Hyalinizing Granuloma
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Unusual condition of unknown origin
May have autoimmune origin
PHG may be associated with conditions with similar histological features, including
Retroperitoneal fibrosis
Sclerosing mediastinitis
Clinical Issues
Epidemiology
Rare occurrence
Any age group, but more common in middle-aged adults
Symptoms
Cough
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Fever
Laboratory findings
Antinuclear antibodies
Rheumatoid factor may be positive
Coombs positive hemolithic anemia may be positive
Microscopic Pathology
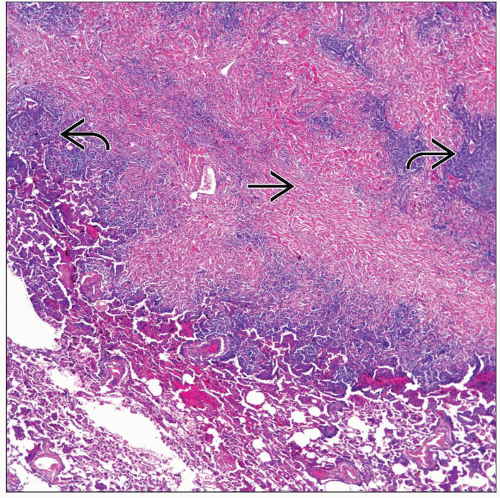
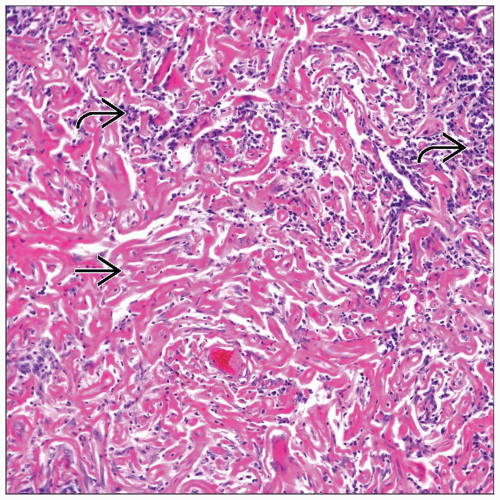
Prominent, dense, fibrocollagenous deposition
Inflammatory reaction
Dilatation of vascular spaces
Focal calcification may be present
Top Differential Diagnoses
Amyloid tumor
Intrapulmonary solitary fibrous tumor (SFT)
Inflammatory pseudotumor, plasma cell type (IP)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Pulmonary hyalinizing granuloma (PHG)
Definitions
Benign reactive process, probably inflammatory or autoimmune
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Unusual condition of unknown etiology
May have autoimmune origin
Associated Conditions
PHG may be associated with conditions with similar histological features, including
Retroperitoneal fibrosis
Sclerosing mediastinitis
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare occurrence
Age
Any age group, but more common in middle-aged adults
Gender
No gender predilection
Presentation
Cough
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Fever
Asymptomatic
Laboratory Tests
Antinuclear antibodies may be positive
Rheumatoid factor may be positive
Coombs positive hemolytic anemia may be positive
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection
Prognosis
Good
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Single or multiple pulmonary nodules
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Nodules are firm and light tan in color
Size
Vary from 1 cm to > 10 cm in diameter
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Prominent, dense, fibrocollagenous deposition
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree