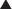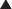Chapter 16 Hematology
Heparins
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
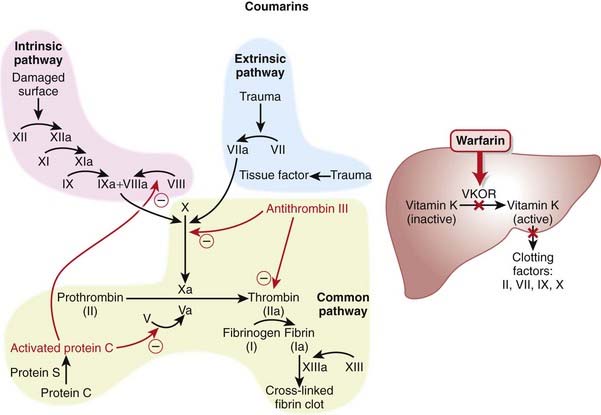
 The coagulation (clotting) system is composed of many proteins. Most of these proteins are procoagulants, which means they contribute to clotting. Some proteins are anticoagulants that serve to keep the coagulation system in balance.
The coagulation (clotting) system is composed of many proteins. Most of these proteins are procoagulants, which means they contribute to clotting. Some proteins are anticoagulants that serve to keep the coagulation system in balance. When a protein is activated, its name is followed by a small letter a. Each activated protein serves as an enzyme for the next protein downstream in the cascade (Figure 16-1).
When a protein is activated, its name is followed by a small letter a. Each activated protein serves as an enzyme for the next protein downstream in the cascade (Figure 16-1). Heparins interfere with the coagulation cascade by amplifying the anticoagulant effect of antithrombin III.
Heparins interfere with the coagulation cascade by amplifying the anticoagulant effect of antithrombin III. Antithrombin III, a natural plasma protease inhibitor, is an anticoagulant, and it inhibits thrombin (IIa) and factor Xa.
Antithrombin III, a natural plasma protease inhibitor, is an anticoagulant, and it inhibits thrombin (IIa) and factor Xa. To inhibit factor IIa, heparins must bind to both antithrombin III and factor IIa (dual binding not shown Figure 16-1).
To inhibit factor IIa, heparins must bind to both antithrombin III and factor IIa (dual binding not shown Figure 16-1). LMWHs are typically too small to bind both antithrombin III and factor IIa. Therefore their anticoagulant effects are exerted largely through factor Xa, with minimal effects on factor IIa.
LMWHs are typically too small to bind both antithrombin III and factor IIa. Therefore their anticoagulant effects are exerted largely through factor Xa, with minimal effects on factor IIa.Pharmacokinetics
Unfractionated Heparin
 Very complex pharmacokinetics exist because there is a large range in molecular weight of the molecules
Very complex pharmacokinetics exist because there is a large range in molecular weight of the molecules The dose-response curve is difficult to predict, so the dose must be individualized in every patient, with frequent measurements (i.e., activated partial thromboplastin time [aPTT]) made to guide titration.
The dose-response curve is difficult to predict, so the dose must be individualized in every patient, with frequent measurements (i.e., activated partial thromboplastin time [aPTT]) made to guide titration. UFH exhibits saturation kinetics, meaning that the elimination half-life (t1/2) increases with increasing dose.
UFH exhibits saturation kinetics, meaning that the elimination half-life (t1/2) increases with increasing dose.Indications
 Treatment and prevention of inappropriate thrombosis
Treatment and prevention of inappropriate thrombosisSide Effects
 Hyperkalemia: Although not a common occurrence, heparin can cause increased serum potassium; it is more likely to occur in patients with diabetes or renal disease. In this regard the action of heparin is similar to that of spironolactone, which is an aldosterone blocker classified as a K-sparing diuretic.
Hyperkalemia: Although not a common occurrence, heparin can cause increased serum potassium; it is more likely to occur in patients with diabetes or renal disease. In this regard the action of heparin is similar to that of spironolactone, which is an aldosterone blocker classified as a K-sparing diuretic.Important Notes
 To measure the effect of UFH, the aPTT test is used (compare this with prothrombin time [PT] or International Normalized Ratio [INR], which is used with warfarin). It is a measure of time to coagulation (in the laboratory) and is measured in seconds. The higher the number, the more strongly a patient is anticoagulated.
To measure the effect of UFH, the aPTT test is used (compare this with prothrombin time [PT] or International Normalized Ratio [INR], which is used with warfarin). It is a measure of time to coagulation (in the laboratory) and is measured in seconds. The higher the number, the more strongly a patient is anticoagulated. Unlike UFH, LMWHs do not prolong the aPTT, and they also have a more predictable pharmacokinetic profile. These important differences make LMWH far more convenient for patients to use, with more stable administration and less rigorous monitoring.
Unlike UFH, LMWHs do not prolong the aPTT, and they also have a more predictable pharmacokinetic profile. These important differences make LMWH far more convenient for patients to use, with more stable administration and less rigorous monitoring. For cases of heparin overdose, protamine sulfate is a strongly basic protein that forms a complex with heparin, acting as a chemical antagonist. LMWH does not have an antidote.
For cases of heparin overdose, protamine sulfate is a strongly basic protein that forms a complex with heparin, acting as a chemical antagonist. LMWH does not have an antidote. Danaparoid works by the same mechanism as the heparins, but it is not structurally related to the heparins; it is therefore considered a heparinoid. Therefore it can be used in the management of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) too.
Danaparoid works by the same mechanism as the heparins, but it is not structurally related to the heparins; it is therefore considered a heparinoid. Therefore it can be used in the management of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) too. Fondaparinux is synthetic and is based on the structure of the antithrombin binding region of heparin. The binding region of heparin is only 5 saccharide units and is the basis for the pentasaccharide structure of fondaparinux. Fondaparinux could be thought of as really low molecular weight heparin.
Fondaparinux is synthetic and is based on the structure of the antithrombin binding region of heparin. The binding region of heparin is only 5 saccharide units and is the basis for the pentasaccharide structure of fondaparinux. Fondaparinux could be thought of as really low molecular weight heparin.Evidence
LMWH versus Warfarin for Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism
 A 2001 Cochrane review (seven studies, N = 1137 participants), updated in 2003, compared warfarin with LMWH for long-term treatment of VTE. There was no difference in the risk of recurrent VTE between warfarin and LMWH. There was a lower risk of bleeding with LMWH (odds ratio [OR] 0.38), and no difference in mortality rates between these two interventions was found.
A 2001 Cochrane review (seven studies, N = 1137 participants), updated in 2003, compared warfarin with LMWH for long-term treatment of VTE. There was no difference in the risk of recurrent VTE between warfarin and LMWH. There was a lower risk of bleeding with LMWH (odds ratio [OR] 0.38), and no difference in mortality rates between these two interventions was found.LMWH and Heparinoids versus UFH for Ischemic Stroke
 A 2008 Cochrane review (nine studies, N = 3137 patients) compared LMWH and heparinoids (danaparoid) with UFH in patients with acute, presumed or confirmed ischemic stroke. The odds of developing a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) were reduced with LMWH compared with UFH (OR 0.55); however, the incidence of key clinical outcomes such as PE, death, and hemorrhage (intracranial or extracranial) was too small to provide a reliable comparison.
A 2008 Cochrane review (nine studies, N = 3137 patients) compared LMWH and heparinoids (danaparoid) with UFH in patients with acute, presumed or confirmed ischemic stroke. The odds of developing a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) were reduced with LMWH compared with UFH (OR 0.55); however, the incidence of key clinical outcomes such as PE, death, and hemorrhage (intracranial or extracranial) was too small to provide a reliable comparison.Direct Factor Xa Inhibitors
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 The coagulation system is composed of many proteins: most of these proteins are procoagulants, which means they contribute to clotting. Some proteins are anticoagulants, which serve to keep the coagulation system in balance.
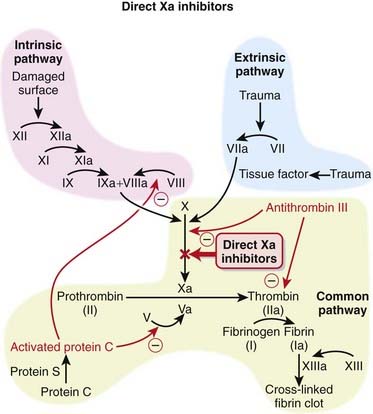
The coagulation system is composed of many proteins: most of these proteins are procoagulants, which means they contribute to clotting. Some proteins are anticoagulants, which serve to keep the coagulation system in balance. When a protein is activated, its name is given a small letter a at the end. Each activated protein serves as an enzyme for the next protein downstream in the cascade (Figure 16-2).
When a protein is activated, its name is given a small letter a at the end. Each activated protein serves as an enzyme for the next protein downstream in the cascade (Figure 16-2). Factor Xa converts prothrombin to thrombin (factor IIa). Thrombin is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the coagulation cascade, the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
Factor Xa converts prothrombin to thrombin (factor IIa). Thrombin is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the coagulation cascade, the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. Fibrin is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh, providing structural rigidity to a clot. The mesh is created by the cross-linking of fibrin, and this cross-linking step is facilitated by factor XIII.
Fibrin is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh, providing structural rigidity to a clot. The mesh is created by the cross-linking of fibrin, and this cross-linking step is facilitated by factor XIII. In addition to converting fibrinogen to fibrin, thrombin also activates factor XIII; thus thrombin not only catalyzes the creation of the key component of the clot, it also facilitates the provision of structural rigidity to the clot.
In addition to converting fibrinogen to fibrin, thrombin also activates factor XIII; thus thrombin not only catalyzes the creation of the key component of the clot, it also facilitates the provision of structural rigidity to the clot. Thrombin also activates factors V, VIII, and XI, therefore amplifying the coagulation cascade. In addition, thrombin activates platelets, leading to their aggregation.
Thrombin also activates factors V, VIII, and XI, therefore amplifying the coagulation cascade. In addition, thrombin activates platelets, leading to their aggregation. Direct factor Xa inhibitors directly inhibit the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin without using antithrombin III as an intermediary. The direct inhibition of thrombin formation results in an anticoagulant effect.
Direct factor Xa inhibitors directly inhibit the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin without using antithrombin III as an intermediary. The direct inhibition of thrombin formation results in an anticoagulant effect.Pharmacokinetics
 Rivaroxaban, the first direct factor Xa inhibitor, is administered orally. It is rapidly absorbed, reaching peak plasma concentrations in 2 to 4 hours, and has an elimination half-life of 9 hours.
Rivaroxaban, the first direct factor Xa inhibitor, is administered orally. It is rapidly absorbed, reaching peak plasma concentrations in 2 to 4 hours, and has an elimination half-life of 9 hours.Important Notes
 There are no monitoring requirements for rivaroxaban. This and the fact that it is an orally administered agent suggest that drugs in its class, and perhaps the direct thrombin inhibitors, will supplant warfarin as the drugs of choice among oral anticoagulants.
There are no monitoring requirements for rivaroxaban. This and the fact that it is an orally administered agent suggest that drugs in its class, and perhaps the direct thrombin inhibitors, will supplant warfarin as the drugs of choice among oral anticoagulants.Advanced
Drug Interactions
 CYP450 3A4 enzymes are involved in the metabolism of rivaroxaban; thus the potential exists for pharmacokinetic drug interactions with inhibitors or inducers of this isozyme. Rivaroxaban is also a P-glycoprotein (Pgp) substrate, and therefore its levels could also be affected by inhibitors or inducers of Pgp.
CYP450 3A4 enzymes are involved in the metabolism of rivaroxaban; thus the potential exists for pharmacokinetic drug interactions with inhibitors or inducers of this isozyme. Rivaroxaban is also a P-glycoprotein (Pgp) substrate, and therefore its levels could also be affected by inhibitors or inducers of Pgp.Evidence
Postsurgical Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 The RECORD trials were a series of double-blind randomized controlled trials that compared rivaroxaban with enoxaparin for the prophylactic treatment of VTE after total hip replacement (RECORD-1 and RECORD-2) or total knee replacement (RECORD-3 and RECORD-4). The trials were all relatively large, randomizing 2509 to 4541 patients between the two treatment groups. Rivaroxaban-treated patients had fewer events of VTE and all-cause deaths compared with enoxaparin in each of the four studies. The risk of bleeding was slightly higher with rivaroxaban than with enoxaparin.
The RECORD trials were a series of double-blind randomized controlled trials that compared rivaroxaban with enoxaparin for the prophylactic treatment of VTE after total hip replacement (RECORD-1 and RECORD-2) or total knee replacement (RECORD-3 and RECORD-4). The trials were all relatively large, randomizing 2509 to 4541 patients between the two treatment groups. Rivaroxaban-treated patients had fewer events of VTE and all-cause deaths compared with enoxaparin in each of the four studies. The risk of bleeding was slightly higher with rivaroxaban than with enoxaparin.FYI
 For a quick summary of the difference between two of the newer oral anticoagulants—direct factor Xa and direct thrombin inhibitors. Direct factor Xa inhibitors inhibit the formation of thrombin, whereas direct thrombin inhibitors allow thrombin to be formed but interfere with the actions of thrombin.
For a quick summary of the difference between two of the newer oral anticoagulants—direct factor Xa and direct thrombin inhibitors. Direct factor Xa inhibitors inhibit the formation of thrombin, whereas direct thrombin inhibitors allow thrombin to be formed but interfere with the actions of thrombin.Direct Thrombin Inhibitors
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 The coagulation (clotting) system is a multistep cascade that eventually leads to the formation of fibrin and development of a clot.
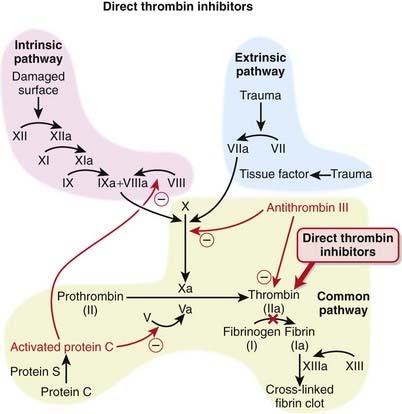
The coagulation (clotting) system is a multistep cascade that eventually leads to the formation of fibrin and development of a clot. Thrombin (factor IIa) is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the coagulation cascade, the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin (Figure 16-3).
Thrombin (factor IIa) is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the coagulation cascade, the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin (Figure 16-3). Fibrin is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh, providing structural rigidity to a clot. The mesh is created by the cross-linking of fibrin, and this cross-linking step is facilitated by factor XIII.
Fibrin is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh, providing structural rigidity to a clot. The mesh is created by the cross-linking of fibrin, and this cross-linking step is facilitated by factor XIII. In addition to converting fibrinogen to fibrin, thrombin also activates factor XIII; thus thrombin not only catalyzes the creation of the key component of the clot, it also facilitates the provision of structural rigidity to the clot.
In addition to converting fibrinogen to fibrin, thrombin also activates factor XIII; thus thrombin not only catalyzes the creation of the key component of the clot, it also facilitates the provision of structural rigidity to the clot. Thrombin also activates factors V, VIII, and XI, therefore amplifying the coagulation cascade. Thrombin also has antiplatelet effects.
Thrombin also activates factors V, VIII, and XI, therefore amplifying the coagulation cascade. Thrombin also has antiplatelet effects. Thrombin has an active site as well as two other sites, referred to as exosite 1, which binds fibrin, and exosite 2, which binds heparin.
Thrombin has an active site as well as two other sites, referred to as exosite 1, which binds fibrin, and exosite 2, which binds heparin. Direct thrombin inhibitors all bind to thrombin directly at its active site. The bivalent inhibitors (-irudins) also bind at exosite 1 (hence the term “bivalent”, indicating two binding sites), while the univalent inhibitors only bind at the active site.
Direct thrombin inhibitors all bind to thrombin directly at its active site. The bivalent inhibitors (-irudins) also bind at exosite 1 (hence the term “bivalent”, indicating two binding sites), while the univalent inhibitors only bind at the active site. The univalent thrombin inhibitors (e.g., argatroban and dabigatran) and bivalirudin all bind reversibly, whereas the other bivalent inhibitors bind thrombin irreversibly.
The univalent thrombin inhibitors (e.g., argatroban and dabigatran) and bivalirudin all bind reversibly, whereas the other bivalent inhibitors bind thrombin irreversibly. The net result of this binding is that the effects of thrombin are inhibited. The inhibition of thrombin results in an anticoagulant effect.
The net result of this binding is that the effects of thrombin are inhibited. The inhibition of thrombin results in an anticoagulant effect.Pharmacokinetics
 Hirudin is administered by either IV or SC injection, with elimination half-life of 60 minutes and 120 minutes, respectively. It is cleared by the kidneys.
Hirudin is administered by either IV or SC injection, with elimination half-life of 60 minutes and 120 minutes, respectively. It is cleared by the kidneys.Important Notes
 All of the agents in this class are approved for prophylaxis of DVT and VTE after orthopedic surgery. Patients undergoing knee or hip replacement surgeries, in particular, are at high risk for developing a DVT or VTE. The risk is so high that these patients receive prophylactic anticoagulants for several days postsurgery.
All of the agents in this class are approved for prophylaxis of DVT and VTE after orthopedic surgery. Patients undergoing knee or hip replacement surgeries, in particular, are at high risk for developing a DVT or VTE. The risk is so high that these patients receive prophylactic anticoagulants for several days postsurgery. The theoretical advantage of direct over indirect thrombin inhibitors such as LMWHs is that the direct inhibitors inactivate fibrin-bound thrombin, in addition to the thrombin in the fluid phase. This may lead to a greater inhibition of the thrombus. Direct thrombin inhibitors may also provide more predictable anticoagulation, as they are not bound to plasma proteins (unlike heparin) and are not neutralized by platelet factor 4 (a protein secreted by platelets) and other factors generated at the site of vascular injury.
The theoretical advantage of direct over indirect thrombin inhibitors such as LMWHs is that the direct inhibitors inactivate fibrin-bound thrombin, in addition to the thrombin in the fluid phase. This may lead to a greater inhibition of the thrombus. Direct thrombin inhibitors may also provide more predictable anticoagulation, as they are not bound to plasma proteins (unlike heparin) and are not neutralized by platelet factor 4 (a protein secreted by platelets) and other factors generated at the site of vascular injury. Warfarin has been the prototypical oral anticoagulant for decades, but with its narrow margin of safety, significant potential for drug-drug and drug-food interactions, and significant variability in response among patients, there is much anticipation that new oral anticoagulants will soon be able to replace it. The direct thrombin inhibitors, which lack any of these limitations associated with warfarin, are one of the classes that might replace warfarin.
Warfarin has been the prototypical oral anticoagulant for decades, but with its narrow margin of safety, significant potential for drug-drug and drug-food interactions, and significant variability in response among patients, there is much anticipation that new oral anticoagulants will soon be able to replace it. The direct thrombin inhibitors, which lack any of these limitations associated with warfarin, are one of the classes that might replace warfarin.Vitamin K Antagonists
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Vitamin K is key cofactor in the hepatic activation of four coagulation factors. The four vitamin K-dependent clotting factors are II, VII, IX, and X (Figure 16-4).
Vitamin K is key cofactor in the hepatic activation of four coagulation factors. The four vitamin K-dependent clotting factors are II, VII, IX, and X (Figure 16-4). To act as a cofactor, vitamin K must be in its reduced form, vitamin K hydroxyquinone. The enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) converts vitamin K to its reduced form.
To act as a cofactor, vitamin K must be in its reduced form, vitamin K hydroxyquinone. The enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) converts vitamin K to its reduced form. Warfarin inhibits the enzyme VKOR. Blocking formation of the reduced form of vitamin K inhibits the activation of these four clotting factors.
Warfarin inhibits the enzyme VKOR. Blocking formation of the reduced form of vitamin K inhibits the activation of these four clotting factors. These clotting factors vary in their half-lives (6 to 50 hours), with factor II having the longest half-life and factor VII having the shortest. This delays the onset of action of warfarin, as one must wait until these clotting factors have been mostly depleted before the full anticoagulant effects have been achieved.
These clotting factors vary in their half-lives (6 to 50 hours), with factor II having the longest half-life and factor VII having the shortest. This delays the onset of action of warfarin, as one must wait until these clotting factors have been mostly depleted before the full anticoagulant effects have been achieved.Pharmacokinetics
 Warfarin requires 2 to 3 days of treatment before anticoagulation takes effect. This is because warfarin prevents vitamin K–dependant protein synthesis, and before anticoagulation occurs the plasma proteins must be cleared from the plasma, which takes about 48 hours.
Warfarin requires 2 to 3 days of treatment before anticoagulation takes effect. This is because warfarin prevents vitamin K–dependant protein synthesis, and before anticoagulation occurs the plasma proteins must be cleared from the plasma, which takes about 48 hours.Indications
 Long-term (home) anticoagulation. Note that heparin would be used first for many of these conditions in the hospital and that warfarin would replace heparin on discharge.
Long-term (home) anticoagulation. Note that heparin would be used first for many of these conditions in the hospital and that warfarin would replace heparin on discharge.Important Notes
 Warfarin therapy is monitored using the International Normalized Ratio (INR), which is a standardized form of the PT test. Because different laboratories use different reagents to test the PT, every laboratory generates a slightly different result, so the INR corrects for this discrepancy among laboratories.
Warfarin therapy is monitored using the International Normalized Ratio (INR), which is a standardized form of the PT test. Because different laboratories use different reagents to test the PT, every laboratory generates a slightly different result, so the INR corrects for this discrepancy among laboratories. Patients must undergo regular blood tests to ensure that their INR levels remain “therapeutic,” which means being in the appropriate range for their problem. For example, DVT treatment requires that the INR be 2.0 to 2.5 but for mechanical valves, the INR should be 2.5 to 3.5.
Patients must undergo regular blood tests to ensure that their INR levels remain “therapeutic,” which means being in the appropriate range for their problem. For example, DVT treatment requires that the INR be 2.0 to 2.5 but for mechanical valves, the INR should be 2.5 to 3.5. The anticoagulant effects of warfarin can be reversed by administration of vitamin K. The time required for vitamin K to work is dependent on the time the liver requires to generate more proteins (many hours).
The anticoagulant effects of warfarin can be reversed by administration of vitamin K. The time required for vitamin K to work is dependent on the time the liver requires to generate more proteins (many hours). Fresh frozen plasma (plasma from another human) can be transfused to immediately replace clotting factors and is the fastest way to correct an overdose of warfarin.
Fresh frozen plasma (plasma from another human) can be transfused to immediately replace clotting factors and is the fastest way to correct an overdose of warfarin. When warfarin is being administered, all vitamin K–dependent protein synthesis is inhibited. This includes the prothrombotic factors II, VII, IX, and X but also includes the antithrombotic factors protein C and protein S. Protein C and S are inhibited very early with warfarin, and thus there can be a short duration of time when only the natural anticoagulants are inhibited and a paradoxical, temporary hypercoagulable state can be induced with warfarin. Therefore it is important to coadminister heparin with warfarin until the patient’s anticoagulation levels (measured by INR) are in the desired range.
When warfarin is being administered, all vitamin K–dependent protein synthesis is inhibited. This includes the prothrombotic factors II, VII, IX, and X but also includes the antithrombotic factors protein C and protein S. Protein C and S are inhibited very early with warfarin, and thus there can be a short duration of time when only the natural anticoagulants are inhibited and a paradoxical, temporary hypercoagulable state can be induced with warfarin. Therefore it is important to coadminister heparin with warfarin until the patient’s anticoagulation levels (measured by INR) are in the desired range.Evidence
Warfarin versus LMWH for Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism
 A 2001 Cochrane review (seven studies, N = 1137 participants), updated in 2003, compared warfarin with LMWHs for long-term treatment of VTE. There was no difference in the risk of recurrent VTE between warfarin and LMWH. There was a lower risk of bleeding with LMWH (OR 0.38), and no difference in mortality rates between these two interventions.
A 2001 Cochrane review (seven studies, N = 1137 participants), updated in 2003, compared warfarin with LMWHs for long-term treatment of VTE. There was no difference in the risk of recurrent VTE between warfarin and LMWH. There was a lower risk of bleeding with LMWH (OR 0.38), and no difference in mortality rates between these two interventions.Warfarin versus Acetylsalicylic Acid for Atrial Fibrillation
 A 2007 Cochrane review (eight studies, N = 9598 participants) compared warfarin with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) in atrial fibrillation patients who had not had a prior stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). Treatment with warfarin led to a lower risk of stroke (OR 0.68), ischemic stroke (OR 0.53), and systemic emboli (OR 0.48). The risk of intracranial hemorrhage was increased with warfarin (OR 1.98). All-cause mortality and vascular deaths were similar between groups, and disabling or fatal strokes and MI were almost reduced with oral anticoagulants, but this did not reach statistical significance.
A 2007 Cochrane review (eight studies, N = 9598 participants) compared warfarin with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) in atrial fibrillation patients who had not had a prior stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). Treatment with warfarin led to a lower risk of stroke (OR 0.68), ischemic stroke (OR 0.53), and systemic emboli (OR 0.48). The risk of intracranial hemorrhage was increased with warfarin (OR 1.98). All-cause mortality and vascular deaths were similar between groups, and disabling or fatal strokes and MI were almost reduced with oral anticoagulants, but this did not reach statistical significance.Salicylates
Prototype and Common Drugs
Salicylates
 Others: sodium salicylate, salsalate, sodium thiosalicylate, choline salicylate, magnesium salicylate
Others: sodium salicylate, salsalate, sodium thiosalicylate, choline salicylate, magnesium salicylateMOA (Mechanism of Action)
Salicylates
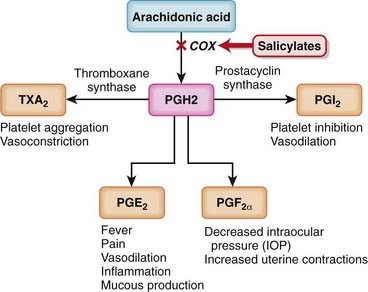
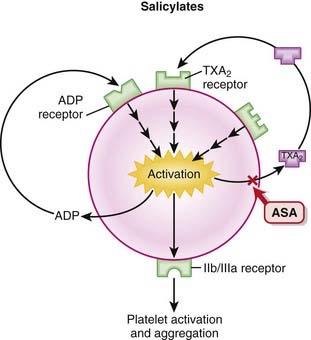
 Like nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the salicylates work by inhibiting the actions of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme (Figure 16-5).
Like nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the salicylates work by inhibiting the actions of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme (Figure 16-5). ASA works by irreversibly inhibiting COX-1, an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cyclic endoperoxide, which in turn is then converted to the following:
ASA works by irreversibly inhibiting COX-1, an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cyclic endoperoxide, which in turn is then converted to the following:Aminosalicylates
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree