30 Immunomodulatory drugs
The immune system has evolved to provide humoral (antibody) and cell-mediated immunity against foreign pathogens (e.g. bacteria, fungus, virus and parasites, but also foreign grafts) and malignancy (cancer); it can also act against self-antigens in pathological conditions (autoimmune disease). A variety of immunocompetent cells, including antigen-presenting cells and T and B lymphocytes, orchestrate the manner in which the body responds to a particular insult (Fig. 3.30.1). Drugs that target the immune cells are of immense benefit in the treatment of a number of diseases that involve overactivity of the immune system (Table 3.30.1) or imbalance (e.g. balance of T helper cell types affects progression of leprosy). The pharmacology of these agents in the context of rheumatoid arthritis will be used as an example.
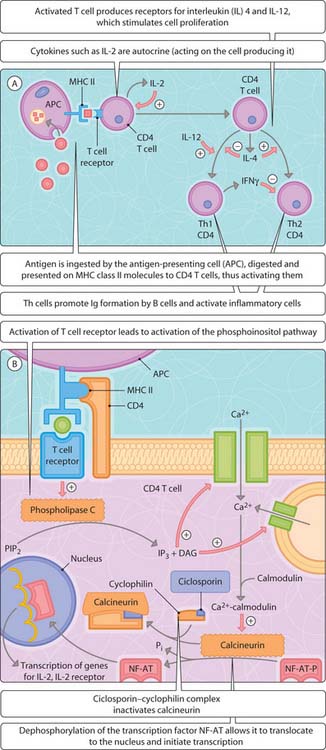
Fig. 3.30.1 Immunomodulation. (A) Activation of CD4 T cells; (B) stimulation of transcription of inflammatory mediators.
Table 3.30.1 T cells in disease
| Cell type | Normal role | Inappropriate deployment |
|---|---|---|
| T helper 1 | Proliferation of CD8 cells, macrophages | Rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, Helicobacter pylori-induced peptic ulcer |
| T helper 2 | Response to extra-cellular antigens, driving antibody production from B cells | Allergy, asthma, schistosome infection |
| Cytotoxic T cells | Removal of cells with intracellular foreign protein production (malignant cells, transplant cells, viruses) | Toxic shock (over-expansion in response to bacterial endotoxins), Kawasaki disease (blood vessel inflammation) |
| B cells | Production of anti-bodies to foreign antigens | Autoimmune thyroiditis, agranulocytosis initiated by drugs |
Rheumatoid arthritis
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-selective (e.g. ibuprofen, aspirin, indometacin) and COX2-selective (e.g. celecoxib) NSAIDs inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins (Ch. 29) implicated in the pain and swelling associated with rheumatoid arthritis. These drugs only provide symptomatic relief and do not prevent destruction of cartilage and bone.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




