Hepatorenal Syndrome/Bile Nephrosis
Anthony Chang, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Elevated blood bilirubin leads to intratubular bile casts
Direct toxicity to tubular epithelial cells by bilirubin and bile salts and subsequent ATN
Distal nephron obstruction
Circulatory disturbance causing decreased perfusion of kidney
Clinical Issues
Presentation
Acute renal failure
Jaundice
Macroscopic Features
Yellow when unfixed; green when fixed
Pigment most prominent in renal pyramids
Microscopic Pathology
Intratubular yellow-green pigmented casts
Hall stain highlights bile casts
Dark red and some green-yellowish discoloration of sloughed cells
Acute tubular injury
Top Differential Diagnoses
Rhabdomyolysis
Hemolysis
Acute tubular injury/acute tubular necrosis
Myeloma cast nephropathy
Diagnostic Checklist
Identification of pigment in casts by Hall stain diagnostically helpful
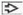
 Gross photograph shows the capsular surface of an autopsy kidney from a 32-year-old man with cirrhosis. The green discoloration of the kidney is accentuated after formalin fixation. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS)
Bile nephrosis (BN)
Synonyms
Cholemic nephrosis
Jaundice-associated acute kidney injury
Jaundice-related renal insufficiency
Definitions
HRS: Renal failure with cirrhosis
Type 1: Rapid reduction of renal function
Type 2: Slowly progressive loss of renal function
Lack of benefit from volume expansion
Absence of other causes
BN: Acute renal failure with bile-containing casts in distal nephron
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Hepatorenal Syndrome
Circulatory disturbance causing decreased perfusion of kidney
Decreased glomerular filtration rate
Acute ischemia of tubules
Reversible when transplanted into noncirrhotic recipient
Bile Nephrosis
Distal nephron casts containing bilirubin and bile salts
Direct toxicity to tubular epithelium by bile salts
Obstruction in distal nephron
Propensity of distal nephron due to admixture of Tamm-Horsfall protein with bile components
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Hepatic failure
Total bilirubin levels often > 20 mg/dL
Jaundice
Acute renal failure
Concentrated urine, low Na
Chronic renal failure
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Liver transplantation if cause of liver failure is irreversible
Drugs
Vasopressors for type 1 HRS
Supportive therapy
Renal replacement therapy
Prognosis
Poor; dependent on reversibility of liver failure
Reduction of bilirubin can lead to recovery of renal function
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Yellow kidneys when fresh or unfixed (bilirubin)
Green kidneys after formalin fixation (biliverdin)
More prominent in pyramids than cortex due to more frequent bile casts in renal medulla
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree