Giant Cell Arteritis
Surya V. Seshan, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Granulomatous arteritis of aorta and its major branches
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Possible triggers include exposure to several upper respiratory disease pathogens
Associated with HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DR4 gene alleles
Cell-mediated immune mechanism
Clinical Issues
Usually > 50 years
Female predilection (M:F = 1:2-6)
Symptoms of polymyalgia rheumatica (50-75%)
Elevation of acute phase reactants in active disease (ESR, CRP)
Rapid response to steroid treatment
Microscopic hematuria, particularly with increased disease activity
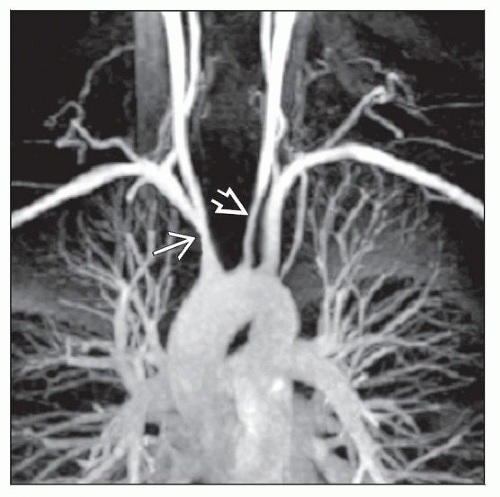
Image Findings
MR angiography and high spatial configuration
Angiography of aorta and great vessels
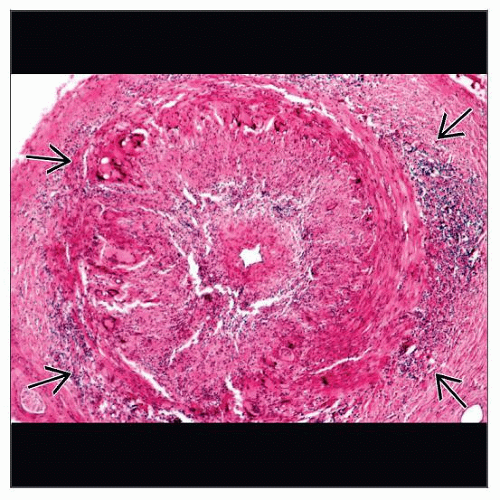
Microscopic Pathology
Granulomatous inflammation extending from media to intima and adventitia with disruption of elastic lamina by giant cells
Top Differential Diagnoses
Takayasu arteritis
Rheumatoid aortitis
Atherosclerotic arterial disease
Other systemic vasculitides
Fibromuscular dysplasia
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Giant cell arteritis (GCA)
Synonyms
Temporal arteritis
Cranial arteritis
Horton syndrome
Definitions
Chapel Hill Consensus Conference
Granulomatous arteritis of aorta and its major branches, with predilection for extracranial branches of carotid artery
Often involves temporal artery
Usually occurs in patients > 50 years of age and is often associated with polymyalgia rheumatica
American College of Rheumatology Criteria
Age ≥ 50 years
New onset of localized headache
Temporal artery tenderness or decreased temporal artery pulse
Elevated ESR ≥ 50 mm/hr
Biopsy of artery with necrotizing arteritis with mononuclear infiltrates or granulomatous process
Presence of any 3 or more of above yields high sensitivity and specificity
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Etiology unknown
Possible triggers include exposure to several upper respiratory disease pathogens
Mycoplasma/Chlamydia pneumoniae
Parvovirus B19, human parainfluenza virus type I
Herpes simplex virus
Genetic
Associated with HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DR4 gene alleles
ICAM-1 gene polymorphism (R241)
Pathogenesis
Autoimmune cell-mediated mechanism
T-cell mediated process
CD4(+) T-helper cells in inflammatory site
T-cell activation locally in arterial wall following activation of antigen presenting cells (e.g., dendritic cells in adventitia)
Activation of monocytes/macrophages responsible for systemic symptom
Destructive vascular inflammation may lead to vaso-occlusive intimal proliferation or aneurysm formation depending on type of arterial vessel involved
Interferon gamma produced from T cells is crucial in giant cell reaction in GCA
Role for humoral-mediated immunity is suggested
Elevated serum immunoglobulins
Detection of circulating immune complexes
Rare immune complex deposition
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
15-25/100,000 in patients > 50 years of age
Low incidence in the Mediterranean and Asian populations
Age
Usually > 50 years
Peaks at 75-85 years
Gender
Female predilection (M:F = 1:2-6)
Ethnicity
Highest in patients of northern European descent
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree