1 Infectious Diseases
Pyrexia of unknown origin (PUO)
Not all cases of PUO are due to infection. In recent-onset PUO, approximately two-thirds of cases are due to infection, compared with only about one-third of cases with long-standing PUO. Other causes include malignancy and autoimmune rheumatic disorders (Table 1.1).
Where would you manage this patient?
Admit to a MAU side room until an infectious aetiology has been ruled out.
What questions should you specifically ask when you see a patient with PUO (in addition to routine questions)?
• Full travel history, including exactly where patient has been and the type of accommodation stayed in
• Vaccination/prophylaxis history
• Contact with animals/sick people
• Occupation: exactly what does the patient do?
• Water exposure: occupational/recreational
• Food history: eating shellfish, drinking dirty water, reheated/raw foods
• Risk behaviour: IV drug usage, unprotected sex
What initial investigations should you perform in a patient presenting with PUO?
Investigations for a PUO
• Urine analysis and microscopy, culture and sensitivity
• Sputum (if producing any) for microscopy, culture and sensitivity, and for acid-fast bacilli
• Stools for ova, cysts and parasites and culture and sensitivity
• Store serum for future serological tests if required
• Wounds: take swabs for culture
• Screen for autoimmune rheumatic disorders
• Additional investigations in this man because of travel abroad: thick and thin blood films for malaria
What should you do now?
• Recheck his history of travel
• Recheck his risk factors for hepatitis and HIV
• Send blood for viral markers for hepatitis
The ultrasound shows a liver abscess in the right lobe and, in view of his travel, an amoebic abscess is a strong possibility. Fortunately, you had sent off an amoebic CFT sample and you ring the reference laboratory urgently. The test is positive (usually positive with an amoebic liver abscess).
Treatment
Remember
• Take a careful history: always repeat
• Examine the patient thoroughly: always repeat
• Initial investigations often give a clue to the diagnosis: often need repeating
• Be patient and don’t give antibiotics until diagnosis is made unless the patient is very sick
• Perform invasive and/or expensive investigations only when appropriate, e.g. echo, CT scan/MRI, bone marrow and culture, lymph node/liver biopsy.
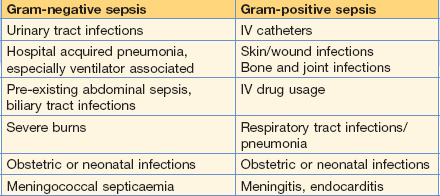
Septicaemia
What factors predispose to septicaemia?
In both Gram-positive and Gram-negative septicaemia, impaired host defences, surgery or instrumentation (including intravenous cannulae, urinary catheters and mechanical ventilation) predispose to septicaemia (Table 1.2).
What would be your initial management of this woman and what investigations would you do?
This patient required supportive therapy (e.g. fluid replacement) because she was dehydrated and oxygen was given and inotropes. Broad-spectrum antibiotics were started after blood and urine cultures had been taken. The antibiotic therapy varies according to local hospital policy and the likely focus of infection. This severely shocked patient was transferred to HDU/ITU (see p. 383).
Investigations
• U&Es, blood sugar, liver biochemistry
• Urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivity
• Sputum (if any produced) for microscopy, culture and sensitivity
• Swabs of any infected-looking lesions (including throat swab if throat appears inflamed)
• Pus (if present) for microscopy, culture and sensitivity
• NAAT (nuclear acid amplification test)
If a urinary tract infection is thought to be the likely source, a broad-spectrum cephalosporin is often appropriate (e.g. cefuroxime) or a quinolone (e.g. ciprofloxacin).
• A broad-spectrum cephalosporin such as IV cefuroxime or IV cefotaxime or IV ceftriaxone.
• Metronidazole should be added if an anaerobic infection is considered likely.
• A broad-spectrum penicillin with β-lactamase inhibitor (e.g. piperacillin/tazobactam). Gentamicin can be added if the patient is very ill.
• A carbapenem (e.g. imipenem, although this is a restricted antibiotic in many hospitals).
Remember
• If you give gentamicin, remember that you need to monitor serum levels. Combining it with a cephalosporin can potentiate its nephrotoxicity.
• Cefuroxime, ceftriaxone and cefotaxime have fairly good activity against staphylococci and streptococci, as well as against many Gram-negative rods; they have poor activity against Pseudomonas spp. Ceftazidime has poor activity against streptococci and staphylococci but excellent activity against Pseudomonas spp. and other Gram-negative organisms. No cephalosporins are active against Enterococcus spp.
• Cephalosporins are associated with C. difficile diarrhoea and should be avoided if possible.
• If a patient develops sepsis while in hospital it is possible that this is due to resistant organisms, e.g. methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) or resistant Gram-negative rods.
• If MRSA infection is considered likely and the patient is very sick, add IV vancomycin 1 g × 2 per day (assuming normal renal function) given over at least 100 minutes while awaiting culture results.
A urine sample was obtained from this patient. Microscopy found it to contain 1000 WCC/mm3 and ++ bacteria.