Chapter 5 Immunity
Immunity
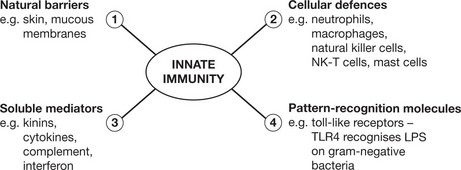
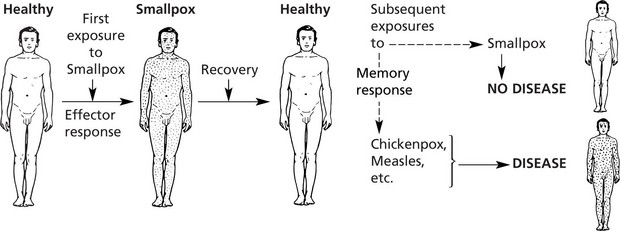
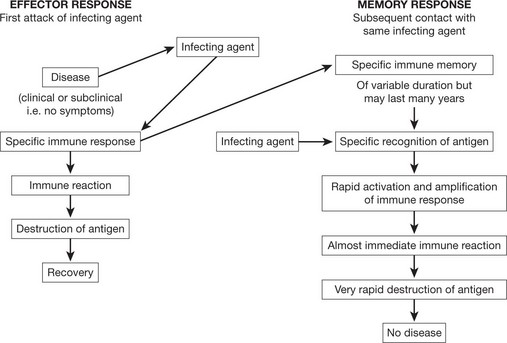
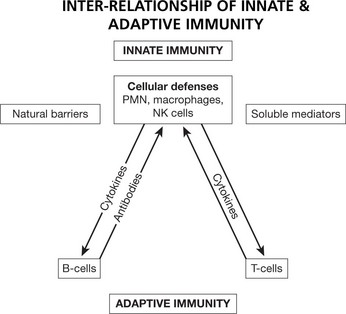
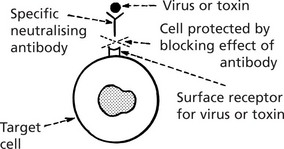
The immune system protects us from invading pathogenic microorganisms and cancer. Immunity – the state of protection from infectious disease – has both a less specific or INNATE and a more specific or ADAPTIVE component.
Cellular Basis of the Adaptive Immune Response
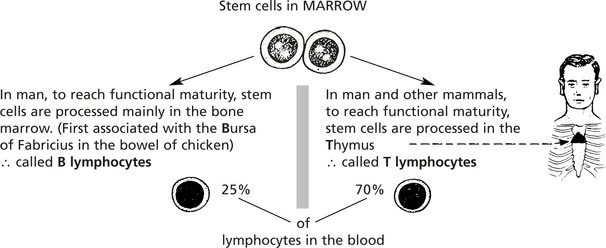
The main cells of the adaptive immune response are the lymphocytes. They are indistinguishable by light microscopy using conventional stains but can be separated by the presence of different surface proteins on T and B cells.
Genetic Influences on the Immune Response
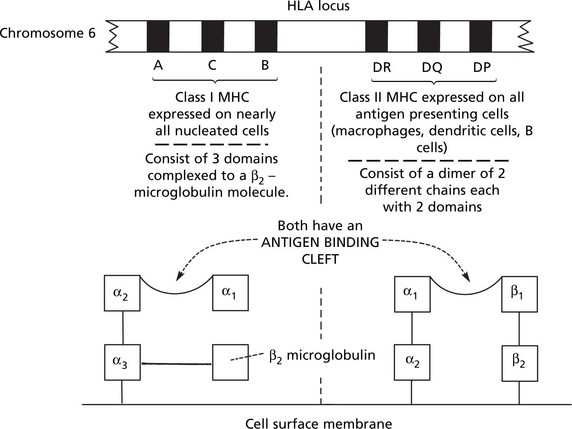
The major histocompatibility complex, also known as the human leucocyte antigen (HLA), has an important role in the immune response and disease.
The important roles of HLA are:
The most striking example is ankylosing spondylitis where >90% of patients carry the allele HLA B27.
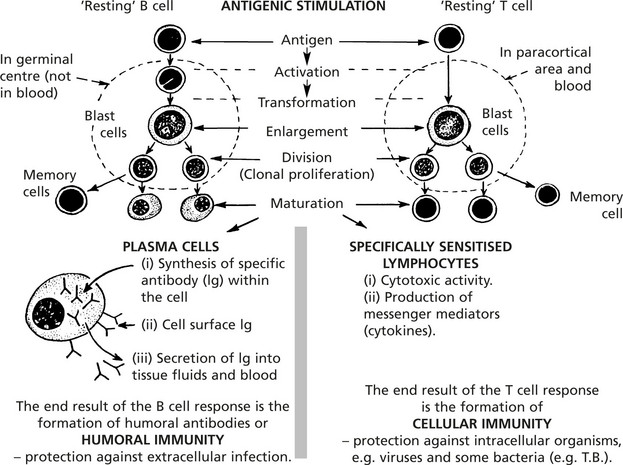
Cellular Immunity
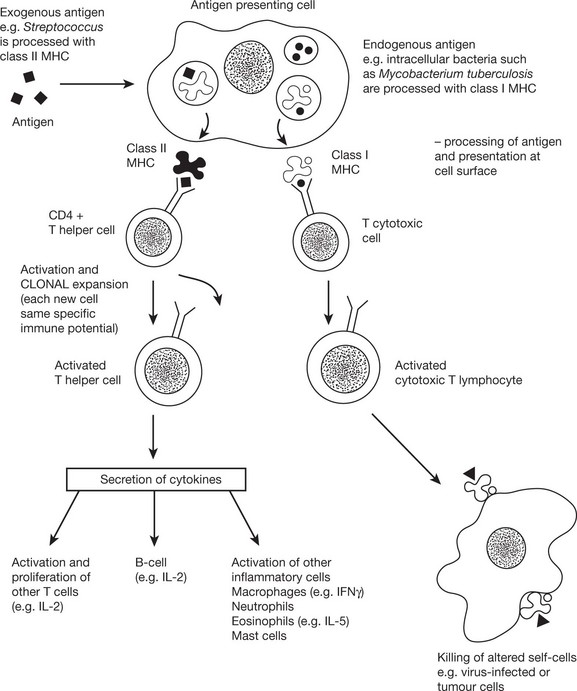
Activation of T cells requires the involvement of antigen presenting cells. Within these cells, foreign antigen is proteolytically digested to short peptides and then presented with HLA molecules to the T cell which possesses a specific receptor for that antigen.
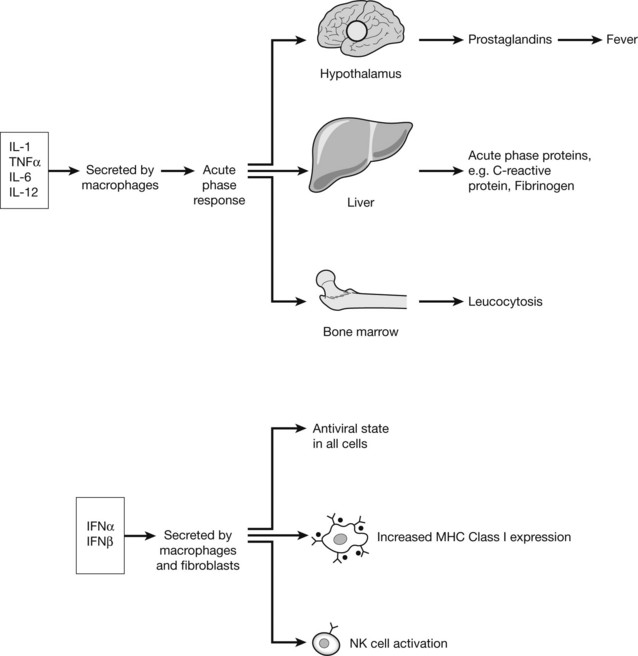
Cytokines
The chemical messengers of immune system are known as CYTOKINES. These small proteins are produced by virtually all cells of the innate and adaptive immune system, particularly CD4+ lymphocytes. The quantity and type of cytokine can positively and negatively regulate cells and cytokine effect is in turn controlled by expression or down-regulation of cytokine receptors on the cell surface.
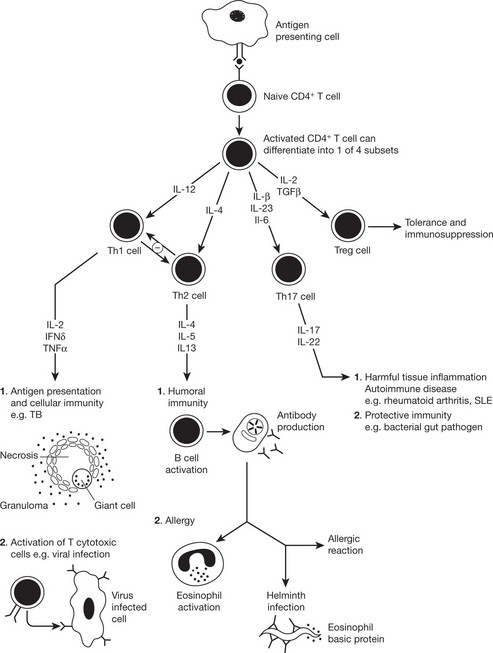
Cytokines Involved in Adaptive Immunity
The immune response to a particular pathogen must induce an appropriate set of effector functions that can eliminate the pathogen from the host. Differences in cytokine secretion patterns among T helper cells are determinants of the type of immune response made to a particular antigenic challenge. Accordingly the cytokines secreting T helper cells are currently divided into 4 subsets:
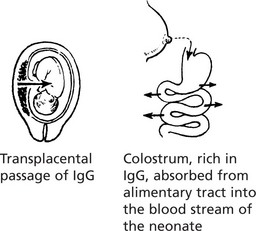
Humoral Immunity
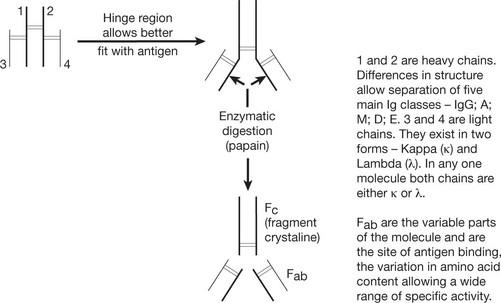
Basic Structure of Immunoglobulin
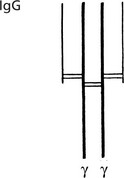
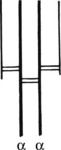
The basic immunoglobulin is a protein molecule consisting of 2 identical LIGHT chains and two identical HEAVY chains. Each light chain is bound to a heavy chain by a disulphide bond. Similarly disulphide bridges link the two heavy and light chain combinations to form the basic four chain structure.
Immunoglobulins
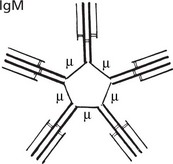
Antibody Classes and Activities
These groups are named according to the composition of the heavy chains.
Note: The numerous (10) antigenbinding sites increase its efficiency.
The natural blood group antibodies, anti-A and anti-B are M globulins.
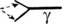
IgG (heavy chain = γ) is a single molecule with two antigen binding sites.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree