Hard Metal Pneumoconiosis Pneumonitis
Key Facts
Terminology
Type of pneumonitis caused by exposure to hard metal (cobalt)
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Exposure to hard metal
Hard metal is combination of tungsten with cobalt
Clinical Issues
Symptoms
Cough
Dyspnea
Rhinitis
Dermatitis
Asthma
Laboratory findings
Increased cobalt in urine
Increased cobalt in blood
Treatment
Corticosteroids
Top Differential Diagnoses
Usual interstitial pneumonitis
Desquamative interstitial pneumonitis
Infectious pneumonia
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Diagnostic Checklist
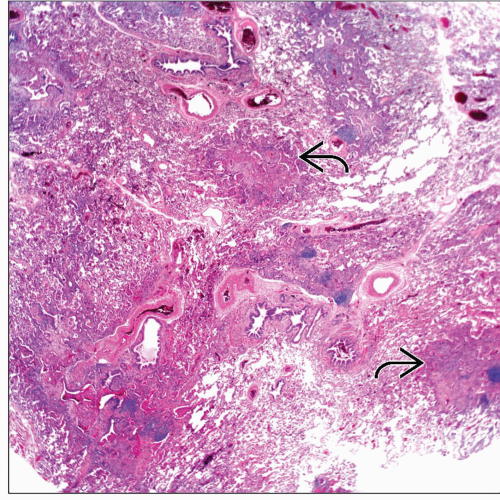
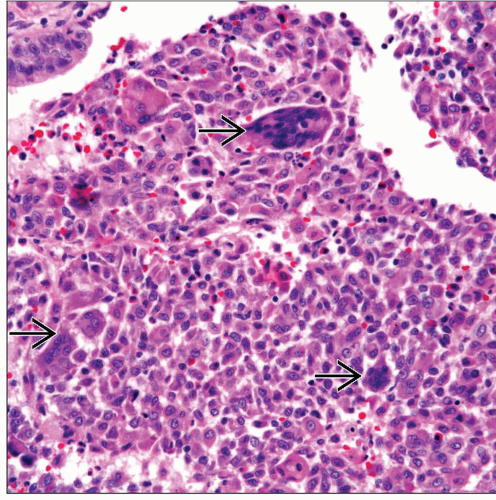
Presence of giant cells
Patchy and subtle nodular appearance
Inflammatory reaction
Lymphoid aggregates
History of exposure to hard metal
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Hard metal lung disease, cobalt lung disease
Definitions
Type of pneumonitis caused by exposure to hard metal (cobalt and others)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Exposure to hard metal
Hard metal is combination of tungsten with cobalt
Pathogenesis
Possibly immunologically mediated disease
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
No hard data documenting true incidence of hard metal lung disease
Age
Adults are more commonly affected
Gender
No apparent gender predilection
Ethnicity
No apparent ethnic predilection
Site
Lung without predilection for any side or segment
Presentation
Cough
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Wheezing
Rhinitis
Conjunctivitis
Dermatitis
Asthma
Malaise
Laboratory Tests
Radiographic features are nonspecific
Increased cobalt in urine
Increased cobalt in blood
IgE antibodies to cobalt may be present in serum
Treatment
Drugs
Corticosteroids
In cases not responding to corticosteroids
Cyclophosphamide
Azathioprine
Lung transplantation
Most important aspect is to avoid contact with cobalt
Prognosis
If patients are kept away form further exposure to cobalt and treated with corticosteroids, their prognosis may be good
Fatal cases have been reported
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree