22 Forearm Fractures
Anatomy of the Forearm
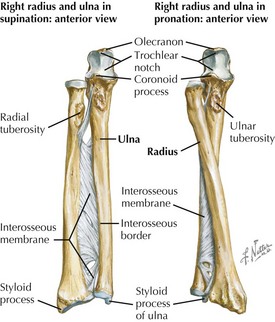
Ulna
• Parts and landmarks: olecranon, trochlear notch, coronoid process, shaft, anterior border, styloid process
• Cylindrical long bone; olecranon palpable subcutaneously at elbow joint; (medial) styloid process distal
Radius
• Parts and landmarks: head, neck, radial tuberosity, shaft, styloid process, carpal articular fossa, scaphoid fossa, lunate fossa, ulnar notch
Elbow Joint
• Ulnar (medial) collateral ligament: from medial epicondyle of humerus to (1) coronoid process and (2) medial olecranon
• Lateral (radial) collateral ligament passes from lateral epicondyle (humerus) to annular ligament.
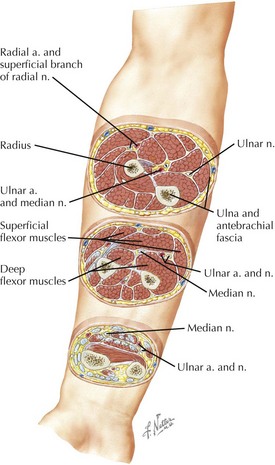
Compartments of the Forearm
• External investing antebrachial fascia is relatively tough and nonexpansile, with fascial septa between compartments.
• Proximal forearm
 Anterior (flexors, pronators)
Anterior (flexors, pronators)
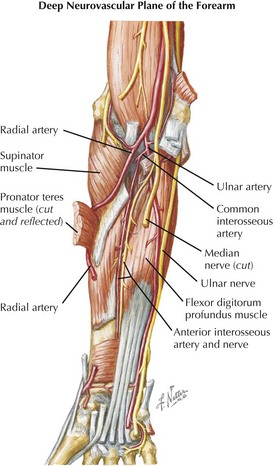
 Median nerve, to all flexors except flexor carpi ulnaris and 2 medial heads of flexor digitorum superficialis (ulnar nerve supplied)
Median nerve, to all flexors except flexor carpi ulnaris and 2 medial heads of flexor digitorum superficialis (ulnar nerve supplied)
 Anterior (flexors, pronators)
Anterior (flexors, pronators) Median nerve, to all flexors except flexor carpi ulnaris and 2 medial heads of flexor digitorum superficialis (ulnar nerve supplied)
Median nerve, to all flexors except flexor carpi ulnaris and 2 medial heads of flexor digitorum superficialis (ulnar nerve supplied)• Lower forearm: flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus tendons, flexor pollicis longus, pronator quadratus
• Spaces around flexors digitorum tendons and sheaths communicate with hand spaces: pathway for forearm-hand compartment syndrome.