Idiopathic Nodular Glomerulopathy
A. Brad Farris, III, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Idiopathic nodular glomerulopathy (ING)/glomerulosclerosis (GS)
Nodular GS, associated with smoking &/or HTN without DM
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Smoking leads to physiologic & molecular derangement (e.g., advanced glycation end product [AGE] production)
Clinical Issues
Patients are typically elderly, male, & white
Renal dysfunction
Nephrotic-range proteinuria
Microscopic Pathology
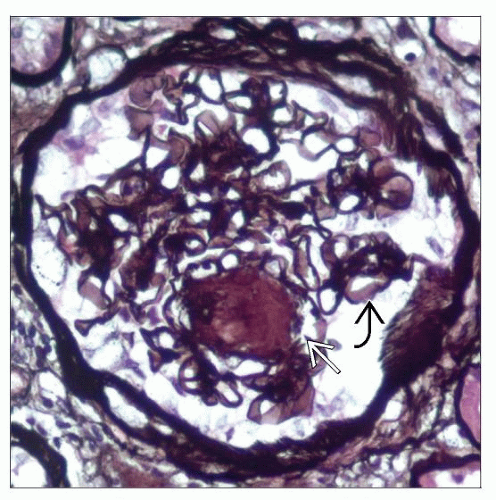
Rounded or nodular acellular PAS-positive areas
Minute endothelial-lined channels
Glomerulomegaly
Moderate to severe arteriosclerosis and arteriolosclerosis with hyalinosis
Ancillary Tests
No immune deposits by immunofluorescence or EM
Segmental GBM thickening and mesangial matrix expansion by EM
Top Differential Diagnoses
Diabetic glomerulosclerosis
MPGN, lobular variant
Monoclonal immunoglobulin deposition disease
Thrombotic microangiopathy
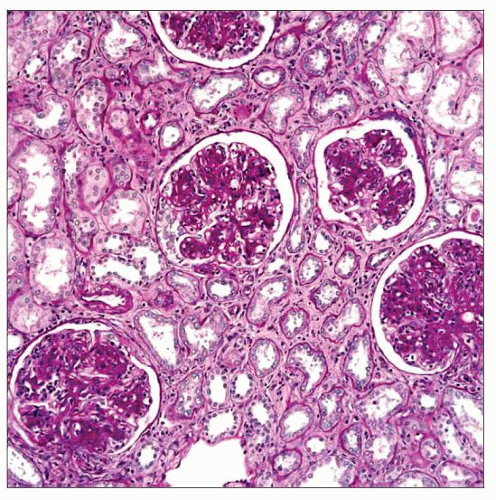 In ING, glomeruli have nodular mesangial expansion, hypertrophy, & hypercellularity incidentally found in a nephrectomy for tumor in a 63-year-old woman with no history of diabetes. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Idiopathic nodular glomerulopathy (ING)/glomerulosclerosis (GS)
Synonyms
Smoking-associated nodular GS
Idiopathic lobular glomerulonephritis
Nodular mesangial sclerosis
Definitions
Nodular GS, associated with smoking &/or hypertension (HTN) without history of diabetes mellitus (DM)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Smoking
Leads to microalbuminuria in healthy individuals
Risk factor for renal dysfunction
Advanced glycation end products (AGE) formation, oxidative stress, angiogenesis, & altered intrarenal hemodynamics
AGE alters extracellular matrix (ECM) by protein crosslinking and interaction with cell surface receptors such as receptor to AGE (RAGE)
Mediators include NF-κB, MAPK, JAK/STAT, Smad, TGF-β, IGF, VEGF, fibrogenic cytokines, PDGF, type IV collagen, laminin, heparan sulfate, & fibronectin
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Activates sympathetic & renin-angiotensin systems, leading to HTN & ECM production
Hypertension
Smoking-induced renal injury probably more likely with preexisting sclerotic insult, such as hypertensive nephrosclerosis
ING has been reported with only history of HTN in absence of smoking
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Elderly
Gender
Male predominance a feature of most series
Ethnicity
White predominance noted in larger series
Presentation
Renal dysfunction (˜ 80% of patients)
Proteinuria, nephrotic range (˜ 70% of patients)
Treatment
Drugs
Angiotensin II blockade
Prognosis
ESRD has been noted
35.3% over 14.2-month period in 1 series
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Glomeruli
Rounded/nodular acellular PAS(+) expansion of mesangium composed of lamellated matrix material
Nuclei often found at periphery of nodules
Minute endothelial-lined channels present in and around nodules
Capillaries compressed or collapsed
Increased capillary density compared with normal controls
Glomerulomegaly
Segmental glomerular basement membrane (GBM) thickening
Little or no GBM duplication
Vessels
Moderate to severe arteriosclerosis and arteriolar hyalinosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree