Histiocytic Sarcoma
Aaron Auerbach, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Histiocytic sarcoma (HS)
Malignant histiocytosis
Extramedullary monocytic tumor
Clinical Issues
Extremely rare tumor
Mostly seen in adults
Usually rash or single lesion on skin
Some patients develop both histiocytic tumors and lymphoid tumors (transdifferentiation)
Microscopic Pathology
Dermal and subcutaneous infiltrate sparing epidermis
Composed of large, noncohesive, atypical epithelioid tumor cells with abundant cytoplasm
Immunohistochemistry: CD163(+), CD68(+), lysozyme(+), CD4 (+/−), S100(-)/focal(+)
B-cell markers, melanoma markers, carcinoma markers, and myeloid markers negative
Ancillary Tests
B- and T-cell gene rearrangements usually negative
Top Differential Diagnoses
Myeloid sarcoma
Langerhans cell histiocytosis and Langerhans cell sarcoma
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL)
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Classic Hodgkin lymphoma
Melanoma
Carcinoma
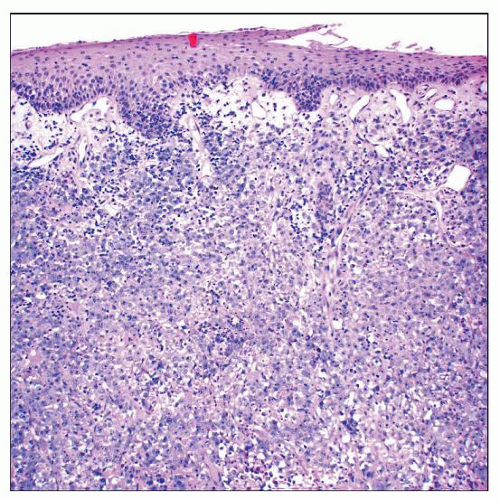 Histiocytic sarcoma at low magnification shows a diffuse, dermal-based sheet-like proliferation of enlarged, undifferentiated-appearing cells at this power. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Histiocytic sarcoma (HS)
Synonyms
Extramedullary monocytic tumor
Malignant histiocytosis
True histiocytic lymphoma
Definitions
Malignant tumor of mature histiocytes
Neoplasms associated with acute monocytic leukemia are excluded
Are now classified as monocytic sarcoma
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Idiopathic
Sometimes associated with germ cell tumors
Also can be associated with lymphoma, leukemia, or myelodysplastic syndrome
Postulated Normal Counterpart
Mature histiocyte
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Extremely rare tumor
Age
Mostly in adults
Median age = 52 years old
Rare in children
Gender
Approximately equal male:female ratio
Ethnicity
No known ethnic predilection
Site
Most cases are extranodal
Skin, gastrointestinal tract, and soft tissue most common
Lymph node less common
Presentation
Often a single painless mass
B symptoms common
Skin
Variable presentation
Can be seen as a rash, a single lesion, or multiple lesions (disseminated)
Gastrointestinal tract
Abdominal pain
Intestinal obstruction
Bone marrow
Focal/patchy bone marrow involvement is considered HS
Diffuse bone marrow involvement is currently classified as acute monocytic leukemia
Laboratory Tests
Cytopenias in some patients
Thrombocytopenia is most common
Natural History
Some patients develop both histiocytic tumors and lymphoid tumors
Lineage promiscuity (a.k.a. transdifferentiation)
Both tumors share molecular findings
HS can have t(14;18)(q32;q21)
HS can have clonal IgH gene rearrangements
Identical IgH rearrangements or BCL2 gene breakpoints in same patients with HS and B-cell lymphoma
Treatment
Prognosis
Low-stage (localized) lesions may be less clinically aggressive
High-stage lesions (multiple lesions, systemic disease, recurrences) resistant to adjuvant therapy
80% of patients die of disease
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Skin with rash or tumor nodule
1 or more firm lesions
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Skin
Dermal and subcutaneous infiltrate with infiltrative borders
Spares epidermis, separated by grenz zone
Lymph node
Usually diffuse effacement of lymph node architecture
Focal involvement is often in paracortex
Rare tumor is seen in sinuses
Hemophagocytosis, sometimes
Emperipolesis in some cases
Mitotic figures
Inflammatory background
Often prominent
Reactive T cells, plasma cells, eosinophils
Especially in HS of central nervous system
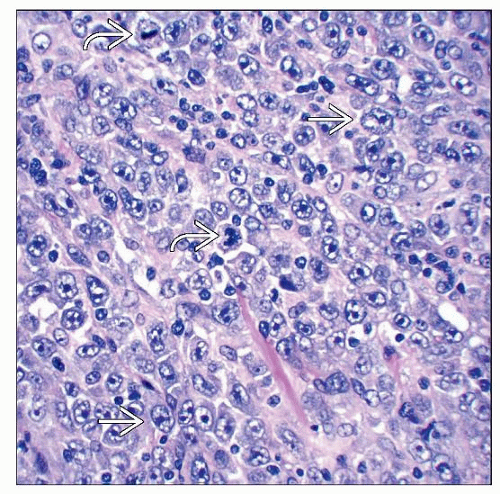
Cytologic Features
Neoplastic cells, large and noncohesive
Nuclei
Usually epithelioid
Rarely spindle-shaped
Often highly pleomorphic cells, sometimes monomorphic
Vesicular chromatin
Nucleoli, prominent sometimes
Multinucleated cells can be seen
Cytoplasm is abundant
Eosinophilic
Cytoplasmic vacuoles sometimes
Xanthomatous appearance sometimes
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
Histiocyte markers positive
CD163, CD68 (KP1), CD68 (PGM1), lysozyme, CD4 (+/−)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree