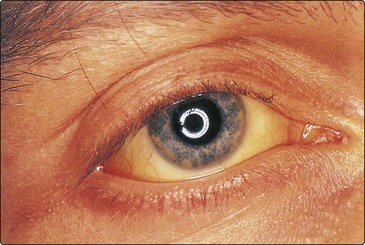
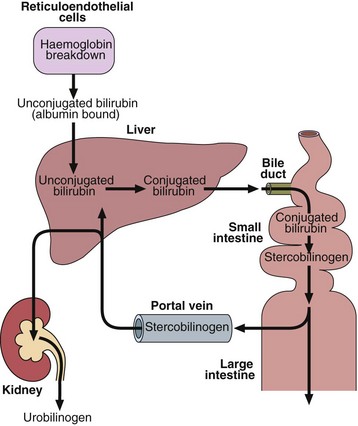
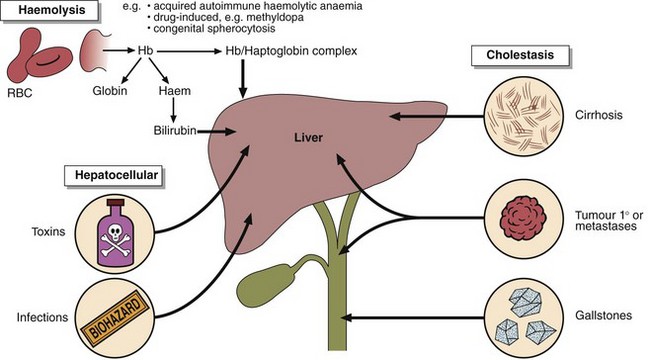
29 Jaundice is a yellow discoloration of the skin or sclera (Fig 29.1). This is due to the presence of bilirubin in the plasma and is not usually detectable until the concentration is greater than about 50 µmol/L. Normally the bilirubin concentration in plasma is less than 21 µmol/L. Bilirubin is derived from the tetrapyrrole prosthetic group found in haemoglobin and the cytochromes. It is normally conjugated with glucuronic acid to make it more soluble, and excreted in the bile (Fig 29.2). There are three main reasons why bilirubin levels in the blood may rise (Fig 29.3).
Jaundice
 Haemolysis. The increased haemoglobin breakdown produces bilirubin, which overloads the conjugating mechanism.
Haemolysis. The increased haemoglobin breakdown produces bilirubin, which overloads the conjugating mechanism.
 Failure of the conjugating mechanism within the hepatocyte.
Failure of the conjugating mechanism within the hepatocyte.
Basicmedical Key
Fastest Basicmedical Insight Engine