Gangliocytic Paraganglioma
Elizabeth A. Montgomery, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Overwhelming majority in duodenum
Benign in majority of cases
Rare reports of regional metastases
No reports of tumor-associated deaths
Microscopic Pathology
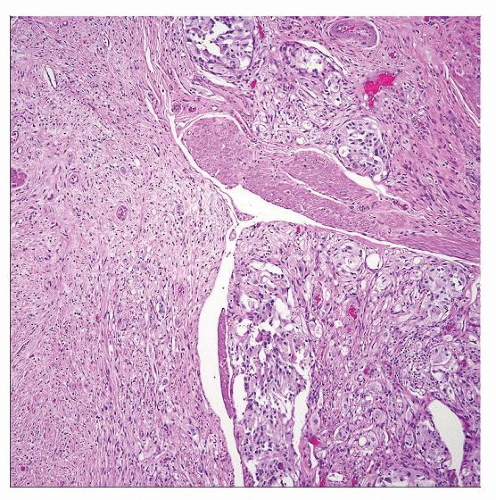
Triphasic (in variable proportions)
Spindle cells with appearance of nerve sheath cells
Ganglion-like cells
Epithelioid cells arranged in nests (“endocrine” pattern), trabeculae or papillary structures
Top Differential Diagnoses
GIST
Nerve sheath tumors
Ganglioneuroma
Carcinoid and carcinoma
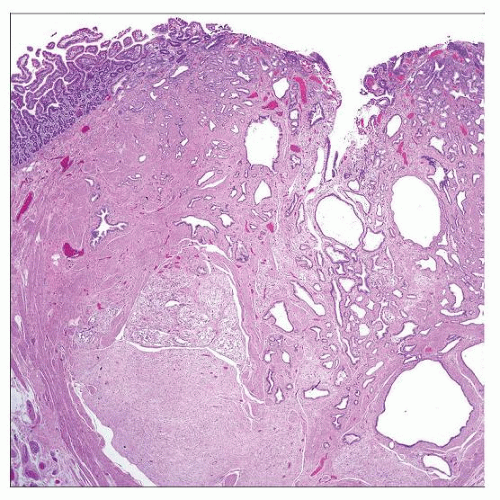 Hematoxylin & eosin shows a gangliocytic paraganglioma involving the ampullary area. Note the dilated ampullary glands at the right of the field. Small intestinal mucosa is seen at the upper left. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Neoplasm composed of admixture of cells showing
Endocrine cell
Schwann cell
Ganglion cell differentiation
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Average: ˜ 54 years
Presentation
Overwhelming majority in duodenum
Rare examples in jejunum or pylorus
Typical presentation
Abdominal pain
Gastric outlet obstruction
Bleeding
Most cases are sporadic
Reported association with neurofibromatosis
Treatment
Excision
Prognosis
Benign in majority of cases
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree