Gingival Fibromatosis
Elizabeth A. Montgomery, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Rare benign fibroproliferative disorder affecting gums, either idiopathic or familial
˜ 1/3 of cases are familial
Virtually identical lesions reported in association with certain medications
Phenytoin, cyclosporine A, nifedipine
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Mutation of human SOS1 (Son of Sevenless-1 gene ) responsible for hereditary gingival fibromatosis type 1
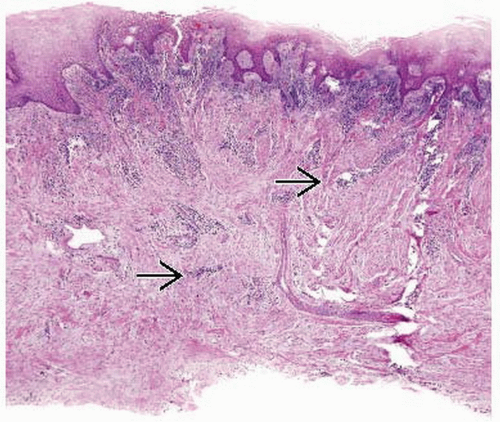
Microscopic Pathology
Calcifications common
Perivascular lymphoplasmacytic inflammation
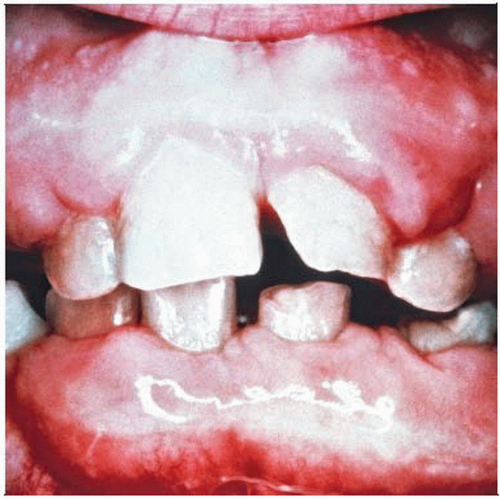 This clinical photograph is from a patient with gingival fibromatosis. The process diffusely involves both the upper and lower gingival tissues. (Courtesy G. Warnock, MD.) |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Idiopathic gingival fibromatosis, hereditary gingival fibromatosis, hereditary gingival hyperplasia, congenital macrogingivae, generalized hypertrophy of gums, gingival elephantiasis
Definitions
Rare benign fibroproliferative disorder affecting gums, either idiopathic or familial
Isolated familial gingival fibromatosis
Isolated idiopathic gingival fibromatosis
Gingival fibromatosis associated with hypertrichosis
Gingival fibromatosis associated with hypertrichosis, mental retardation, &/or epilepsy
Gingival fibromatosis associated with mental retardation, &/or epilepsy
Gingival fibromatosis associated with other syndromes
Zimmerman-Laband syndrome (autosomal dominant with skeletal anomalies and hepatosplenomegaly)
Cherubism (Ramon syndrome)
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome (vascular malformations)
˜ 1/3 of cases are familial
Virtually identical lesions reported in association with certain medications
Phenytoin, cyclosporine A, nifedipine
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree