Intrapulmonary Thymoma
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Intraparenchymatous location within lung parenchyma; central and peripheral
Incidental finding on chest x-ray in 50% of patients
Image Findings
0.5-10 cm in greatest dimension
Macroscopic Features
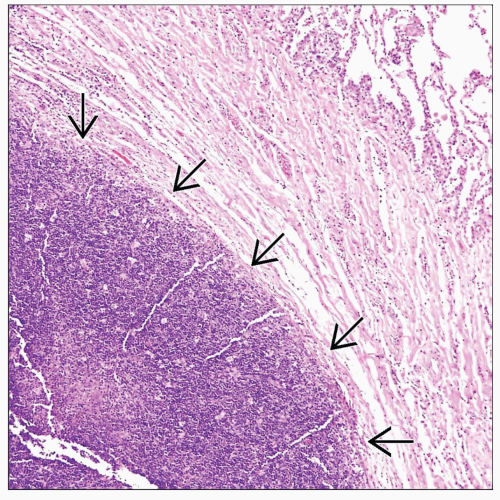
Well-circumscribed tumor surrounded by normal lung parenchyma
Microscopic Pathology
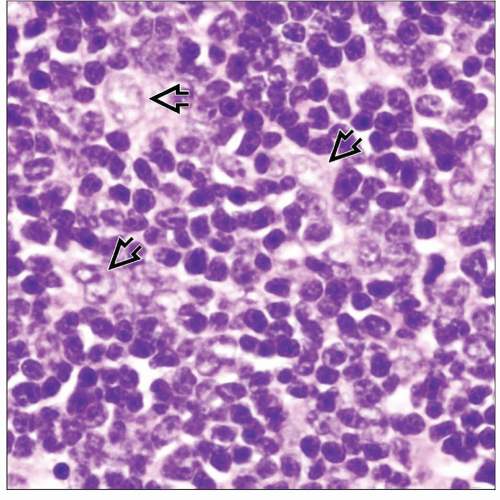
Well-circumscribed cellular proliferation showing various admixtures of epithelial cells and lymphocytes
Lymphocyte-rich thymoma (WHO types B1-B2)
Epithelial-rich thymoma (WHO type B3)
Spindle cell thymoma (WHO types A and AB)
Epithelial cells in intrapulmonary thymomas are bland, with minimal atypia
Tumor cells are intimately admixed with small T lymphocytes in varying proportions
Ancillary Tests
Neoplastic epithelial cells show positive cytoplasmic staining for cytokeratins (AE1/AE3, CAM5.2, CK19)
Neoplastic epithelial cells show strong nuclear positivity for p63
Lymphocytes stain as immature T lymphoblasts (CD1a, CD3, TdT, and CD99 positive)
Spindle cells are negative for mesenchymal markers of differentiation (S100 protein, SMA, desmin, CD34)
Spindle cells may stain positive for calretinin and Bcl-2
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Intrapulmonary thymoma (IPT)
Definitions
Primary thymic epithelial neoplasm arising from embryologically displaced elements within the lung
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Aberrant embryological development of the thymus gland in ectopic locations
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
25-77 years
Gender
Female predilection (M:F = 1:7)
Site
Intraparenchymatous location within lung parenchyma; central and peripheral
Predilection for right lobe of lung
May be multifocal
Presentation
Cough
Chest pain
Incidental finding on chest x-ray in 50% of patients
Not commonly associated with myasthenia gravis, aplastic anemia, or other paraneoplastic syndromes
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lobectomy
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree