Karyomegalic Interstitial Nephritis
Robert B. Colvin, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Idiopathic
Genetic risk factor suspected, but unproved
DNA toxins suspected in some cases (ochratoxin)
Clinical Issues
Rare; < 30 cases reported
Proteinuria, asymptomatic
Chronic renal failure
Microscopic Pathology
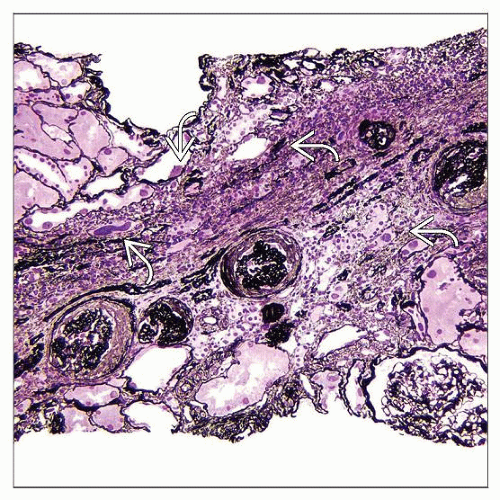
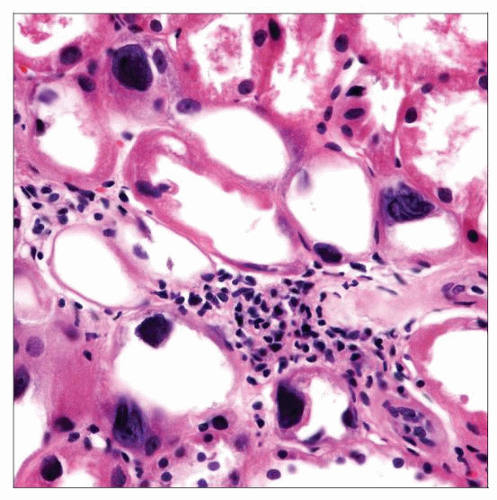
Karyomegaly in tubules throughout the nephron
Interstitial nephritis, fibrosis and tubular atrophy
Karyomegaly in most organs
Probably overlooked diagnosis
Top Differential Diagnoses
Viral infection due to adenovirus, Polyomavirus, Cytomegalovirus
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Karyomegalic interstitial nephritis (KIN)
Synonyms
Systemic karyomegaly
Definitions
Chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis with prominent karyomegaly in tubular epithelium
Initially reported by Mihatsch and colleagues in 1979
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Sporadic and Familial Cases
Genetic risk factor suspected, but unproved
Possible association with HLA (B27/35)
Environmental Toxins
Suspected in some cases
Ochratoxin has been implicated in cases in Tunisia
Animal Models
Various toxins in rats
Ochratoxin
Cisplatin
Glutathione depletion (1-cyano-3,4-epithiobutane)
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare; < 30 cases reported
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree