Histoplasmosis
Key Facts
Terminology
Disease caused by inhalation of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum
Clinical Issues
Clinical forms of histoplasmosis include benign self-limited, acute, chronic, progressive disseminated, and with mediastinal involvement
Immunosuppressed patients generally develop progressive disseminated disease involving other organs
Microscopic Pathology
Acute infection characterized by acute fibrinous pneumonia with abundant organisms within macrophages in alveolar spaces
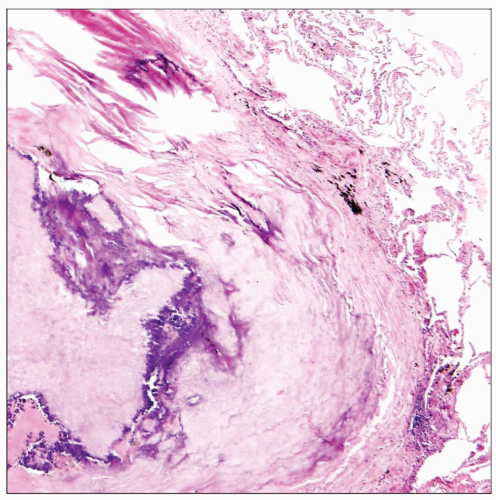
Disseminated infection characterized by granulomatous inflammation that may show central areas of necrosis
Granulomas may show characteristic lamellar patten of concentric fibrosis with progressive stages of calcification
Organisms are round or oval, small (2-4 µm), uninucleated, and devoid of a capsule, with single narrow-based buds
Organisms can also show a small, dark-staining central “dot” similar to those seen in Pneumocystis
Cytoplasm of the yeast can be retracted from the cell wall, forming a “halo” that resembles a capsule
Organisms are highlighted in tissue sections with GMS stains
PAS also stains Histoplasma but more weakly
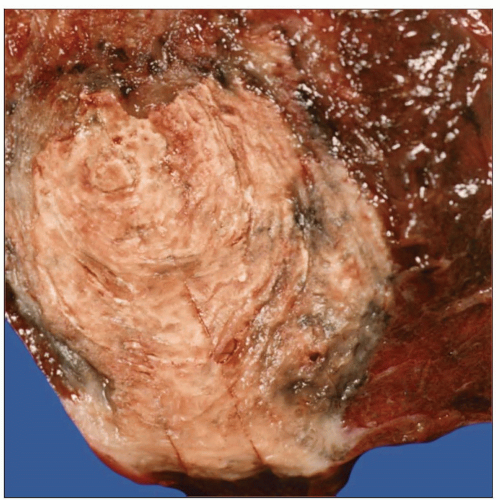 Gross appearance of a pulmonary histoplasma granuloma shows a distinctive lamellar pattern of concentric fibrosis with progressive stages of calcification. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Disease caused by inhalation of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
The fungus lives in soil and is endemic to the south-central United States, especially the Mississippi and Ohio valleys
Infection caused by inhalation of infected dust, most commonly from bird droppings
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Approximately 500,000 new cases occur annually
Presentation
Clinical forms of histoplasmosis include benign self-limited, acute, chronic, progressive disseminated, and with mediastinal involvement
Most patients with primary pulmonary infection are asymptomatic (75% of patients)
Patients with acute pulmonary histoplasmosis present with a self-limited disease in the upper lobes that resolves spontaneously
Patients exposed to a large inoculum may develop life-threatening infection with acute respiratory distress syndrome
Symptoms usually develop 2 weeks after exposure and include fever, chills, cough, and muscle pain
Complications of the infection include calcified pulmonary nodules, chronic cavitary lesions, or mediastinal fibrosis
Immunosuppressed patients generally develop progressive disseminated disease involving other organs
Treatment
Drugs
Progressive disseminated disease requires treatment with antifungal agents such as amphotericin B, ketoconazole, etc.
Prognosis
Acute primary infection is self-limited and resolves spontaneously without treatment
Progressive disseminated disease in immunocompromised patients is associated with 80% mortality without treatment
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Majority of patients with primary infection have normal chest x-rays
Acute infection shows focal or multifocal parenchymal consolidation associated with ipsilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
Resolving phase will show the development of nodular opacities (histoplasmoma)
Pulmonary nodules and hilar adenopathy often show central calcification
Mediastinal involvement presents with focal densities or with diffuse fibrosing mediastinitis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree