Herpes Zoster
Laura W. Lamps, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Any level of GI tract may be infected
Fever, vomiting, diarrhea common symptoms
Difficulty swallowing if esophagus involved
Patients may have cutaneous findings of shingles, chicken pox
Macroscopic Features
Erosions and ulcers similar to herpes simplex virus
Microscopic Pathology
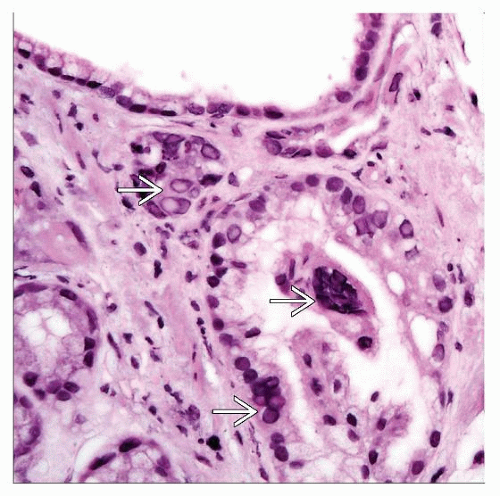
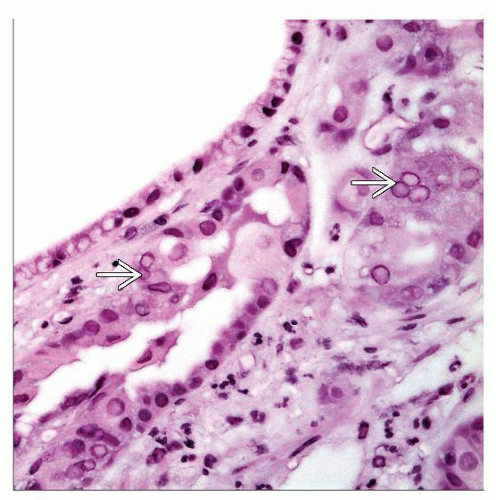
Viral inclusions present at edges of ulcers
Diagnostic Checklist
Immunohistochemistry, culture, molecular testing required to distinguish from herpes simplex virus
Particularly dangerous in immunocompromised patients
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Herpes (varicella) zoster virus (HZV)
Synonyms
Herpes zoster
Varicella zoster
Definitions
Gastrointestinal infection by herpes (varicella) zoster virus
Particularly important to be aware of this in patients with shingles or chicken pox who have gastrointestinal complaints
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Exposure to herpes zoster virus
Particularly when patients are immunocompromised
CLINICAL ISSUES