Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (Odontogenic Keratocyst)
Brenda L. Nelson, DDS, MS
Key Facts
Terminology
Odontogenic keratocyst (OKC)
Distinct developmental odontogenic cyst that may be locally aggressive
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Arise from cells of dental lamina
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Gorlin syndrome) is associated with multiple odontogenic keratocysts
Clinical Issues
Predilection for mandible
Multiple recurrences
Ovarian fibromas
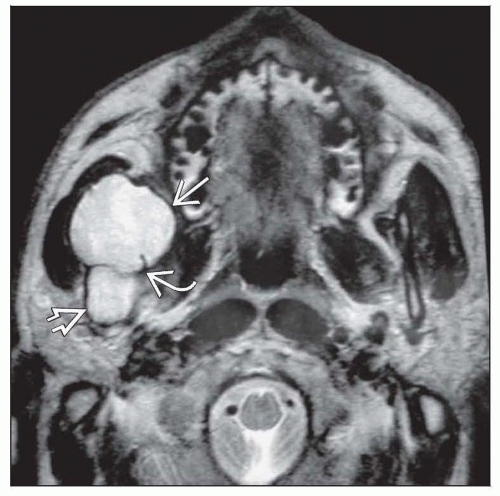
Image Findings
Well-defined, unilocular radiolucency
Smooth, corticated borders
Macroscopic Features
Thin, friable soft tissue
Keratinaceous debris
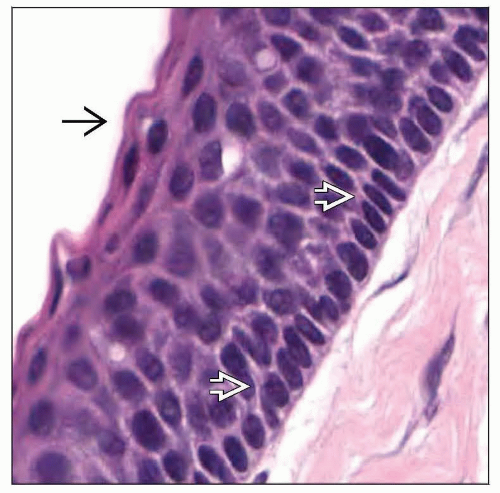
Microscopic Pathology
Epithelial lining
6-8 cells thick
Lacks rete ridges
Parakeratotic epithelial cells
Wavy or corrugated surface
Basal layer shows palisading and hyperchromicity
Inflammation may alter characteristic histology
Top Differential Diagnoses
Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst
Dentigerous cyst
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Odontogenic keratocyst (OKC)
Primordial cyst
Odontogenic keratocystoma
Definitions
Distinct developmental odontogenic cyst that may be locally aggressive
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Histogenesis
May arise from cells of dental lamina
May arise from extensions of basal cells from overlying oral epithelium
Inherited Condition
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS; Gorlin syndrome)
Autosomal dominant trait
High penetrance, variable expression
Spontaneous mutations
9q22, involving PTCH gene
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
4-12% of developmental cysts
Age
Wide range, usually 10-40 years
Cysts found at earlier age in those with NBCCS
Gender
Slight male predilection
Ethnicity
Caucasians affected most commonly
Site
Predilection for mandible (60-80%)
Posterior and ascending ramus
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree