Hepatitis C Virus
Anthony Chang, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Hepatitis C virus (HCV)
Wide spectrum of immune complex-mediated glomerular injuries in association with HCV infection
Clinical Issues
Over 200 million people worldwide are infected
Infected children have high rate of spontaneous resolution
17-55% of HCV-infected patients progress to cirrhosis
2-23% develop HCC
Microscopic Pathology
Spectrum of glomerular injury
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN)
Cryoglobulinemic GN
Membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN)
Fibrillary GN
Immunotactoid glomerulopathy
IgA nephropathy
Top Differential Diagnoses
HCV-associated focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Hepatitis B virus-associated immune complex disease
Lupus nephritis
HIV-associated immune complex disease
Diagnostic Checklist
No pathognomonic features for HCV infection
Coinfection with HIV is common
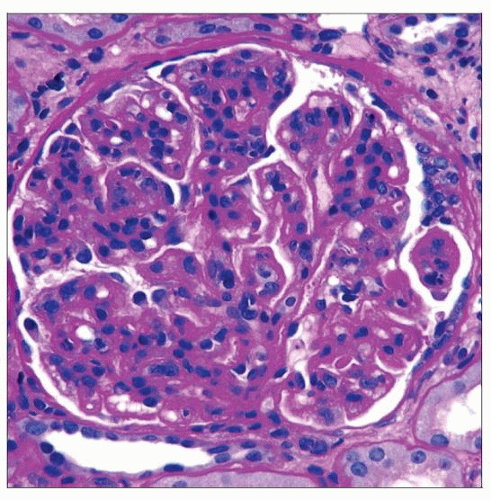 Periodic acid-Schiff reveals increased cellularity that highlights the lobularity of the glomerular tufts, which is characteristic of a membranoproliferative injury pattern. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Hepatitis C virus (HCV)
Definitions
Wide spectrum of immune complex-mediated glomerular injuries in association with HCV infection
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
HCV
RNA virus: Single-stranded, positive sense
Infects hepatocytes and B lymphocytes
Blood-to-blood with rare sexual transmission
Unknown pathogenic mechanism of kidney diseases
Possible contributing factors include
Circulating immune complexes of HCV antigen and antibodies
Cryoglobulins
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Over 200 million people worldwide are infected
Age
Infected children have high rate of spontaneous resolution
Gender
Young females may spontaneously resolve and are less likely than males to develop cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
Presentation
Proteinuria
Hematuria
Laboratory Tests
Serologic test
HCV antibodies
PCR
HCV viral load
HCV genotyping
Natural History
17-55% of HCV-infected patients progress to cirrhosis
2-23% develop HCC
Treatment
Drugs
Ribavirin
Pegylated interferon-α
Kidney &/or liver transplantation
Prognosis
HCV genotype 2A and 3A have high cure rates
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
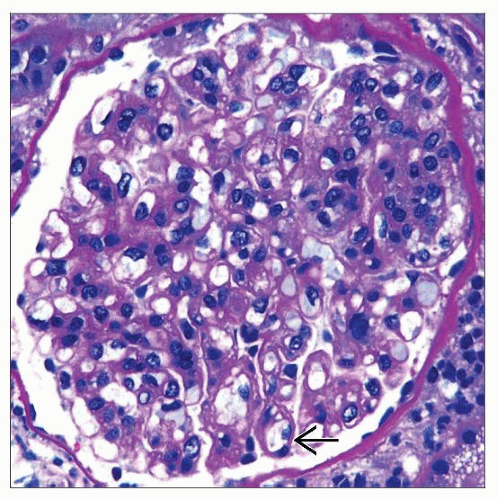
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN)
Accentuation of glomerular tuft/lobules
Duplication of glomerular basement membranes or “tram track”
Cryoglobulinemic GN
Endocapillary hypercellularity
“Wire loop” or hyaline “thrombi” deposits
PAS positive
Membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN)
Thickened glomerular basement membranes with subepithelial “spike” formation
Fibrillary GN
Mesangial expansion
Immunotactoid glomerulopathy
Mesangial expansion
IgA nephropathy
Variable mesangial hypercellularity
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunofluorescence
MPGN
IgG and C3 granular staining of glomerular capillary walls and mesangial regions
Cryoglobulinemic GN
IgG &/or IgM staining along glomerular capillaries and mesangial areas
Polyclonal or rare monoclonal light chain staining
MGN
IgG granular staining of the capillary walls and some mesangial areas
Fibrillary GN
IgG granular staining of capillary walls and mesangial areas
Polyclonal staining for kappa and lambda light chains
Immunotactoid glomerulopathy
IgG granular staining of mesangial areas and capillary walls
Monoclonal light chain staining is typical
IgA nephropathy
IgA granular mesangial staining with variable involvement of capillary walls
Electron Microscopy
MPGN
Subendothelial & mesangial electron-dense deposits
Duplication of GBM
Cryoglobulinemic GN
Subendothelial & mesangial electron-dense deposits
Substructural organization of deposits may be present
MGN
Subepithelial & mesangial electron-dense deposits
Fibrillary GN
Randomly arranged fibrils ˜ 20 nm in diameter
Immunotactoid glomerulopathy
Microtubules with hollow centers arranged in parallel arrays measuring > 30 nm in diameter
IgA nephropathy
Mesangial electron-dense deposits with variable subendothelial or subepithelial involvement
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
HCV-associated Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
Segmental sclerosis of glomeruli
Absence of immune complex deposition
Hepatitis B Virus-associated Immune Complex Disease
Pathologically identical to HCV-associated immune complex disease
Lupus Nephritis
Spectrum of glomerular injury mimics HCV-associated immune complex disease
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree