Hairy Polyp
Bruce M. Wenig, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Developmental (congenital) anomaly predominantly composed of ectodermal and mesodermal tissue
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Presence of skin suggests classification as choristoma
Possibly of 1st branchial arch origin
Clinical Issues
Occurs in newborns or infants
Difficulties in breathing, swallowing, or sucking
Cured following surgical resection
Microscopic Pathology
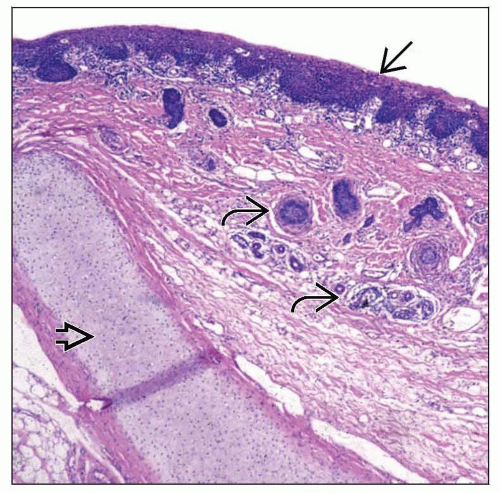
Combination of various ectodermal and mesodermal tissues including
Skin (keratinizing squamous epithelium) and cutaneous adnexa
Cartilage, bone, muscle, fibrous tissue, mature adipose tissue, vascular tissue
 Hairy polyp is also known as a nasopharyngeal dermoid. This lesion occurred in a neonate with airway obstruction and appears as a polypoid solid mass with identifiable hairs on the surface. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Nasopharyngeal dermoid or teratoid lesion
Definitions
Developmental (congenital) anomaly predominantly composed of ectodermal and mesodermal tissue but lacking endodermal-derived tissues
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Proposed classification includes
1st branchial arch origin
Presence of skin, including hair follicles and sebaceous glands and identification of elastic cartilage
Findings identical to those of congenital accessory auricles akin to accessory tragus, which is of 1st branchial arch origin
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree