Inflammatory Pseudotumor
Key Facts
Terminology
Myofibroblastic tumor
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Some cases linked to HHV-8
Clonality demonstrated in some cases
Clinical Issues
Tumor more common in young individuals < 40 years old
Macroscopic Features
Central tumor may grow in polypoid fashion, obstructing airway
Peripheral tumors are larger with yellowish color
Extrapulmonary involvement may be seen in some cases
Tumors vary in size from 1-10 cm in diameter
Microscopic Pathology
Plasma cell variant
Fibrohistiocytic variant
Top Differential Diagnoses
Plasmacytoma
Plasma cells in IPT are polyclonal
Sarcoma
IPT fibrohistiocytic variant does not show nuclear atypia or increased mitotic activity
Diagnostic Checklist
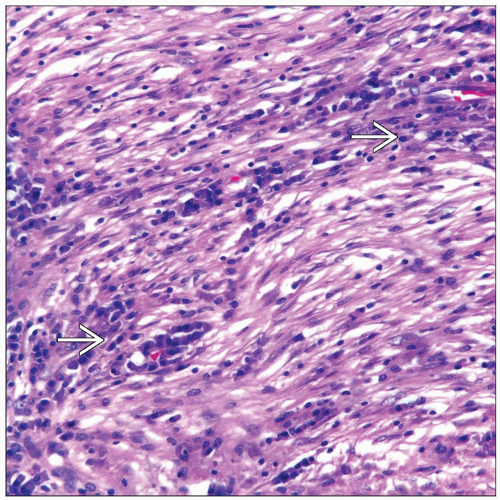
Plasma cell admixed with spindle fibroblastic proliferation
Spindle cell fibrohistiocytic proliferation lacking nuclear atypia and increased mitotic activity
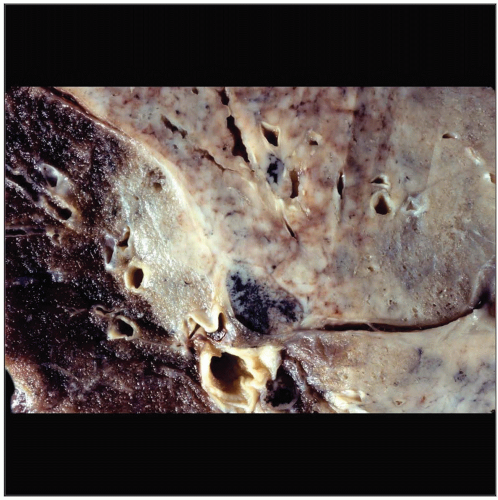 Gross photograph shows an ill-defined tumor mass growing along vascular and bronchial structures. The tumor is grayish in color and does not show areas of necrosis &/or hemorrhage. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Inflammatory pseudotumor (IPT)
Synonyms
Myofibroblastic tumor
Definitions
Benign neoplasm of uncertain histogenesis
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Considerable debate whether IPT represents true tumor or inflammatory reaction
Some cases may be associated to HHV-8
Clonality has been demonstrated in some cases
Uncertain histogenesis
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Tumor more common in individuals < 40 years old
Site
Central tumor in endobronchial location
Peripheral tumor
Presentation
Cough
Fever
Chest pain
Asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection
Spontaneous regression has been documented
Prognosis
Good
Recurrence if not completely resected
Plasma cell variant appears to follow a less aggressive course
Fibrohistiocytic variant appears to be more aggressive
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Central tumor may grow in polypoid fashion, obstructing airway
Peripheral tumors are larger with yellowish color
Extrapulmonary involvement may be seen in some cases
Size
Tumors vary in size from 1-10 cm in diameter
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Marked plasma cell component
Presence of Russel bodies
Plasma cell proliferation admixed with spindle myofibroblastic cells
Predominant fibrohistiocytic spindle cell proliferation
Mitotic activity rare but occasional mitoses may be seen
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Mixed
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Histiocyte/macrophage
Plasma cell
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree