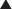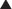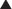Chapter 18 Infectious Diseases
Introduction to Antibiotics
Suggestions
 Know which category the individual drugs belong to, and learn the category as a whole. For example, ceftriaxone is a third-generation cephalosporin. Therefore learn about cephalosporins in general, and then know the general differences among first-, second-, third-, and fourth-generation cephalosporins. In some circumstances there might be one or two extra important bits of information pertaining to individual drugs that are important to learn.
Know which category the individual drugs belong to, and learn the category as a whole. For example, ceftriaxone is a third-generation cephalosporin. Therefore learn about cephalosporins in general, and then know the general differences among first-, second-, third-, and fourth-generation cephalosporins. In some circumstances there might be one or two extra important bits of information pertaining to individual drugs that are important to learn. Antibiotics can usually be classified in terms of the categories of bacteria they kill. These categories include the following:
Antibiotics can usually be classified in terms of the categories of bacteria they kill. These categories include the following: You will have to learn “bugs” (not covered in this text) and drugs in at least three different frameworks:
You will have to learn “bugs” (not covered in this text) and drugs in at least three different frameworks:Important Considerations
 It is required that you learn the mechanism of action (MOA) of a drug and also the mechanism of resistance, which enables an organism to live in the presence of the drug. This is important because when you are selecting an antibiotic, if your first choice does not work, you will have a better understanding of why it did not work and will be better educated to select a different antibiotic that will have a greater probability of killing the organism. For example, if a penicillin (a β-lactam) was given and the bug is known to produce β-lactamase, a third-generation cephalosporin (another β-lactam) might be a poor next choice.
It is required that you learn the mechanism of action (MOA) of a drug and also the mechanism of resistance, which enables an organism to live in the presence of the drug. This is important because when you are selecting an antibiotic, if your first choice does not work, you will have a better understanding of why it did not work and will be better educated to select a different antibiotic that will have a greater probability of killing the organism. For example, if a penicillin (a β-lactam) was given and the bug is known to produce β-lactamase, a third-generation cephalosporin (another β-lactam) might be a poor next choice. Make sure that the drug you select can get to the tissue in which the infection is located. Special examples include the following:
Make sure that the drug you select can get to the tissue in which the infection is located. Special examples include the following: Gut (intraintestinal, not intraperitoneal) infections are often best treated with oral medications that cannot be absorbed into the body (because they remain in the gut, which is where the infection is)—for example, oral vancomycin for C. difficile colitis.
Gut (intraintestinal, not intraperitoneal) infections are often best treated with oral medications that cannot be absorbed into the body (because they remain in the gut, which is where the infection is)—for example, oral vancomycin for C. difficile colitis. Central nervous system (CNS) infections: Some drugs do not penetrate the blood-brain barrier. These would be poor choices for treatment of bacterial meningitis.
Central nervous system (CNS) infections: Some drugs do not penetrate the blood-brain barrier. These would be poor choices for treatment of bacterial meningitis. The choice of antibiotic (oral versus intravenous, broad-spectrum versus narrow-spectrum agents) is usually determined by how sick the patient is and how certain you are about which bacterium is causing the infection. If you are uncertain, choose a broad-spectrum drug.
The choice of antibiotic (oral versus intravenous, broad-spectrum versus narrow-spectrum agents) is usually determined by how sick the patient is and how certain you are about which bacterium is causing the infection. If you are uncertain, choose a broad-spectrum drug. If you can do cultures, try to do them before the patient starts taking antibiotics, because after you administer antibiotics the drug will be in the patient’s system and will inhibit growth of specimens collected from the patient after that point in time.
If you can do cultures, try to do them before the patient starts taking antibiotics, because after you administer antibiotics the drug will be in the patient’s system and will inhibit growth of specimens collected from the patient after that point in time. Broad-spectrum drugs tend to be more expensive and more “powerful” and should be reserved for situations in which narrow-spectrum agents are not indicated. Development of resistance is a very real risk every time an antibiotic is used. Always using the powerful drugs will result in bacterial resistance to them. Then what will you use?
Broad-spectrum drugs tend to be more expensive and more “powerful” and should be reserved for situations in which narrow-spectrum agents are not indicated. Development of resistance is a very real risk every time an antibiotic is used. Always using the powerful drugs will result in bacterial resistance to them. Then what will you use?Viruses are technically not alive, so antivirals are usually not referred to as antimicrobials.
Advanced Killing Techniques
Knowledge of pharmacokinetics is required to enable a clinician to be really good at knowing how to kill off an infection. Understanding some very important fundamental concepts are required (Figure 18-1).
 Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC): The MIC of an antimicrobial is the minimum concentration that will inhibit growth of a pathogen. Obviously, it is desirable to have the concentration in the patient’s infected tissues to be greater than the MIC. If drug A has a lower MIC than drug B, then drug A kills the pathogen at a lower concentration of drug and would therefore be better at killing that particular pathogen, assuming all other factors are identical. When the MIC level of a drug for a given pathogen is low, the pathogen is considered sensitive to the drug (i.e., the drug will kill it). When the MIC is a moderate value, the pathogen’s sensitivity to the drug will be intermediate, and when the MIC is high, the pathogen will be resistant to that drug. Laboratory values often report sensitivities as S, I, or R to report sensitive, intermediate, and resistant, respectively.
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC): The MIC of an antimicrobial is the minimum concentration that will inhibit growth of a pathogen. Obviously, it is desirable to have the concentration in the patient’s infected tissues to be greater than the MIC. If drug A has a lower MIC than drug B, then drug A kills the pathogen at a lower concentration of drug and would therefore be better at killing that particular pathogen, assuming all other factors are identical. When the MIC level of a drug for a given pathogen is low, the pathogen is considered sensitive to the drug (i.e., the drug will kill it). When the MIC is a moderate value, the pathogen’s sensitivity to the drug will be intermediate, and when the MIC is high, the pathogen will be resistant to that drug. Laboratory values often report sensitivities as S, I, or R to report sensitive, intermediate, and resistant, respectively.Now, exactly how the concentration of the antimicrobial stays above the MIC in the body is very important and is different for different drugs. The most important concepts are illustrated in Figure 18-1 and include:
 Time dependence is the total length of time that a drug level stays above the MIC. What matters is the total duration that the concentration is above the MIC. These drugs are called time-dependent antimicrobials. β-Lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems) all fall into this category. Note that it does not matter if the drug level is just barely above the MIC or is 10 times the MIC.
Time dependence is the total length of time that a drug level stays above the MIC. What matters is the total duration that the concentration is above the MIC. These drugs are called time-dependent antimicrobials. β-Lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems) all fall into this category. Note that it does not matter if the drug level is just barely above the MIC or is 10 times the MIC. CMAX/MIC is the maximum concentration of the drug compared with the MIC. In other words, some drugs kill better when the maximum concentration of the drug is very high. These drugs are called concentration-dependent antimicrobials. As a general rule, it is important to measure drug concentrations of these drugs. Vancomycin and aminoglycosides fall into this category and it is common to measure levels of both of them. Note that it does not matter how long the concentration stays above the MIC for these drugs, which is in complete contrast to the time-dependent drugs.
CMAX/MIC is the maximum concentration of the drug compared with the MIC. In other words, some drugs kill better when the maximum concentration of the drug is very high. These drugs are called concentration-dependent antimicrobials. As a general rule, it is important to measure drug concentrations of these drugs. Vancomycin and aminoglycosides fall into this category and it is common to measure levels of both of them. Note that it does not matter how long the concentration stays above the MIC for these drugs, which is in complete contrast to the time-dependent drugs.Penicillins
Moa (Mechanism of Action)
 All β-lactams (penicillins, carbapenems, and cephalosporins) act through this common sequence of events.
All β-lactams (penicillins, carbapenems, and cephalosporins) act through this common sequence of events.Binding
 Different bacteria have different amounts and different types of penicillin-binding proteins. For example, Escherichia coli has seven types, and Staph. aureus has four.
Different bacteria have different amounts and different types of penicillin-binding proteins. For example, Escherichia coli has seven types, and Staph. aureus has four.Cell Wall Destruction
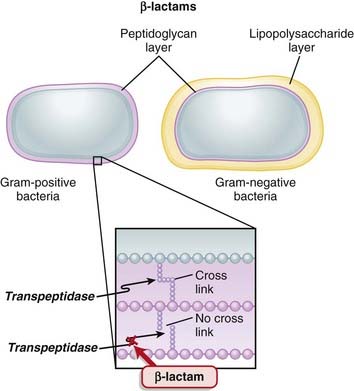
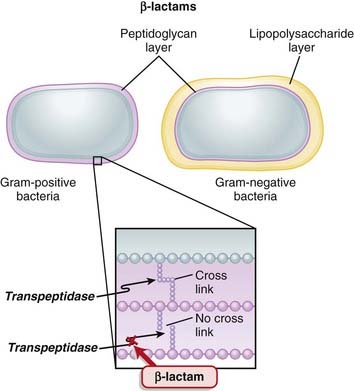
 Transpeptidases are enzymes that cross-link peptidoglycan molecules in bacterial cell walls. Cross-linking these molecules gives strength to the cell wall.
Transpeptidases are enzymes that cross-link peptidoglycan molecules in bacterial cell walls. Cross-linking these molecules gives strength to the cell wall. β-Lactams work by inhibiting transpeptidase, preventing it from forming cross-links. This results in a bacterium with a structurally deficient cell wall, typically leading to bacterial lysis (Figure 18-2).
β-Lactams work by inhibiting transpeptidase, preventing it from forming cross-links. This results in a bacterium with a structurally deficient cell wall, typically leading to bacterial lysis (Figure 18-2). Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer, but external to this layer is a lipopolysaccharide layer. This lipopolysaccharide layer protects the peptidoglycan layer from β-lactam activity, and therefore gram-negative bacteria are significantly more resistant to β-lactams.
Gram-negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer, but external to this layer is a lipopolysaccharide layer. This lipopolysaccharide layer protects the peptidoglycan layer from β-lactam activity, and therefore gram-negative bacteria are significantly more resistant to β-lactams. β-Lactamase inhibitors are added to some β-lactam antibiotics to overcome resistance caused by β-lactamase. Although β-lactamase inhibitors do contain a β-lactam, they are not toxic to the bacteria; they merely bind to β-lactamase. Examples of β-lactamase inhibitors include the following:
β-Lactamase inhibitors are added to some β-lactam antibiotics to overcome resistance caused by β-lactamase. Although β-lactamase inhibitors do contain a β-lactam, they are not toxic to the bacteria; they merely bind to β-lactamase. Examples of β-lactamase inhibitors include the following: Narrow-spectrum penicillins contain a larger molecule on the penicillin molecule side chain that confers steric hindrance: the inability to twist the molecule into other stereoisomers. This results in these penicillins being resistant to β-lactamase but at the same time restricts their spectrum of activity (thus they are said to be narrow-spectrum agents).
Narrow-spectrum penicillins contain a larger molecule on the penicillin molecule side chain that confers steric hindrance: the inability to twist the molecule into other stereoisomers. This results in these penicillins being resistant to β-lactamase but at the same time restricts their spectrum of activity (thus they are said to be narrow-spectrum agents). Aminopenicillins have an added amino group (NH2) that makes the molecule more hydrophilic and thus able to cross the lipopolysaccharide layer more easily. Therefore aminopenicillins have greater activity against gram-negative bacteria.
Aminopenicillins have an added amino group (NH2) that makes the molecule more hydrophilic and thus able to cross the lipopolysaccharide layer more easily. Therefore aminopenicillins have greater activity against gram-negative bacteria. Broad-spectrum penicillins are modifications of aminopenicillins: nitrogen and carbon atoms are added to the molecule. This increases the range of bacteria that are sensitive to the antibiotic. These penicillins are usually coadministered with a β-lactamase inhibitor because they are β-lactamase sensitive (a common example is “Pip/Tazo,” which is piperacillin and tazobactam).
Broad-spectrum penicillins are modifications of aminopenicillins: nitrogen and carbon atoms are added to the molecule. This increases the range of bacteria that are sensitive to the antibiotic. These penicillins are usually coadministered with a β-lactamase inhibitor because they are β-lactamase sensitive (a common example is “Pip/Tazo,” which is piperacillin and tazobactam).Mechanisms of Resistance
 Gram-negative bacteria, as described previously, inherently have an outer protective lipopolysaccharide layer that guards the peptidoglycan layer from attack by some β-lactams.
Gram-negative bacteria, as described previously, inherently have an outer protective lipopolysaccharide layer that guards the peptidoglycan layer from attack by some β-lactams. The main mechanisms of resistance to β-lactams include the following:
The main mechanisms of resistance to β-lactams include the following: Production of β-lactamase, which enzymatically destroys the four-carbon β-lactam ring
Production of β-lactamase, which enzymatically destroys the four-carbon β-lactam ring• Genes for β-lactamase may exist on plasmids or on bacterial chromosomes and may be produced constitutively (all the time) or can be induced.
• Genes that are on plasmids can readily be passed from one bacterium to another; thus resistance can be transmitted to different species.
Pharmacokinetics
 Eighty percent of penicillin is cleared by the kidneys within 4 hours. Therefore it is very quickly eliminated from the body, which is an undesirable characteristic if the goal is to expose the bacterial infection to prolonged concentrations of the drug.
Eighty percent of penicillin is cleared by the kidneys within 4 hours. Therefore it is very quickly eliminated from the body, which is an undesirable characteristic if the goal is to expose the bacterial infection to prolonged concentrations of the drug. Probenecid, a uricosuric, competes with penicillin in the organic acid transporter in the kidney and therefore decreases renal clearance of penicillin, thereby prolonging high tissue concentrations and a longer half life. It is coadministered with penicillin.
Probenecid, a uricosuric, competes with penicillin in the organic acid transporter in the kidney and therefore decreases renal clearance of penicillin, thereby prolonging high tissue concentrations and a longer half life. It is coadministered with penicillin. Most penicillins are renally cleared, and the dose must be adjusted in patients with renal dysfunction. However, cloxacillin is hepatically cleared and does not require dose adjustment in patients with renal dysfunction.
Most penicillins are renally cleared, and the dose must be adjusted in patients with renal dysfunction. However, cloxacillin is hepatically cleared and does not require dose adjustment in patients with renal dysfunction.Important Notes
 Methicillin is no longer used clinically, because of toxicity. It is, however, used to determine whether a staphylococcal infection is sensitive to the penicillins in its class. The term methicillin-resistant Staph. aureus (MRSA) is now commonly used to describe these organisms.
Methicillin is no longer used clinically, because of toxicity. It is, however, used to determine whether a staphylococcal infection is sensitive to the penicillins in its class. The term methicillin-resistant Staph. aureus (MRSA) is now commonly used to describe these organisms.FYI
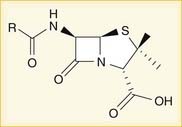
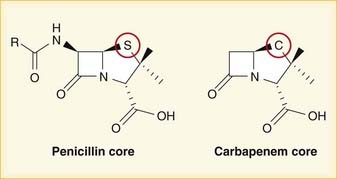
 A lactam is a chemical ring. A β-lactam is a four-molecule ring (three carbons and one nitrogen) and is the nucleus of the penicillin molecule. The penicillin nucleus is shown in Figure 18-3. Modifications to the five-membered ring are the basis on which cephalosporins and carbapenems (two other β-lactam antibiotics) were derived.
A lactam is a chemical ring. A β-lactam is a four-molecule ring (three carbons and one nitrogen) and is the nucleus of the penicillin molecule. The penicillin nucleus is shown in Figure 18-3. Modifications to the five-membered ring are the basis on which cephalosporins and carbapenems (two other β-lactam antibiotics) were derived. Peptidoglycans are polymers of sugars and amino acids. Cross-linking of these polymers results in a rigid crystal structure.
Peptidoglycans are polymers of sugars and amino acids. Cross-linking of these polymers results in a rigid crystal structure. The clinically significant difference between amoxicillin and ampicillin is that amoxicillin is generally administered orally whereas ampicillin is generally administered IV.
The clinically significant difference between amoxicillin and ampicillin is that amoxicillin is generally administered orally whereas ampicillin is generally administered IV. It would be nice for memorization if penicillin G were given in the gut and penicillin V were given IV; unfortunately, it is the other way around.
It would be nice for memorization if penicillin G were given in the gut and penicillin V were given IV; unfortunately, it is the other way around. Uricosurics are drugs that promote the excretion of uric acid and are used in patients who have gout (high uric acid levels leading to uric acid crystal formation in joints).
Uricosurics are drugs that promote the excretion of uric acid and are used in patients who have gout (high uric acid levels leading to uric acid crystal formation in joints).Cephalosporins
Prototypes and common drugs
Moa (Mechanism of Action)
 All β-lactams (penicillins, carbapenems, and cephalosporins) act through this common sequence of events.
All β-lactams (penicillins, carbapenems, and cephalosporins) act through this common sequence of events.Binding
 Different bacteria have different amounts and different types of penicillin-binding proteins. For example, E. coli has seven types and S. aureus has four.
Different bacteria have different amounts and different types of penicillin-binding proteins. For example, E. coli has seven types and S. aureus has four.Cell Wall Destruction
 Transpeptidases are enzymes that cross-link peptidoglycan molecules in bacterial cell walls. Cross-linking these molecules gives strength to the cell wall (see Figure 18-2).
Transpeptidases are enzymes that cross-link peptidoglycan molecules in bacterial cell walls. Cross-linking these molecules gives strength to the cell wall (see Figure 18-2). β-lactams work by inhibiting transpeptidase, preventing it from forming cross-links. This results in a bacterium with a structurally deficient cell wall, typically leading to bacterial lysis.
β-lactams work by inhibiting transpeptidase, preventing it from forming cross-links. This results in a bacterium with a structurally deficient cell wall, typically leading to bacterial lysis.Mechanisms of Resistance
 The main mechanisms of resistance to β-lactams include the following:
The main mechanisms of resistance to β-lactams include the following: Production of β-lactamase, which enzymatically destroys the four-carbon β-lactam ring
Production of β-lactamase, which enzymatically destroys the four-carbon β-lactam ring• Genes for β-lactamase may exist on plasmids or on bacterial chromosomes and may be produced constitutively (all the time) or can be induced.
• Genes that are on plasmids can readily be passed from one bacterium to another; thus resistance can be transmitted to different species.
Pharmacokinetics
 Penetration to the brain through the blood-brain barrier is a very important factor for antibiotics because it will determine whether or not an antibiotic will be effective against bacterial meningitis. Third-generation cephalosporins have good CNS penetration.
Penetration to the brain through the blood-brain barrier is a very important factor for antibiotics because it will determine whether or not an antibiotic will be effective against bacterial meningitis. Third-generation cephalosporins have good CNS penetration.Contraindications
 Nonanaphylactic allergy to penicillins is a relative contraindication; however, the cross-reactivity is reported to be 2% to 10%, and cephalosporins have been used frequently in patients with a penicillin allergy.
Nonanaphylactic allergy to penicillins is a relative contraindication; however, the cross-reactivity is reported to be 2% to 10%, and cephalosporins have been used frequently in patients with a penicillin allergy.Side Effects
 Hematologic: rare cases of bone marrow suppression resulting in a low white blood cell (WBC) count (aka neutropenia or granulocytopenia)
Hematologic: rare cases of bone marrow suppression resulting in a low white blood cell (WBC) count (aka neutropenia or granulocytopenia)Important Notes
FYI
 Note how the four-membered ring (the β-lactam) is the same as in penicillins; however, the other ring is six-membered, whereas in penicillins it is five-membered. The diagram shows the core nucleus of cephalosporins. There are currently four generations of cephalosporins (Figure 18-4).
Note how the four-membered ring (the β-lactam) is the same as in penicillins; however, the other ring is six-membered, whereas in penicillins it is five-membered. The diagram shows the core nucleus of cephalosporins. There are currently four generations of cephalosporins (Figure 18-4). Cephalosporins were first isolated from Cephalosporium acremonium from the sea near a sewer outlet in 1948. They were initially found to cure Staph. aureus infection and typhoid.
Cephalosporins were first isolated from Cephalosporium acremonium from the sea near a sewer outlet in 1948. They were initially found to cure Staph. aureus infection and typhoid. The suffix -penia means low cell counts. WBCs are granulocytes. The most abundant type of WBC is the neutrophil. Thus a low WBC count can be referred to as granulocytopenia or neutropenia.
The suffix -penia means low cell counts. WBCs are granulocytes. The most abundant type of WBC is the neutrophil. Thus a low WBC count can be referred to as granulocytopenia or neutropenia. Eosinophilia occurs in drug hypersensitivity reactions and also in other conditions. The mnemonic CHINA can help you remember the common causes of eosinophilia:
Eosinophilia occurs in drug hypersensitivity reactions and also in other conditions. The mnemonic CHINA can help you remember the common causes of eosinophilia: Pseudomembranous colitis is treated with antibiotics that kill C. difficile: metronidazole or vancomycin. Because the infection is in the gut, oral administration of these antibiotics delivers high concentrations of drug to the site of infection.
Pseudomembranous colitis is treated with antibiotics that kill C. difficile: metronidazole or vancomycin. Because the infection is in the gut, oral administration of these antibiotics delivers high concentrations of drug to the site of infection.Carbapenems
Moa (Mechanism of Action)
 All β-lactams (penicillins, carbapenems, and cephalosporins) act through this common sequence of events.
All β-lactams (penicillins, carbapenems, and cephalosporins) act through this common sequence of events.Binding
 Different bacteria have different amounts and different types of penicillin-binding proteins. For example, E. coli has seven types and S. aureus has four.
Different bacteria have different amounts and different types of penicillin-binding proteins. For example, E. coli has seven types and S. aureus has four.Cell Wall Destruction
 Transpeptidases are enzymes that cross-link peptidoglycan molecules in bacterial cell walls. Cross-linking these molecules gives strength to the cell wall (Figure 18-5).
Transpeptidases are enzymes that cross-link peptidoglycan molecules in bacterial cell walls. Cross-linking these molecules gives strength to the cell wall (Figure 18-5). β-Lactams work by inhibiting transpeptidase, preventing it from forming cross-links. This results in a bacterium with a structurally deficient cell wall, typically leading to bacterial lysis.
β-Lactams work by inhibiting transpeptidase, preventing it from forming cross-links. This results in a bacterium with a structurally deficient cell wall, typically leading to bacterial lysis.Mechanisms of Resistance
 The main mechanisms of resistance to β-lactams include the following:
The main mechanisms of resistance to β-lactams include the following: Production of β-lactamase, which enzymatically destroys the four-carbon β-lactam ring
Production of β-lactamase, which enzymatically destroys the four-carbon β-lactam ring• Genes for β-lactamase may exist on plasmids or on bacterial chromosomes and may be produced constitutively (all the time) or can be induced.
• Genes that are on plasmids can readily be passed from one bacterium to another; thus resistance can be transmitted to different species.
• There are a few different classification schemes for β–lactamases, and there are many different individual β-lactamase enzymes. Some other names of β–lactams include penicillinase and carbapenemase.
Pharmacokinetics
 Imipenem is hydrolyzed by renal tubular dipeptidase. Imipenem is therefore always combined with cilastatin, which inhibits this breakdown. Other carbapenems do not require coadministration with cilastatin because they are not metabolized by dipeptidase.
Imipenem is hydrolyzed by renal tubular dipeptidase. Imipenem is therefore always combined with cilastatin, which inhibits this breakdown. Other carbapenems do not require coadministration with cilastatin because they are not metabolized by dipeptidase. Doses must be reduced in patients with renal dysfunction. With imipenem, there is increased risk for seizures in patients with renal dysfunction.
Doses must be reduced in patients with renal dysfunction. With imipenem, there is increased risk for seizures in patients with renal dysfunction.Side Effects
 Fever: This can cause diagnostic dilemmas because carbapenems are administered to patients with suspected infections, who usually already have a fever. If the drug starts to create a fever, then it can be very difficult to know when the infection is gone (which is usually accompanied by a normalization of the patient’s temperature).
Fever: This can cause diagnostic dilemmas because carbapenems are administered to patients with suspected infections, who usually already have a fever. If the drug starts to create a fever, then it can be very difficult to know when the infection is gone (which is usually accompanied by a normalization of the patient’s temperature).Important Notes
 MRSA is an important resistant strain of S. aureus. It is not sensitive to carbapenems. It is treated with vancomycin.
MRSA is an important resistant strain of S. aureus. It is not sensitive to carbapenems. It is treated with vancomycin. VRE is another important resistant strain. About 50% of VRE infections are sensitive to carbapenems.
VRE is another important resistant strain. About 50% of VRE infections are sensitive to carbapenems. Carbapenems are very broad-spectrum agents. They are considered “big guns” and are used only in patients who are very sick or suspected of having resistant organisms. They are generally not used as first-line treatment.
Carbapenems are very broad-spectrum agents. They are considered “big guns” and are used only in patients who are very sick or suspected of having resistant organisms. They are generally not used as first-line treatment.FYI
 Carbapenems differ structurally from penicillins in that the five-membered ring that is attached to the β-lactam ring contains a carbon atom instead of a sulfur atom. The name carbapenem comes from carbon and penicillin. Figure 18-6 shows the core structure of a carbapenem but does not show the side chains.
Carbapenems differ structurally from penicillins in that the five-membered ring that is attached to the β-lactam ring contains a carbon atom instead of a sulfur atom. The name carbapenem comes from carbon and penicillin. Figure 18-6 shows the core structure of a carbapenem but does not show the side chains. The entero- in Enterobacteriaceae refers to enteral, or within the GI tract, which is where Enterobacteriaceae (and Enterococcus) colonize.
The entero- in Enterobacteriaceae refers to enteral, or within the GI tract, which is where Enterobacteriaceae (and Enterococcus) colonize.Glycopeptides
Moa (Mechanism of Action)
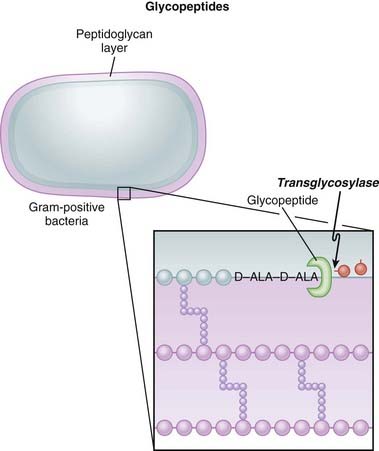
 Glycopeptides inhibit cell wall synthesis by attaching to the end of the peptidoglycan precursor units (a short four– or five–amino acid sequence called the d-alanyl-d-alanine [D-ALA-D-ALA] terminus) that are required to be laid down into the matrix. This step is catalyzed by transglycosylase. Because the glycopeptide binds to the end of the precursor, the precursor is not released from the carrier and thus peptidoglycan synthesis stops (Figure 18-7).
Glycopeptides inhibit cell wall synthesis by attaching to the end of the peptidoglycan precursor units (a short four– or five–amino acid sequence called the d-alanyl-d-alanine [D-ALA-D-ALA] terminus) that are required to be laid down into the matrix. This step is catalyzed by transglycosylase. Because the glycopeptide binds to the end of the precursor, the precursor is not released from the carrier and thus peptidoglycan synthesis stops (Figure 18-7). Glycopeptides are bactericidal in organisms that are dividing, because a dividing bacterium requires new cell wall synthesis, and the absence of the new cell wall results in death of the organism.
Glycopeptides are bactericidal in organisms that are dividing, because a dividing bacterium requires new cell wall synthesis, and the absence of the new cell wall results in death of the organism. As a result of targeting the peptidoglycan layer, glycopeptides are effective only against gram-positive organisms. This is because gram-negative bacteria possess a thick outer layer of lipopolysaccharide that covers the peptidoglycan layer.
As a result of targeting the peptidoglycan layer, glycopeptides are effective only against gram-positive organisms. This is because gram-negative bacteria possess a thick outer layer of lipopolysaccharide that covers the peptidoglycan layer.Mechanisms of Resistance
 A change to the end of the amino acid precursor (which has a d-alanyl-d-alanine terminus) can result in the drug not binding to the precursor. This is the most common method by which Enterococcus becomes resistant (and is then called VRE, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus).
A change to the end of the amino acid precursor (which has a d-alanyl-d-alanine terminus) can result in the drug not binding to the precursor. This is the most common method by which Enterococcus becomes resistant (and is then called VRE, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus). Biofilm production: Staphylococcus epidermidis can produce a film that can block penetration of the antibiotic. This is a slimy way to become resistant.
Biofilm production: Staphylococcus epidermidis can produce a film that can block penetration of the antibiotic. This is a slimy way to become resistant.Pharmacokinetics
 The half-life of vancomycin is 6 hours, whereas the half-life of teicoplanin is much longer, as high as 100 hours (assuming normal kidney function).
The half-life of vancomycin is 6 hours, whereas the half-life of teicoplanin is much longer, as high as 100 hours (assuming normal kidney function). Glycopeptides are very poorly absorbed from the GI tract. If the infection that is being treated is inside the GI tract (for example, C. difficile colitis, also called “C diff colitis,” or pseudomembranous colitis), then administering the drug orally provides the highest exposure of antibiotic to the infection.
Glycopeptides are very poorly absorbed from the GI tract. If the infection that is being treated is inside the GI tract (for example, C. difficile colitis, also called “C diff colitis,” or pseudomembranous colitis), then administering the drug orally provides the highest exposure of antibiotic to the infection. If the infection is anywhere other than inside the GI tract (e.g., blood, soft tissues, brain, heart), then the drug must be administered via the intravenous route—or, for teicoplanin, also intramuscularly.
If the infection is anywhere other than inside the GI tract (e.g., blood, soft tissues, brain, heart), then the drug must be administered via the intravenous route—or, for teicoplanin, also intramuscularly. They are renally cleared, and in patients who have renal dysfunction or renal failure, the frequency of administration must be dramatically reduced (sometimes as infrequently as one dose every 2 to 3 days) and should be guided by drug levels in the blood. Because teicoplanin has a longer half-life, it can actually be administered once a week in patients without any renal function.
They are renally cleared, and in patients who have renal dysfunction or renal failure, the frequency of administration must be dramatically reduced (sometimes as infrequently as one dose every 2 to 3 days) and should be guided by drug levels in the blood. Because teicoplanin has a longer half-life, it can actually be administered once a week in patients without any renal function. Glycopeptides are cleared by dialysis. This is important because patients on dialysis usually get dialyzed three times a week. The best time to administer vancomycin would be just after dialysis, which would result in the drug remaining at high levels in the blood and tissues for the full 2 to 3 days until next dialysis. It would not be logical to give the drug right before dialysis.
Glycopeptides are cleared by dialysis. This is important because patients on dialysis usually get dialyzed three times a week. The best time to administer vancomycin would be just after dialysis, which would result in the drug remaining at high levels in the blood and tissues for the full 2 to 3 days until next dialysis. It would not be logical to give the drug right before dialysis.Side Effects
 Flushing: When vancomycin is administered quickly, the blood pressure can fall because of histamine release. Therefore vancomycin must be administered slowly (usually over 1 hour). The flushing caused by histamine release has been called red man syndrome and is not an allergy but a predictable response to rapidly administered vancomycin.
Flushing: When vancomycin is administered quickly, the blood pressure can fall because of histamine release. Therefore vancomycin must be administered slowly (usually over 1 hour). The flushing caused by histamine release has been called red man syndrome and is not an allergy but a predictable response to rapidly administered vancomycin. Ototoxicity is very rare, unless vancomycin is administered with another ototoxic agent such as aminoglycosides.
Ototoxicity is very rare, unless vancomycin is administered with another ototoxic agent such as aminoglycosides. Nephrotoxicity is rare (6% to 7%), unless administered with another nephrotoxic agent such as aminoglycosides. The role of vancomycin as a nephrotoxic agent is probably overestimated, and it should probably be considered to be only very weakly nephrotoxic.
Nephrotoxicity is rare (6% to 7%), unless administered with another nephrotoxic agent such as aminoglycosides. The role of vancomycin as a nephrotoxic agent is probably overestimated, and it should probably be considered to be only very weakly nephrotoxic.Important Notes
 Although vancomycin can kill S. aureus organisms that are resistant to cloxacillin (or methicillin [i.e., MRSA]), cloxacillin has a lower MIC than vancomycin for strains that are β-lactam susceptible. Therefore cloxacillin is a better killer of S. aureus when there is no resistance. Vancomycin is not a stronger antibiotic. It is simply a different but paradoxically slightly weaker one that avoids β-lactam resistance.
Although vancomycin can kill S. aureus organisms that are resistant to cloxacillin (or methicillin [i.e., MRSA]), cloxacillin has a lower MIC than vancomycin for strains that are β-lactam susceptible. Therefore cloxacillin is a better killer of S. aureus when there is no resistance. Vancomycin is not a stronger antibiotic. It is simply a different but paradoxically slightly weaker one that avoids β-lactam resistance.Fluoroquinolones
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
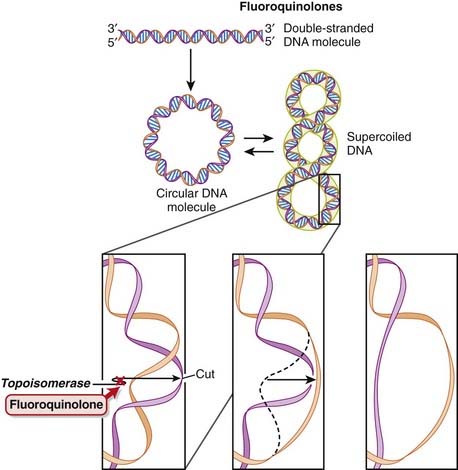
 DNA is normally supercoiled. Supercoiled DNA is under too much tension to be separated, so an extra step is required before replication and transcription can occur. DNA gyrase relaxes supercoiled DNA by cutting it, allowing rotation to occur, and then reattaching it.
DNA is normally supercoiled. Supercoiled DNA is under too much tension to be separated, so an extra step is required before replication and transcription can occur. DNA gyrase relaxes supercoiled DNA by cutting it, allowing rotation to occur, and then reattaching it. Fluoroquinolones bind to and inhibit DNA gyrase (also called topoisomerase II) and topoisomerase IV. Fluoroquinolones inhibit DNA gyrase in gram-negative organisms and topoisomerase IV in gram-positive organisms (Figure 18-8).
Fluoroquinolones bind to and inhibit DNA gyrase (also called topoisomerase II) and topoisomerase IV. Fluoroquinolones inhibit DNA gyrase in gram-negative organisms and topoisomerase IV in gram-positive organisms (Figure 18-8). The fluoroquinolones inhibit DNA gyrase after the cutting step, preventing reattachment from occurring. At high doses this leads to the release of these broken segments of DNA. It is thought that the accumulation of these DNA fragments leads to cell death, accounting for the bactericidal action of fluoroquinolones.
The fluoroquinolones inhibit DNA gyrase after the cutting step, preventing reattachment from occurring. At high doses this leads to the release of these broken segments of DNA. It is thought that the accumulation of these DNA fragments leads to cell death, accounting for the bactericidal action of fluoroquinolones. Inhibiting topoisomerase IV interferes with separation of replicated chromosomal DNA into the respective daughter cells during cell division. Thus cell division is halted.
Inhibiting topoisomerase IV interferes with separation of replicated chromosomal DNA into the respective daughter cells during cell division. Thus cell division is halted.Pharmacokinetics
 Fluoroquinolones can enter human cells easily and therefore are often used to treat intracellular pathogens.
Fluoroquinolones can enter human cells easily and therefore are often used to treat intracellular pathogens. Fluoroquinolones are absorbed very well from the gut. Therefore if a person can tolerate oral medication, he or she can usually be switched from an intravenous form to an oral form.
Fluoroquinolones are absorbed very well from the gut. Therefore if a person can tolerate oral medication, he or she can usually be switched from an intravenous form to an oral form. Most fluoroquinolones are cleared renally, and dose adjustment may be required in patients with renal impairment.
Most fluoroquinolones are cleared renally, and dose adjustment may be required in patients with renal impairment.Important Notes
 Originally, quinolones were mainly effective against gram-negative bacteria, but newer agents are useful against gram-positive cocci as well.
Originally, quinolones were mainly effective against gram-negative bacteria, but newer agents are useful against gram-positive cocci as well. Drugs from a different but similarly named class called quinolines do not have antibacterial properties but rather are antimalarials.
Drugs from a different but similarly named class called quinolines do not have antibacterial properties but rather are antimalarials.FYI
 As the name suggests, fluoroquinolones possess a fluorine ion. They all contain two six-membered rings. Ciprofloxacin is shown in the diagram (Figure 18-9). Earlier generations of fluoroquinolones were not fluorinated and were simply called quinolones. They are infrequently used now.
As the name suggests, fluoroquinolones possess a fluorine ion. They all contain two six-membered rings. Ciprofloxacin is shown in the diagram (Figure 18-9). Earlier generations of fluoroquinolones were not fluorinated and were simply called quinolones. They are infrequently used now. An isomerase converts a molecule from one isomer to another isomer. Topo- refers to topographic, or surface shape. Therefore topoisomerase enzymes convert DNA molecules from one shape to another shape.
An isomerase converts a molecule from one isomer to another isomer. Topo- refers to topographic, or surface shape. Therefore topoisomerase enzymes convert DNA molecules from one shape to another shape.Aminoglycosides
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
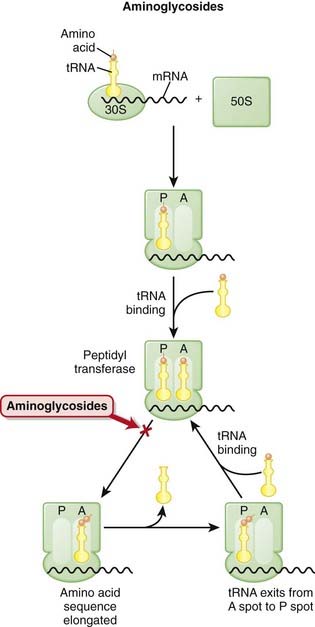
 The production of proteins from mRNA is called translation; this step requires ribosomes, transfer RNA (tRNA), and messenger RNA (mRNA) (Figure 18-10).
The production of proteins from mRNA is called translation; this step requires ribosomes, transfer RNA (tRNA), and messenger RNA (mRNA) (Figure 18-10). mRNA contains the sequencing code based on DNA; tRNA contains single amino acids and binds to a three-base sequence of mRNA; ribosomes are like assembly line processing machinery, bringing the mRNA and tRNA together to assemble sequences of amino acids.
mRNA contains the sequencing code based on DNA; tRNA contains single amino acids and binds to a three-base sequence of mRNA; ribosomes are like assembly line processing machinery, bringing the mRNA and tRNA together to assemble sequences of amino acids. The ribosomes are different sizes:
The ribosomes are different sizes: Ribosomes have different binding sites, named:
Ribosomes have different binding sites, named: Peptidyl (P): This is where the existing amino acid chain (connected to tRNA) is elongated when the incoming amino acid is transferred to it through the action of peptidyl transferase.
Peptidyl (P): This is where the existing amino acid chain (connected to tRNA) is elongated when the incoming amino acid is transferred to it through the action of peptidyl transferase. There are two theories about how aminoglycosides work:
There are two theories about how aminoglycosides work:1 Aminoglycosides are protein synthesis inhibitors. They irreversibly bind the 30S ribosomal subunit (RSU). At low concentrations they cause misreading of the mRNA by ribosomes, leading to synthesis of proteins with incorrect amino acid sequences. At higher concentrations they halt protein synthesis, trapping the ribosomes at the AUG start codon. Accumulation of these abnormal initiation complexes halts translation.
 Many other protein synthesis inhibitors are bacteriostatic (only inhibit replication of bacteria versus killing bacteria). The action of aminoglycosides on the outer bacterial membrane, in addition to its protein synthesis inhibition, is thought to be the reason that aminoglycosides are bactericidal.
Many other protein synthesis inhibitors are bacteriostatic (only inhibit replication of bacteria versus killing bacteria). The action of aminoglycosides on the outer bacterial membrane, in addition to its protein synthesis inhibition, is thought to be the reason that aminoglycosides are bactericidal.Pharmacokinetics
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree