Goblet Cell Carcinoid/Mixed Adenocarcinoma-Carcinoid
Scott R. Owens, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Goblet cell carcinoid
Proliferation of mucin-producing cells with features of both neuroendocrine and crypt/glandular differentiation
Clinical Issues
Some suggest regional resection (right hemicolectomy) even for localized tumors
GCC more aggressive than conventional carcinoid tumor
MA-GCC behaves more like conventional adenocarcinoma
Macroscopic Features
GCC (especially MA-GCC) may spread directly to other organs &/or transperitoneally
Entire appendix should be submitted when GCC is suspected or found
Microscopic Pathology
Presence of goblet-like cells, Paneth cells, and enterochromaffin cells suggest “recapitulation” of normal crypt structure
Diagnostic Checklist
Careful evaluation of appendiceal margin and extent of infiltration through appendiceal wall is important
GCC/MA-GCC must be kept in mind as possible primary source when evaluating disseminated mucinous/signet-ring carcinomas
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Goblet cell carcinoid (GCC)
Mixed adenocarcinoma-goblet cell carcinoid (MA-GCC)
Enterochromaffin cell (ECC)
Neuroendocrine (NE)
Synonyms
Adenocarcinoid
Crypt cell carcinoma
Microglandular carcinoma
Mucinous carcinoid
Definitions
GCC
Proliferation of mucin-producing cells with features of both NE and crypt/glandular differentiation
MA-GCC
More aggressive tumor in which unequivocal adenocarcinoma is found in conjunction with (presumably arising from) a GCC
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown
Some genetic alterations noted
Loss of heterozygosity in 11q, 16q, and 18q
Mutations in KRAS, β-catenin, SMAD4 genes absent or low-level in some studies
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare
Age
Occurs in older individuals than conventional carcinoid does
Presentation
Acute appendicitis
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea
Perforation
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Controversial
Appendectomy may be sufficient for tumors confined to appendix
Some suggest regional resection (right hemicolectomy) even for localized tumors
Regional resection important for aggressive tumors that involve proximal appendiceal margin &/or those with transmural extension
Transperitoneal spread treated as disseminated adenocarcinoma
Adjuvant chemotherapy advocated by some
Prognosis
GCC more aggressive than conventional carcinoid tumor
Behaves more like low-grade adenocarcinoma
Source of “crypt cell carcinoma” as alternate name
Best outcomes in tumors that are confined to appendix
5-year survival reported to be around 75-85%
MA-GCC behaves more like conventional adenocarcinoma
Lower survival rates
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Most common by far in appendix but can sometimes occur elsewhere in gastrointestinal tract
Most often do not create discrete tumor mass
Diffuse wall thickening common
GCC (especially MA-GCC) may spread directly to other organs &/or transperitoneally throughout abdomen
May produce disseminated carcinoma strongly resembling signet-ring cell carcinoma
Ovarian involvement common (Krukenberg tumor-like appearance)
Possible pseudomyxoma peritonei-like presentation
Sections to Be Submitted
Entire appendix should be submitted if GCC is suspected or found
Careful evaluation of proximal margin particularly important
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Key Descriptors
Predominant pattern/injury type
Neoplastic
Infiltrative
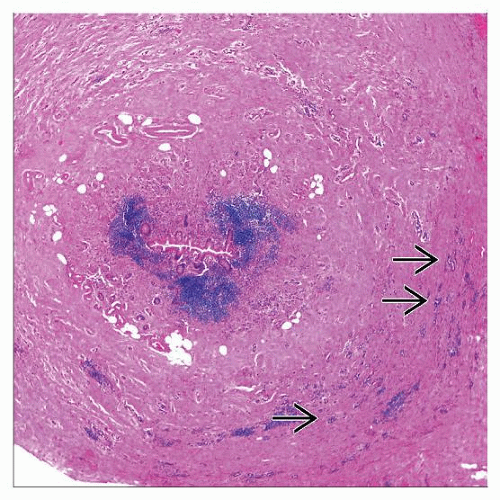
Concentric pattern of infiltration through appendiceal wall
Unique low-power microscopic appearance
Extensiveness of infiltration best seen on keratin or mucin stains
Mucinous
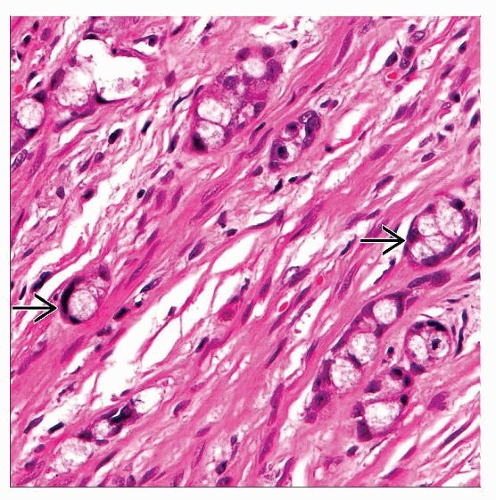
Distended mucin-filled cells resembling goblet cells
Pools of mucin occasionally present
Small islands and nested
Small round “microglandular” collections of goblet-like cells
True lumen formation is rare
May also form linear collections infiltrating through appendiceal wall
MA-GCC has frankly carcinomatous tubules (less mucin, more pleomorphic and malignant-appearing epithelial cytology)
Predominant cell/compartment type
Epithelial, mucinous
Epithelial, neuroendocrine
Enterochromaffin cells admixed with goblet cell-like epithelial cells
Histologic features
Mucosa often involved
Tumor may originate in deep mucosa
Overlying dysplastic epithelial precursor (i.e., adenoma) is absent however
Scattered Paneth cells may be seen within microglandular structures
Presence of goblet-like cells, Paneth cells, and enterochromaffin cells suggest “recapitulation” of normal crypt structure
Features of aggressive behavior must be carefully sought
Angiolymphatic invasion
Individually infiltrating signet-ring-type cells
High mitotic count (> 20/high-power field)
Significant component recognizable as adenocarcinoma (> 50%)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree