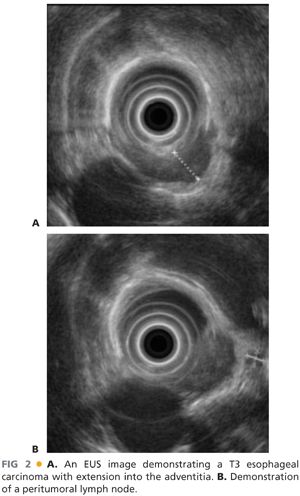
■ Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a critical staging technique for esophageal cancer (FIG 2). The EUS determines the depth of invasion of the tumor into the esophageal wall (T stage). Esophageal tumors that penetrate through the esophageal wall are considered locally advanced and have a high propensity to metastasize to locoregional lymph nodes. Periesophageal lymph nodes that are enlarged can be visualized with EUS and fine needle aspiration biopsy can be performed to determine locoregional lymph node involvement. Patients with biopsy-proven lymph node involvement will typically be referred for preoperative chemotherapy or combined chemoradiation.
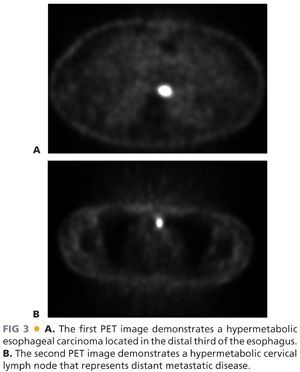
■ All patients who are being considered for esophagectomy should undergo a computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis to evaluate the primary tumor in the esophagus and the locoregional lymph nodes. The liver, celiac lymph nodes, bone, and adrenal glands are common sites for metastatic disease secondary to esophageal carcinoma. Positron emission tomography (PET) is an essential staging technique for esophageal carcinoma (FIG 3). PET scans can detect occult metastatic disease that was not identified on standard CT scans in about 10% to 15% of cases. This detection of occult metastatic disease will prevent patients with stage IV esophageal carcinoma from undergoing an unnecessary esophageal resection.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
Preoperative Planning
■ Any patient who is being evaluated for an Ivor Lewis esophagectomy should undergo a complete and thorough cardiopulmonary evaluation prior to the operation. Cardiac disease and respiratory compromise should be identified in the preoperative period to properly access perioperative risk of complications and mortality.
■ Pulmonary function tests should be obtained to measure the forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) and diffusion capacity. Patients with a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) will have diminished values for FEV1 and diffusing capacity of lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO); therefore, they will be at increased risk for perioperative respiratory complications.
■ A transthoracic echocardiogram is obtained to assess the left ventricular ejection fraction left ventricular wall motion. A treadmill stress test should be obtained when the echocardiogram findings are abnormal.
■ Prior to surgical resection, a patient’s nutritional status should be optimized. A preoperative feeding access for enteral nutrition may be necessary in cases of severe malnutrition. A prealbumin level can be measured to further assess the patient’s nutritional status.
■ Perioperative antibiotics should be given within 30 minutes of the first incision. Compression boots are placed on the lower extremities and subcutaneous unfractionated heparin is given to minimize the risk of postoperative deep venous thrombosis (DVT).
■ An arterial line and central venous catheter should be placed for intraoperative hemodynamic monitoring.
■ An epidural catheter should be placed for postoperative pain management. Epidural infusion of local anesthetic minimizes postthoracotomy pain and allows patients to participate in pulmonary toilet exercises.
Positioning
■ The Ivor Lewis esophagectomy technique uses two incisions. Patients are positioned in the supine position first for the midline laparotomy incision (FIG 4). The second portion of the operation is performed through a right posterior lateral thoracotomy (FIG 5). Patients are positioned in the left lateral decubitus position. A beanbag is used to help hold patients into position. The operating room bed is flexed to open the rib spaces.
TECHNIQUES
MOBILIZATION OF THE GASTRIC CONDUIT
■ The patient is positioned supine on the operating table. A double lumen endotracheal tube is placed for single lung isolation. An arterial line, central venous catheter, and epidural catheter are placed by the anesthesia team. Compression boots and subcutaneous heparin are given for DVT prophylaxis.
■ A midline laparotomy incision is performed from the xiphoid down to the umbilicus. A full inspection of the abdominal cavity is performed to rule out tumor dissemination on peritoneal surfaces or liver metastasis. A Bookwalter retractor is used to provide exposure. The triangular ligament of the left lobe of the liver is divided and the left lateral segment is retracted cephalad to expose the esophageal hiatus.
■ The dissection of the gastric conduit begins by entering the lesser sac along the great curvature of the stomach. The right gastroepiploic artery should be identified and preserved. The greater omentum is divided along the greater curvature of the stomach with an ultrasonic dissector by divided branches of the right gastroepiploic arcade and carefully preserving the gastroepiploic trunk (FIG 6).
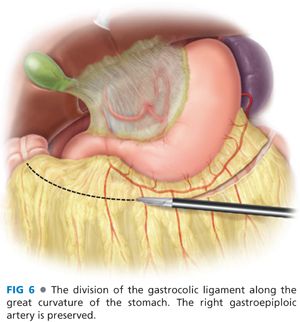
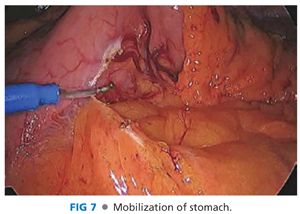
■ The gastrocolic omentum is divided toward the duodenum. The stomach is retracted upward and any adhesions between the stomach and pancreas should be carefully divided (FIG 7). The duodenum is then mobilized with the Kocher maneuver.
■ The short gastric vessels are ligated using the ultrasonic dissector. The short gastric vessels should be ligated close to the spleen to avoid thermal injury to the stomach.
■ The lesser omentum is then divided toward the esophageal hiatus. A replaced left hepatic artery should be identified and preserved if present. The right gastric artery can be preserved in most cases when the anastomosis is performed in the right thorax.
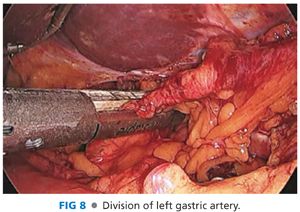
■ The left gastric pedicle is identified along the lesser curvature of the stomach. The left gastric pedicle is divided at the origin from the celiac axis using an Endo GIA linear stapler. The surrounding adipose tissue and lymph nodes should be swept upward prior to ligation of the left gastric pedicle (FIG 8).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


