Chapter 10 Ingrown Nail Removal
Common indications
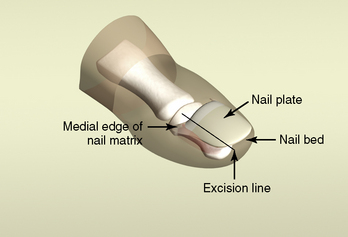
A wedge excision of the margins of the great toe nail is performed to treat recurrent infection of the ingrown nail. Ablation of the outer edges of the nail matrix with electrocautery or chemical cautery can prevent recurrence of an ingrown nail. The anatomy and terminology of the nail are detailed in Figure 10-1.
Equipment
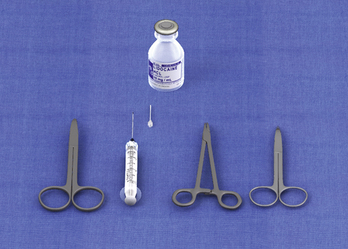
Iris scissors, suture scissors, a hemostat, and a local anesthetic tray are needed for this procedure. Straight iris scissors are preferred, but curved scissors can also be used (Figure 10-2).
Key steps
2. Anesthesia: Perform a digital block of the great toe by passing the needle ventrally alongside the base of the proximal phalanx of the great toe at 2 o’clock and 10 o’clock positions. Inject 2 to 3 cc on each side of the toe, passing the needle deep toward the 4 o’clock and 8 o’clock positions, respectively (Figure 10-3). Take care to avoid direct intra-arterial injection of anesthetic by aspirating before injection. Inject 2 to 3 cc along the needle track while pulling the needle back toward the skin surface. This will block all four digital nerve branches.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree