Chapter 8 Herbal Medications
Use of Herbal Medicines
Practice Points
 The patient should be informed that just because herbals are natural products, they are not necessarily any safer than conventional drugs.
The patient should be informed that just because herbals are natural products, they are not necessarily any safer than conventional drugs. In addition, it is important to educate patients about the potential for interaction between herbal medications and conventional drugs and other interventions (e.g., surgery).
In addition, it is important to educate patients about the potential for interaction between herbal medications and conventional drugs and other interventions (e.g., surgery). The physician should refer the patient to reliable sources of patient information on herbals. Most countries maintain a national registry of herbal medications; these registries, which can be found at regulatory agency websites (e.g., NCCAM at the National Institutes of Health [NIH] in the United States and the HMPC monographs in the European Union), serve as valuable sources of information.
The physician should refer the patient to reliable sources of patient information on herbals. Most countries maintain a national registry of herbal medications; these registries, which can be found at regulatory agency websites (e.g., NCCAM at the National Institutes of Health [NIH] in the United States and the HMPC monographs in the European Union), serve as valuable sources of information.Reliability of Herbal Products
 Part of plant used—biologically active ingredients may reside in different parts of the plant (e.g., stem vs leaf)
Part of plant used—biologically active ingredients may reside in different parts of the plant (e.g., stem vs leaf) Standardization
Standardization Often the active ingredient is not known. Thus standards for ingredients and recommended doses are not established. Similarly, standards for labeling may also not have been established.
Often the active ingredient is not known. Thus standards for ingredients and recommended doses are not established. Similarly, standards for labeling may also not have been established. Even when the active ingredient is known, herbal medicines have shown considerable variability in consistency. In one analysis of 25 ginseng products, the quantity of active ingredients varied from 10% to 300% of the labeled amount. A similar analysis of Echinacea products showed that less than 50% of Echinacea products contained the labeled amount of the herb.
Even when the active ingredient is known, herbal medicines have shown considerable variability in consistency. In one analysis of 25 ginseng products, the quantity of active ingredients varied from 10% to 300% of the labeled amount. A similar analysis of Echinacea products showed that less than 50% of Echinacea products contained the labeled amount of the herb.Efficacy of Herbal Medications
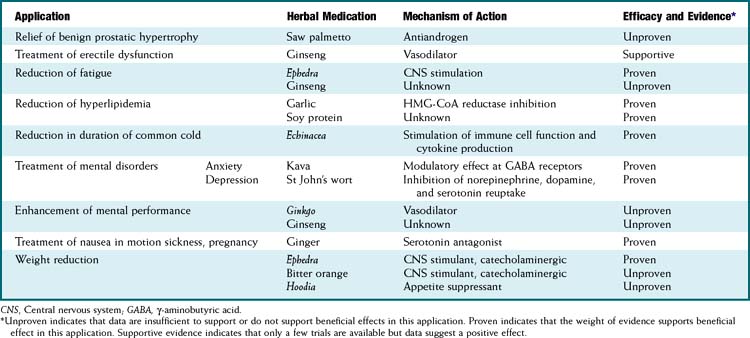
In response to increased demand for herbal products, in 1998 the NIH established NCCAM, which oversees and awards funds for research into complementary and alternative therapies, including herbal medications. In addition, in the European Union, HMPC requires efficacy and safety data before licensing an herbal medication. Nevertheless, compared with mainstream drugs, systematic research into the efficacy of herbal medications is relatively sparse for a number of reasons. The difficulty in obtaining standardized products, lack of knowledge of active principles, and the inability to standardize doses confounds both basic science research and clinical trials. In addition, lack of regulations requiring effectiveness and safety data and lack of patent protection in some countries have limited private investment in herbal research. Moreover, even within existing trials, many conflicting reports exist, perhaps in part because of issues of consistency of products tested (Table 8-1).
Specific Herbal Medications
Full discussion of the wide array of herbal medications used in various forms is well beyond the scope of this text. However, a relatively short list of the most commonly used herbal medications is presented. Table 8-2 presents side effects and drug interactions of some commonly used herbal remedies.
TABLE 8-2 Side Effects and Drug Interactions of Common Herbal Remedies
| Herbal Medication | Side Effects | Drug Interactions |
|---|---|---|
| Echinacea | Allergic reactions | Potential inhibition of CYP450 isoforms |
| Ephedra | ||
| Garlic | Odor, diaphoresis, bleeding | |
| Ginger | No major adverse effects | Potential potentiation of anticoagulant antiplatelet drugs (controversial) |
| Ginkgo | No major adverse effects | Synergistic interaction with other stimulants (e.g., caffeine) |
| Ginseng | No major adverse effects | No consistent reports |
| Kava | Hepatotoxicity | |
| St John’s wort | Serotonin syndrome when combined with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants | |
| Soy | Gastrointestinal disturbance | Inhibition of actions of tamoxifen |
| Saw palmetto | None | No major interactions reported |
CNS, Central nervous system.