Glomerulocystic Disease
Aleksandr Vasilyev, MD, PhD
Anthony Chang, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
2-3x dilatation of Bowman space, > 5% of glomeruli in absence of other kidney diseases
GCKD reserved for uromodulin or HNF1β mutations
Etiology/Pathogenesis
GCKD
HNF1β mutation (TCF1)
Uromodulin mutation (UMOD)
Secondary glomerular cysts in many diseases
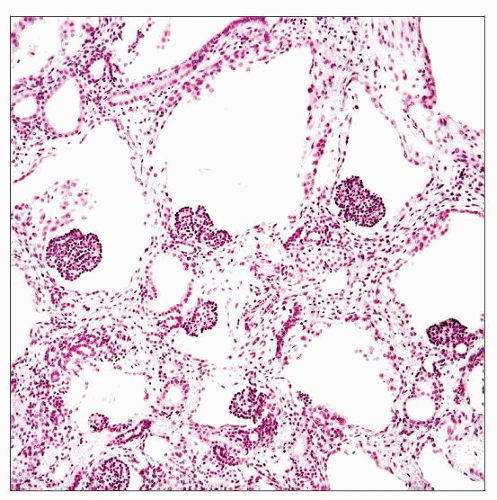
Microscopic Pathology
Dilation of Bowman capsule
Glomerulus on side of cyst (atubular glomeruli)
No connection with proximal tubule
Top Differential Diagnoses
ADPKD and ARPKD
Nephronophthisis
Cystic renal dysplasia
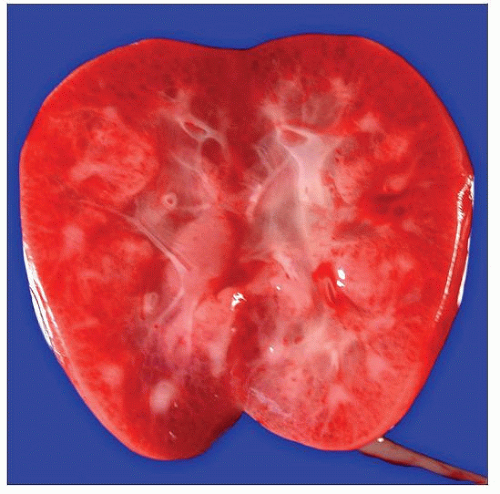 Bisected kidney with GCKD from 20-week-old fetus is shown. There are numerous small cysts throughout the cortical renal parenchyma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Glomerulocystic kidney disease (GCKD)
Glomerulocystic kidney (GCK) refers to pattern of injury irrespective of cause
Synonyms
Autosomal dominant glomerulocystic kidney disease (ADGCKD)
Definitions
Cystic dilatation of Bowman space to 2-3x normal, > 5% of glomeruli in absence of other kidney diseases
Glomerulocystic kidneys are divided into 5 clinicopathologic categories
1: Familial
2: Associated with other hereditary diseases
3: Syndromic nonhereditary
4: Sporadic
5: Acquired
GCKD reserved for diseases caused by mutations in uromodulin or HNF1β genes
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Glomerulocystic Kidney Disease
Familial hypoplastic GCKD (OMIM 137920)
HNF1β mutation (TCF1)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree