Glycogen Storage Disease
Monica P. Revelo, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Inherited autosomal recessive disorders due to deficiency in lysosomal enzymes resulting in glycogen accumulation that causes cellular dysfunction and progressive damage of liver, heart, and skeletal muscle
Macroscopic Features
Massive cardiomegaly
Marked thickening of ventricular walls
Microscopic Pathology
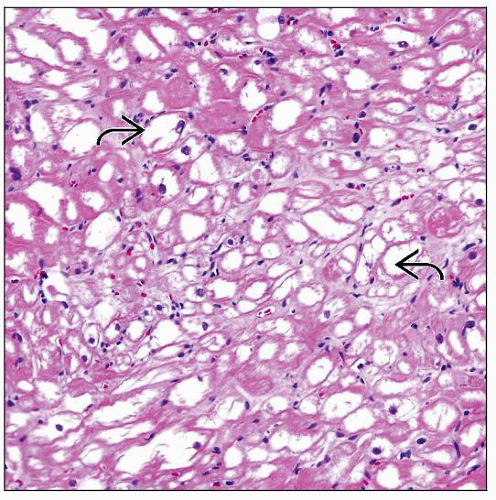
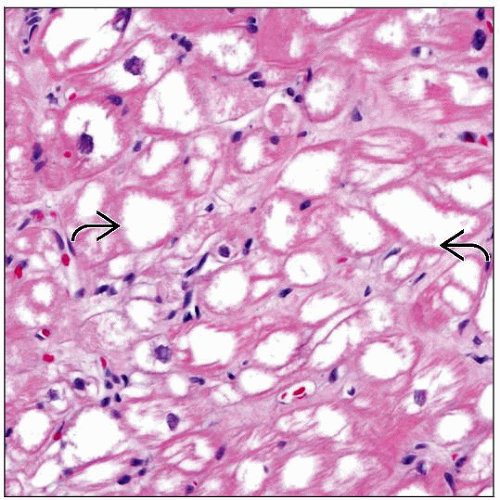
Marked vacuolar change of myocyte cytoplasm with lacework appearance
Variable degree of interstitial fibrosis
Ancillary Tests
Myocardial glycogen deposits washed out after diastase treatment
EM shows cytoplasmic accumulation of glycogen in myocardium with granular or fibrillary appearance
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Inherited autosomal recessive disorders due to deficiency in lysosomal enzymes resulting in glycogen accumulation that causes cellular dysfunction and progressive damage of liver, heart, and skeletal muscle
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Inherited Enzyme Deficiency
Glycogen storage disease II (Pompe disease): α-1,4-glucosidase
Glycogen storage disease III (Cori disease): Amylo-1,6-glucosidase
Glycogen storage disease IV (Andersen disease): α-1,4-glucan 6-glycosyl transferase
AMP-activated protein kinase deficiency: γ-2 regulatory subunit of enzyme controlling uptake of glucose
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation