Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma/Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma
Bruce M. Wenig, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
High grade, pleomorphic, malignant, mesenchymal
Diagnosis is one of excluding another more specific sarcoma or nonsarcomatous neoplasm
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Majority occur de novo
Represents most common post-irradiation sarcoma
Clinical Issues
Approximately 3% occur in head and neck
Sinonasal tract most common site of occurrence
Neck 2nd most common site of occurrence
Recurrence rate: ˜ 27% reported
Metastatic rate: ˜ 35% reported
Microscopic Pathology
Histologic variants include
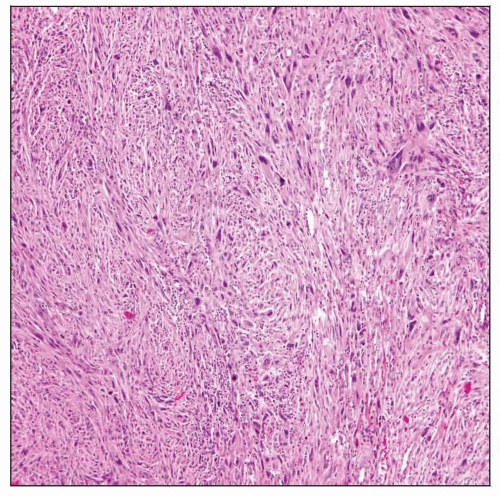
Storiform-pleomorphic
Myxoid
Giant cell
Inflammatory (xanthomatous)
Storiform-pleomorphic type most common histologic variant in sinonasal tract
Fascicular and storiform growth patterns
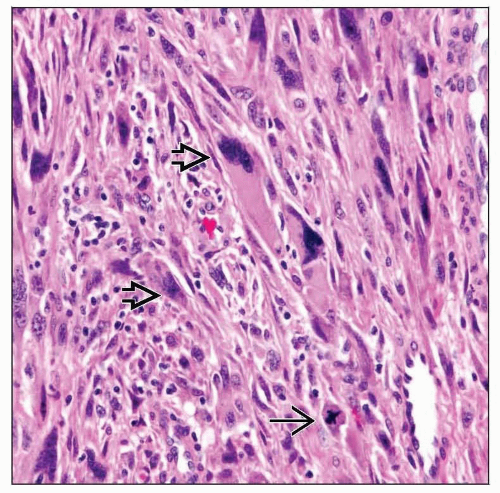
Marked nuclear pleomorphism, increased mitotic activity, including typical and atypical forms
Multinucleated giant cells
Heterologous elements, including bone and cartilage, may be present in any histologic subtype
Ancillary Tests
No specific immunoreactivity
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH)
Definitions
High-grade pleomorphic malignant mesenchymal neoplasm
Diagnosis made by excluding another more specific sarcoma or nonsarcomatous neoplasm
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Idiopathic
Majority occur de novo
Post Radiation
Represents most common post-irradiation sarcoma
To qualify as post-irradiation sarcoma
Must develop in radiation field
Latency period of at least 3 years between irradiation and development of malignancy
Histologic confirmation
Documentation that region of sarcoma was normal prior to irradiation
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Once considered one of the more common soft tissue sarcomas of late adult life
With more advanced diagnostic techniques (e.g., immunohistochemistry) classification into another class of sarcomas decreased incidence
Uncommon neoplasm in head and neck
Approximately 3% occur in head and neck
Age
Occurs over wide range
Most commonly seen in adults
Gender
Male > Female
Site
Sinonasal tract most common site of occurrence
Maxillary sinus > ethmoid sinus and nasal cavity
Rare occurrence in frontal and sphenoid sinuses
Neck 2nd most common site of occurrence
Rare in other head and neck sites
Presentation
Mass with or without associated pain, nasal obstruction, epistaxis, facial asymmetry, proptosis
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical excision is treatment of choice
Lymph node metastasis occurs in less than 15% of cases
Unless clinically suspect for nodal disease, neck dissection of limited value
Adjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy used in presence of metastasis
Radiation
Radiotherapy may be used for tumors with positive surgical margins or close surgical margins
Prognosis
5-year overall, disease-free, and disease-specific survival rates reported as 55%, 44%, and 69%, respectively
Recurrence rate: ˜ 27% reported
Metastatic rate: ˜ 35% reported
Occurs to lung > lymph nodes > liver and bone
Prognosis dependent on
Depth of tumor
Deep soft tissue tumors more likely to metastasize compared to tumors of subcutis
Size of tumor
Smaller tumors (less than 2.5 cm) less likely to metastasize compared to larger tumors
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree