most have multiple myeloma (may be smoldering) or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)
Also associated with Waldenström macroglobulinemia and B-cell lymphomas
Normal light chains reabsorbed by proximal tubule, where they are degraded
In LCFS, abnormal light chain, usually kappa (VK1 subgroup), is resistant to enzymatic breakdown
Nephrotoxic light chains crystallize or precipitate within lysosomes in proximal tubules
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare (68 cases reported as of 2000)
Presentation
Fanconi syndrome (acquired)
Normoglycemic glycosuria
Aminoaciduria
Uricosuria
Hyperphosphaturia with hypophosphatemia
Type II renal tubular acidosis
Chronic renal failure, slowly progressive
Monoclonal gammopathy
Bence Jones proteinuria
Plasma cell dyscrasia or lymphoma
Adult-acquired Fanconi syndrome with monoclonal light chain raises suspicion of LCFS
Treatment
Treatment of underlying plasma cell dyscrasia or lymphoma
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Glomeruli
Normal
Tubules
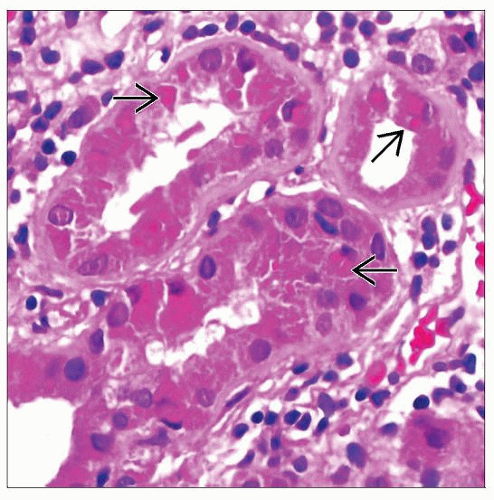
Intracellular crystalline inclusions within proximal tubular epithelial cells
Similar crystals in bone marrow plasma cells
Not all cases with Fanconi syndrome have crystals (10% in 1 series)
Acute and chronic tubular injury
May show other manifestations of monoclonal protein deposition
Crystal-storing histiocytosis with monoclonal light chains
Myeloma cast nephropathy
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree